microRNA:
The 2024 Nobel Prize for Medicine has been awarded to scientists Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their discovery of microRNA — tiny molecules which play a crucial role in how genes function.
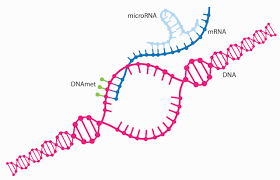
- MicroRNAs, or miRNAs, are small, non-coding molecules of RNA.
- They are typically around 19-24 nucleotides long and play an important role in determining how much messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries genetic information, eventually gets translated into protein.
- These microRNAs act as molecular switches, fine-tuning the expression of genes in different cell types and under varying conditions.
- They regulate the production of proteins by bonding with and subsequently silencing the mRNA at an appropriate juncture.
- The process is called post-transcriptional gene regulation.
- MicroRNAs help fine-tune various cellular processes like development, growth, and metabolism.
- Their role is essential in maintaining normal cell function, and disruptions in microRNA activity have been linked to diseases such as cancer.
- Mutations in genes coding for microRNAs have been found in humans, causing conditions such as congenital hearing loss, eye and skeletal disorders.
- The discovery of microRNAs has provided scientists with new tools to investigate gene regulation and has significantly expanded our understanding of how genetic information is processed and utilized in living organisms.




