Today’s Current Affairs: 29th August 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Fixed-Dose Combination : Banned

The Indian government has recently banned 156 Fixed-Dose Combination (FDC) drugs.
- Fixed-dose combination (FDC) drugs are medications that combine two or more Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) in a single dosage form, such as a pill, capsule, or injection.
- These drugs are often prescribed for conditions requiring multiple medications, such as tuberculosis, diabetes, and hypertension, to enhance patient compliance by reducing the number of pills taken daily.
- The rationale for the Ban: The banned FDCs were deemed “irrational” by the central government, as they do not provide any additional therapeutic benefits.
- The combinations in these FDCs may involve ingredients that either do not work synergistically or include unnecessary components that do not require simultaneous administration.
- FDCs can improve patient compliance, especially for chronic diseases where multiple medications are required.
- Some FDCs may include unnecessary components, leading to patients consuming drugs they don’t need.
- For example, Cheston Cold includes paracetamol, cetirizine, and phenylephrine, which are not necessary for treating bacterial infections but are used for managing cold symptoms.
- Banned FDCs: The recent ban includes various drug combinations:
- Gastrointestinal treatments: Enzyme combinations for digestive issues.
- Anti-allergy treatments: Combinations of levocetirizine with nasal decongestants, and cough syrups with mucus-breaking properties.
- Skin treatments: FDCs like menthol with aloe vera, and silver sulfadiazine with antiseptics.
- Migraine and menstrual pain: Combinations for treating migraines and menstrual cramps.
- Erectile dysfunction: Combinations involving sildenafil (Viagra) with other drugs affecting blood vessels and muscles.
Typhoon Shanshan:

Typhoon Shanshan has intensified into a “very strong” storm as it approaches Japan’s southwestern coast, prompting warnings from weather agencies.
- Tropical Cyclone originate over warm ocean waters near the equator. Warm, moist air rises from the ocean surface, creating a low-pressure area.
- Surrounding higher-pressure air moves towards this low-pressure zone, causing the air to warm up and rise further. As the rising air cools, it forms clouds.
- This system of spinning clouds and wind intensifies with the ocean’s heat. As wind speeds increase, an eye forms at the centre.
Quasar:

Using the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT), astronomers recently identified a quasar described as the “brightest of its kind” and the “most luminous object ever observed.
- A quasar is an extremely active and luminous type of Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN).
- An AGN isnothing more than a supermassive black hole that is active and feeding at the center of a galaxy.
- All quasars are AGNs, but not all AGNs are quasars.
- Quasar is short for quasi-stellar radio source because astronomers first discovered quasars in 1963 as objects that looked like stars but emitted radio waves.
- Quasars are intense sources of X-raysas well as visible light. They are the most powerful type of X-ray source yet discovered.
- They are among the most luminous, powerful, and vibrant objects known in the universe.
- Quasars are thought to form in regions of the universe where the large-scale density of matter is much higher than average.
- An active galaxy is one in which the central supermassive black hole is consuming large amounts of matter.
- The infall of matter into the black hole is so great that all the material can’t enter the black hole at the same time, so it forms a queue as a spiralling accretion disk.
- The matter—in the form of huge clouds—falls into the disk, with the inner parts of the cloud closer to the black hole orbiting faster than the outer parts (just like planets closer to the sun orbit faster than those farther away).
- This creates a shear force that twists the clouds, causing them to bump into their neighbours as they move around the black hole at velocities ranging from 10% of the speed of light up to over 80%.
Northern bald ibis:

Biologist Johannes Fritz and the Waldrappteam increased the Central European northern bald ibis population from zero to nearly 300 since 2002, moving it from “critically endangered” to “endangered.”
- Northern Bald Ibis: Scientific Name: Geronticus eremita
- Conservation status: Endangered (formerly Critically Endangered)
- Once native to Central Europe until the 17th century, also found in North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
- The species became extinct in Central Europe by the 17th century due to excessive hunting.
- The Northern Bald Ibis is known for its black plumage with an iridescent green sheen, a bald red head adorned with black markings, and a long, downward-curved beak.
- Their red beak and legs stand out against their dark feathers. There is no sexual dimorphism in this species.
- They primarily feed on insect larvae, earthworms and other invertebrates, using their long, slender beak to probe the ground, guided by their sense of touch.
- These ibises prefer open areas with short grass, such as meadows, pastures, or even sports fields like golf courses. Despite their bald head resembling that of a vulture, they are not scavengers.
- Northern Bald Ibises are social birds, historically forming large colonies with thousands of individuals.
- They engage in a ritual greeting involving crest-spreading and bowing, which often triggers a similar response throughout
- Typically, seasonally monogamous, breeding partnerships often change yearly, though some pairs may stay together for multiple years.
- They choose steep rock faces with protective nooks for nesting, laying up to four greenish eggs.
- Incubation begins with the first egg, leading to staggered hatching times.
- Young birds fledge within 42-50 days, initially following their parents before joining juvenile groups.
- They learn migration routes by following experienced birds during the fall migration.
Geoglyphs:

The Maharashtra government recently declared 1,500 geoglyphs spread across 70 locations in a 210-square-kilometre area of the Ratnagiri district as a ‘protected monument’.
- A geoglyph refers to a design that is drawn on the earth.
- Geoglyphs are typically formed of durable elements of the landscape, such as stones, gravel, or earth.
- A geoglyph is usually longer than four metres.
- Geoglyphs are difficult to see or even identify on the ground but are easily appreciated when seen from the sky.
- There are two types of geoglyphs, namely a positive and negative geoglyph.
- A positive geoglyphis formed by the arrangement and alignment of materials on the ground in a manner akin to petroforms (which are simply outlines created using boulders).
- A negative geoglyphis formed by removing part of the natural ground surface to create differently coloured or textured ground in a manner akin to petroglyphs.
- There is another variation of a geoglyph that involves seeding plants in a special design.
- The design usually takes years to see since it depends on the plants growing. This type of geoglyph is called an arborglyph.
- Another type of geoglyph often referred to as ‘chalk giants’ are those carved into hillsides, exposing the bedrock beneath.
- The most famous geoglyphs are the Nasca lines in Peru and the horse and human figures cut into hillsides in southern England (e.g., the Uffington White Horse and the Cerne Giant).
Mimetus spinatus And Mimetus parvulus : New Species Of Spiders
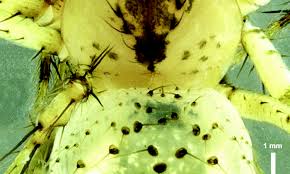
The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) recently discovered two new species of spiders named Mimetus spinatus and Mimetus parvulus from the southern Western Ghats.
- Mimetus spinatus and Mimetus parvulus are two new species of spiders discovered in the southern Western Ghats, a biodiversity hotspot.
- Mimetus spinatus and Mimetus parvulus were collected from the Mookambika Wildlife Sanctuary, Karnataka and Ernakulam district of Kerala, respectively.
- Both species belong to the spider family Mimetidae, commonly known as pirate or cannibal spiders due to their unique predatory behaviour.
- These spiders infiltrate the webs of other spiders, mimicking the vibrations of prey or mates to deceive and kill the host spider.
- Mimetus spinatus is characterised by its medium size, pale yellow head, and dull grey-white abdomen, with scattered light green mottling.
- It possesses long, black, flattened spine-like hairs on the dorsal head, which inspired its name.
- In contrast, Mimetus parvulus is distinguished by its pale creamy-rose head with dense grey-black mottling and a triangular-shaped, dull grey-white abdomen.
- The discovery marks the report of the genus Mimetus after 118 years of the discovery of the last Mimetus species (i.e. Mimetus indicus) from India.
- The addition of two new species brings the number of Mimetus species in India to three, all of which were spotted from the southern part of the country.
Ten Years Of Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana:

On August 28, 2024, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) accomplished a decade, marking a significant milestone in financial inclusion.
- Accounts increased from 72 crore in March 2015 to 53.13 crore by August 2024.
- Deposits in PMJDY accounts surged from ₹15,670 crore (March 2015) to over ₹2.31 lakh crore (August 2024).
- Financial Year 2024-25 target: The government aims to open an additional 3 crore PMJDY accounts.
- Operative accounts: Out of 173 crores CASA accounts in the country, over 53 crores are PMJDY accounts, with an 80% operation rate.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) launch date: August 28, 2014
- Objective is to promote financial inclusion by providing access to financial services, including banking/savings accounts, remittance, credit, insurance, and pensions, affordably.
- It Forms the backbone for several government economic initiatives and facilitates Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs).
- The applicant should be an Indian National.
- The applicant should be aged between 18 and 59 years.
- If minors above ten years apply, they will require support from their legal guardians to administer their PMJDY account.
- An individual can open an account under this scheme with any bank branch or Business Correspondent (Bank Mitra) outlet.
- Accounts opened under PMJDY can be opened with zero balance. However, if the account holder wishes to get a chequebook, she/he will have to fulfil the minimum balance criteria.
- The account holders under this scheme will be given a RuPay debit card which can be used across all ATMs for cash withdrawal.
Scheme highlights:
- Zero-balance accounts: Accounts can be opened with no minimum balance requirement.
- RuPay debit card: Provides a free RuPay debit card with in-built accident insurance coverage.
- Accident insurance: Up to ₹2 lakh.
- Life insurance: Up to ₹30,000 for eligible first-time account holders.
- Overdraft facility: Up to ₹10,000 is available to one account per household, with an additional ₹5,000 loan after six months of satisfactory account activity.
- Coverage focus:6% of accounts are in rural and semi-urban areas, with 55.6% of account holders being women.
- Banking access: 95% of inhabited villages have banking facilities within a 5 km radius.
Recent developments:
SLIM Moon Mission:

Japan’s space agency, JAXA, has concluded operations of its Moon lander, the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM), also known as the “Moon Sniper,” after losing communication with it.
- This operation was halted after the failure of multiple attempts to establish connection with the SLIM spacecraft.
- SLIM is a small-scale lunar lander designed for precise landings, reduced equipment size and weight, and investigating the Moon’s origins.
- It was an uncrewed spacecraft that also aimed to test low-gravity exploration technology essential for future solar system exploration.
- It is nicknamed the “Moon Sniper” because of its ability to land very precisely on the Moon’s surface.
- It made a soft landing on the Moon in January 2024, making Japan the 5th nation to achieve this feat.
- Other countries that have successfully achieved a soft lunar landing are India, Russia, the United States, and China.
- ISRO’s Chandrayaan 3 Mission successfully soft-landed a lander on the moon, in the natural satellite’s south pole region.
Skull For The Humanoid On The Gaganyaan Mission:
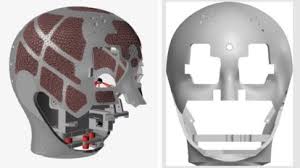
The Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) Thiruvananthapuram unit has finalised the design of the skull for the humanoid on the Gaganyaan mission.
- It weighs 800 grams and measures 200 mm x 220 mm. It is made from a high-strength aluminium alloy that can endure pressure and vibration.
- Before launching astronauts for the Gaganyaan mission in 2025, ISRO will send a humanoid robot, Vyommitra, into space to test spacecraft safety.
- Vyommitra will resemble the upper human body, featuring movable arms, face, and neck equipped with sensors to perform human-like functions and assess the impacts of space travel.
- It will carry three Indian astronauts into space, about 400 km from the Earth’s surface, for three days.
- Indian Air Force pilots Prasanth Balakrishnan Nair, Ajit Krishnan, Angad Pratap and Shubhanshu Shukla have been selected for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Shubhanshu Shukla has been shortlisted for a joint ISRO-NASA space flight in 2025 which will take him to the International Space Station.
Bharat Biotech Unveils Oral Cholera Vaccine Amid Global Shortage:
Bharat Biotech International Ltd has launched Hillchol (BBV131), a novel single-strain oral cholera vaccine (OCV) developed under license from Hilleman Laboratories. This launch is critical as global demand for OCVs exceeds 100 million doses annually, and there has been a deficit of approximately 40 million doses due to limited supply.
Bharti Airtel Announces Content Partnership with Apple:
Bharti Airtel has unveiled a new content partnership with Apple, set to offer exclusive Apple Music and Apple TV+ deals to customers in India later this year. As part of this collaboration, Apple TV+ will be integrated into Airtel’s Xstream video-streaming service available through premium Wi-Fi and postpaid plans.
‘Mukhya Mantri Sukh Shiksha Yojana’:
The Himachal Pradesh government has allocated Rs 53.21 crore annually to fund the ‘Mukhya Mantri Sukh Shiksha Yojana,’ aimed at supporting the education and well-being of children from vulnerable families.
SBI Research Anticipates Q1 GDP Growth At 7.1%:
India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is projected to grow by 7.0 per cent to 7.1 per cent in the first quarter of the fiscal year 2024-25 (Q1FY25), according to the latest SBI Ecowrap report released on August 26.
Jana Small Finance Bank Sweeps 4 Awards At ICC Emerging Asia Banking Conclave:
Jana Small Finance Bank has once again cemented its status as a frontrunner in the Indian banking industry. The bank’s commitment to excellence and innovation was recognized at the prestigious 2nd ICC Emerging Asia Banking Conclave & Awards, where it clinched four coveted awards
Singapore Hosts 2nd India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable (ISMR):
Singapore hosted the 2nd India-Singapore Ministerial Roundtable (ISMR) on 26 August 2024. This high-level platform, established to discuss and shape bilateral relations, follows the inaugural ISMR held in New Delhi on 17 September 2022.
ICAR-CIFE And VAMNICOM Sign MoU To Enhance Cooperative Management In Fisheries:
The Central Institute of Fisheries Education (ICAR-CIFE) and the Vaikunth Mehta National Institute of Cooperative Management (VAMNICOM) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on August 26, 2024.This collaboration aims to advance cooperative management in the fisheries sector and supports the vision of establishing 200,000 Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
Centre Appoints B Srinivasan as New NSG Director General:
The Centre has appointed senior IPS officer B Srinivasan as the new Director General of the National Security Guard (NSG), according to a Personnel Ministry order issued on August 27. Srinivasan, a 1992 batch Indian Police Service (IPS) officer from the Bihar cadre, will serve as the NSG DG until August 31, 2027.




