Maple Syrup Urine Disease:
Scientists have created a new gene therapy for a debilitating genetic disorder called maple syrup urine disease (MSUD).
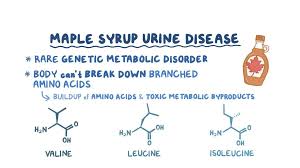
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease is a rare genetic disorder characterized by deficiency of an enzyme complex (branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase) that is required to break down (metabolize) the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) leucine, isoleucine and valine, in the body.
- It’s inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. A child is born with MSUD when both parents are carriers of the specific gene mutation and pass it on.
- The loss of this complex prevents the body from properly breaking down several amino acids, eventually leading to neurological symptoms and life-threatening brain damage.
- It is the most severe and also the most common. Symptoms usually develop within the first three days of birth.
- It is less severe than classic MSUD. Symptoms typically appear in children between 5 months and 7 years old.
- Children with intermittent MSUD develop as expected until an infection or period of stress causes symptoms to appear. People with intermittent MSUD usually tolerate higher levels of the three amino acids than those with classic MSUD.
- This type of MSUD responds to treatment using high doses of vitamin B1 (thiamine) along with a restricted diet.
- Symptoms: A sweet, syrupy smell in their pee, sweat or earwax, Lethargy (they may move slowly or appear tired or weak), Irritability or fussiness
- The main treatment for MSUD is a low-protein diet with low levels of the three amino acids.




