Zero-Day Vulnerability:
Google Chrome has been hit with another zero-day vulnerability, which has set the alarm bells ringing among users and cyber experts.
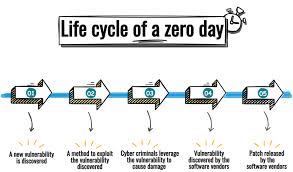
- Zero-Day Vulnerability is a system or software vulnerability unknown to the vendor and for which no patch or means of mitigation are available at the time it is discovered.
- The term ZDV refers to the flaw itself, while zero-day attack refers to an attack that has zero days between the time the vulnerability is discovered and the first attack.
- Zero-day exploit refers to the method or technique hackers use to take advantage of a ZDV, often via malware, and execute the attack.
- Thus, a zero-day attack occurs when threat actors develop and release malware that targets the ZDV.
- Because they were discovered before security researchers and software developers became aware of them—and before they can issue a patch— ZDVs pose a higher risk to users for the following reasons:
- Cybercriminals race to exploit these vulnerabilities to cash in on their schemes.
- Vulnerable systems are exposed until a patch is issued by the vendor.
- Once a ZDV has been made public, it is known as an n-day or one-day vulnerability.




