Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 16th November 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP):
- Vital statistics of India based on the Civil Registration System”::
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan 3.0.”:
- Pneumonia and Diarrhoea Progress Report:
- Forest Rights Act, 2006:
- New Ramsar Sites:
- Other important current affairs
1. Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP):

The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) has come into existence on the sidelines of the 37th ASEAN Summit.
- It has laid down the path for restarting discussion that had failed to admit India earlier and said “new” developments would be taken into consideration if India re-applies.
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership:
- It consists of 10 Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) members, as well as South Korea, China, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand.
- It excludes the USA, which withdrew from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) in 2017.
- Negotiations over the RCEP deal began in 2012.
- India was also part of the negotiations but it pulled out in 2019 over concerns that lower tariffs could hurt local producers.
- Members of the RCEP makeup nearly a third of the world’s population and account for 29% of global gross domestic product (GDP).
- The China-backed group will emerge as the largest free trade agreement (FTA) in the world surpassing both the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement and the European Union (EU).
- It is expected to eliminate a range of tariffs on imports within 20 years and also includes provisions on intellectual property, telecommunications, financial services, e-commerce, and professional services.
- Under RCEP, parts from any member nation would be treated equally, which might give companies in RCEP countries an incentive to look within the trade region for suppliers.
- Businesses with global supply chains might face tariffs even within an FTA because their products contain components that are made elsewhere.
- The deal could increase global national income by USD 186 billion annually by 2030 and add 0.2% to the economy of its member states.
- However, some analysts think the deal is likely to benefit China, Japan, and South Korea more than other member states.
- However, it could be some time before any country sees the benefits because six Asean nations and three other nations have to ratify it before it takes effect.
- Ratification will likely be tricky in national parliaments, owing to both anti-trade and anti-China sentiments among the countries.
2.Vital statistics of India based on the Civil Registration System”::
The report was published recently by the Registrar-General of India. It throws light on Sex Ratios of various states in the country.
- Sex ratio at birth is the number of females born per 1,000 males.
Key Findings:
- State with best Sex Ratio: Arunachal Pradesh (1084).
- Worst: Manipur (757).
- Arunachal Pradesh is followed by Nagaland (965) Mizoram (964), Kerala (963) and Karnataka (957).
- Delhi recorded a sex ratio of 929, Haryana 914 and Jammu and Kashmir 952.
- The number of registered births increased to 2.33 crore in 2018 from 2.21 crore registered births the previous year.
- The level of registration of births has increased to 89.3% in 2018 from 81.3% in 2009.
It is implementing many schemes. These include:
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY).
- Girl Child Protection Scheme.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandhana Yojana (PMMVY).
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK).
3.Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan 3.0.”:

The Government has announced a fresh set of relief and stimulus measures for the economy worth ₹1.19 lakh crore. This is being called “Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan 3.0.”
- Such measures in the last seven months reinforce the ‘fiscal conservatism’ ideology of the government — rather than large cash transfers, the growth philosophy centers around creating an ecosystem that aids domestic demand, incentivizes companies to generate jobs and boost production, and simultaneously extends benefits to those in severe distress, be it firms or individuals.
- Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said the country had entered into a technical recession in the first half of 2020-21.
- However, the RBI also predicts a strong return to proper growth for the economy. Even ratings agency Moody’s Investor Service had revised its GDP projections for India upwards.
Technical recession:
- It refers to the sequential decline in GDP for the past two quarters.
- This presents economic contraction since the GDP measures the value of all goods and services produced in a country during a specific period of time, in other words, the total expenditure in the economy.
5. Pneumonia and Diarrhoea Progress Report:
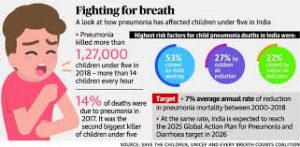
The annual Pneumonia and Diarrhoea Progress Report has been released by the International Vaccine Access Centre (IVAC).
- IVAC, founded in 2009, accelerates equitable access to vaccines through the generation, synthesis, and use of evidence to inform decision-making and action. It is located in the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, USA.
About the Report:
- It evaluates the progress across 10 high-impact indicators outlined in the Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (GAPPD) in the 15 countries with the greatest burden of under-five pneumonia and diarrhoea deaths and how they are delivering key interventions to prevent these.
- These interventions include breastfeeding, immunization, care-seeking and antibiotics, Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS), and zinc supplementation.
- These measures are proven to help prevent deaths due to these illnesses and could help achieve the Sustainable Development Goal-3 (Good Health and Well-Being) target of reducing under-five mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births by 2030.
- In 2009, the World Health Organisation (WHO) and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) launched the GAPPD, which proposes a multi-sectoral, integrated approach to reduce the incidence of severe pneumonia and diarrhoea, reduce the number of children under-five who are stunted, and end preventable childhood deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea.
- This year’s report also addresses the emerging impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- It monitors the coverage of five vaccines which are Diphtheria, Pertussis, and Tetanus (DPT) vaccine, Measles-containing-vaccine first dose, Haemophilus influenzae type B, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV), and rotavirus vaccine.
Global Status:
- Nearly every country included in the report lagged in access to treatments against pneumonia and diarrhoea.
- Overall the world’s health systems are falling short of ensuring that children have access to prevention and treatment services.
India’s Performance:
- Of the 15 focus countries included in the report, India is one of the countries that exceeded targets for exclusive breastfeeding.
- The World Health Assembly (WHA) has set a target to increase the global rate of exclusive breastfeeding to at least 50% by 2025.
- Exclusive Breastfeeding: It means that the infant receives only breast milk. No other liquids or solids are given, not even water, with the exception of ORS, or drops/syrups of vitamins, minerals or medicines.
- India has made significant progress in its vaccination coverage to prevent child pneumonia and diarrhoea deaths.
- India has achieved the global target of 90% coverage for three of the five vaccines whose coverage is monitored in the report.
- However, India failed to reach all targets for treatment and the treatment for diarrhoea had the lowest coverage, with only 51% of children receiving ORS and 20% getting zinc.
- 90% treatment coverage for children with suspected pneumonia, including care by an appropriate health care provider and antibiotics and 90% treatment coverage for children with diarrhoea, including treatment with ORS and zinc supplements by 2025.
- Although there was progress in India in 2019, the Covid-19 pandemic threatens the gains because of disruptions caused in routine health services like immunization and access to medical oxygen.
6.Forest Rights Act, 2006:

Review petitions of approximately 1200 tribals for recognition of their claims over forest land under the Scheduled Tribes and Other Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 was rejected by the local authorities in Mysuru (Karnataka).
- A large number of people, especially the scheduled tribes have lived in and around forests for a long period in symbiotic relationships.
- During the colonial time, the focus shifted from the forests being used as a resource base for sustenance of local communities to a State resource for commercial interests and development of land for agriculture.
- Several Acts and policies such as the three Indian Forest Acts of 1865, 1894 and 1927 of the Central Govt and some state forest Acts curtailed centuries‐old, customary‐use rights of local communities.
- This continued even after independence till much later until enactment of The Scheduled Tribes and Other
- Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- The Supreme Court in 2019 ordered the eviction of nearly a million people across India whose claims under the Forest Rights Act, 2006 had been rejected.
Provisions of the Forest Rights Act:
- The Act recognizes and vests the forest rights and occupation in Forest land in Forest Dwelling Scheduled Tribes (FDST) and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (OTFD) who have been residing in such forests for generations.
- Forest rights can also be claimed by any member or community who has for at least three generations (75 years) prior to the 13th day of December 2005 primarily resided in forest land for bona fide livelihood needs.
- It strengthens the conservation regime of the forests while ensuring livelihood and food security of the FDST and OTFD.
- The Gram Sabha is the authority to initiate the process for determining the nature and extent of Individual Forest Rights (IFR) or Community Forest Rights (CFR) or both that may be given to FDST and OTFD.
- The Act identifies four types of rights:
- Title rights: It gives FDST and OTFD the right to ownership to land farmed by tribals or forest dwellers subject to a maximum of 4 hectares. Ownership is only for land that is actually being cultivated by the concerned family and no new lands will be granted.
- Use rights: The rights of the dwellers extend to extracting Minor Forest Produce, grazing areas etc.
- Relief and development rights: To rehabilitate in case of illegal eviction or forced displacement and to basic amenities, subject to restrictions for forest protection.
- Forest management rights: It includes the right to protect, regenerate or conserve or manage any community forest resource which they have been traditionally protecting and conserving for sustainable use.
7.New Ramsar Sites:
The Meteor lake at Lonar in Buldhana district of Maharashtra and the Soor Sarovar at Agra have been declared Ramsar sites, a conservation status conferred by International Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- Earlier this year Kabartal Wetland (Bihar) and Asan Conservation Reserve (Uttrakhand) were also designated as Ramsar sites.
- With the latest inclusions, the total number of Ramsar sites in India is 41, the highest in South Asia.
Lonar Lake

- The Lonar lake, situated in the Deccan Plateau’s volcanic basalt rock, was created by the impact of a meteor 35,000 to 50,000 years ago.
- The lake is part of Lonar Wildlife Sanctuary which falls under the unified control of the Melghat Tiger Reserve (MTR).
- It is also known as Lonar crater and is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument. Geo-heritage refers to the geological features which are inherently or culturally significant offering insight to earth’s evolution or history to earth science or that can be utilized for education.
- It is the second Ramsar site in Maharashtra after Nandur Madhmeshwar Bird Sanctuary in Nashik district.
- The water in the lake is highly saline and alkaline, containing special microorganisms like anaerobes, Cyanobacteria and phytoplankton.
Soor Sarovar Lake:

- It is also known as Keetham lake situated within the Soor Sarovar Bird Sanctuary, which was declared as a bird sanctuary in the year 1991.
- This lake is situated alongside river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh.
- The Soor Sarovar bird sanctuary covered an area of 7.97 sq km.
- It is today home to more than 165 species of migratory and resident birds.
- It also has a Bear Rescue centre for rescued dancing bears.
Other important current affairs:
1.The birth anniversary of Birsa Munda was observed on November 15th.
- In recognition of his impact on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was created on his birth anniversary in 2000.
- Bisra Munda was a folk hero and a tribal freedom fighter hailing from the Munda tribe.
- He was a spearhead behind the Millenarian movement that arose in the Bihar and Jharkhand belt in the 19th century under the British colonization.
- He is also known as ‘Dharti Abba’ or the Earth Father.
- Birsait: Bisra wanted to reform the tribal society and so, he urged them to let go of beliefs in witchcraft and instead, stressed the importance of prayer, staying away from alcohol, having faith in God, and observing a code of conduct. Based on these, he started the faith of ‘Birsait’.
2.Janata Dal (United) president Nitish Kumar has been elected leader of the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) legislature party in Bihar. He will now take oath as Chief Minister of the State for the fourth consecutive term.
- The Chief Minister is appointed by the governor.
- 164 of the Constitution provides that there shall be a Council of Ministers with the Chief Minister at its hand to aid and advise the governor.
- After general election to the State Legislative Assembly, the party or coalition group which secures a majority in this House elects its leader and communicates his name to the Governor.
- The Governor then formally appoints him as the Chief Minister and asks him to form his Council of Ministers.
- When no party gets a clear majority in the State Legislative Assembly, the Governor normally asks the leader of the single largest party to form the government.
- Theoretically, the Chief Minister holds office during the pleasure of the Governor. However, in actual practice the Chief Minister remains in the office so long as he continues to be the leader of the majority in the State Legislative Assembly.
- The Governor can dismiss him in case he loses his majority support.
- The State Legislative Assembly can also remove him by passing a vote of no-confidence against him.
3.In a judgment, the Supreme Court has held that an accused, irrespective of the merits of the case against him, should be granted “default” or “compulsive” bail if the investigating agency does not complete the probe within a prescribed time limit.
- An accused has an “indefeasible right” to default bail under Section 167(2) of the Code of Criminal Procedure if the probe agency failed to complete the investigation on time.
- Under Section 167, an accused can be detained in custody for a maximum of 90 days for a crime punishable with death, life imprisonment, or a sentence of over 10 years. It is 60 days of detention if the probe relates to any other offense.
- Also, Magistrates have to mandatorily inform the accused, especially those from the poor sections, of their statutory right to apply for default bail.
4.China has begun work on a strategically significant railway line that will link Sichuan province with Nyingchi in Tibet, which lies close to Arunachal Pradesh border.
- This will be the second such route linking Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) with mainland China.
- Earlier Qinghai-Tibet railway line connected Lhasa to the hinterland.
- Implications on India:
- Security Concerns:
- The railway line will largely improve the efficiency and convenience of military personnel and material transportation and logistical supplies in the border area.
- In situations of a direct standoff near the Arunachal Pradesh border, as was seen during Doklam or the recent Ladakh standoff, China might be at an advantageous position.
- Doklam Issue: Indian troops intervened to block the path of Chinese soldiers engaged in building road-works on the Doklam plateau of Bhutan’s territory that Beijing laid claim.
- Ecological Concerns:
- The fragile ecological environment along the project line may have ecological concerns for India.
- Security Concerns:
5.The United Arab Emirates will extend its “golden” visa system to certain professionals, specialized degree-holders, and others.
- After first announcing a long-term visa plan in 2018, the UAE in 2019 started granting 5- and 10-year renewable visas to certain foreign investors, entrepreneurs, chief executives, scientists, and outstanding students.
- About the ‘Golden Card’ Permanent Residency Scheme:
- The United Arab Emirates (UAE) had launched this Scheme to woo wealthy individuals and exceptional talents from all over the world.
- The “Golden Card” visa includes categories:
- General investors who will be granted a 10-year permanent residency visa.
- Real Estate Investors, who can get a visa for a 5-year visa.
- Entrepreneurs and Talented Professionals like doctors, researchers, and innovators can get 10 years visa.
- ‘Outstanding students’. These will also be permitted 5 years permanent residency visas.
6.Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully test-fired the Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile system (QRSAM).
- The test was conducted at the Integrated Test Range, Chandipur off Odisha coast.
- The Test was in continuation of a series of missile tests conducted by DRDO over the past two months.
- QRSAM is a canister-based system, which means that it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus along with making its transport and storage easier, the shelf life of weapons also improves significantly.
- The system is capable of detecting and tracking targets on the move and engaging targets with short halts.
Range and mobility: - It is a short-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, primarily designed and developed by DRDO to provide a protective shield to moving armored columns of the Army from enemy aerial attacks.
- The entire weapon system has been configured on a mobile and manoeuvrable platform and is capable of providing air defence on the move.
- It has been designed for induction into the Army and has a range of 25 to 30 km.
6.Puerto Rico: For the third time in ten years, the United States territory of Puerto Rico has voted in favour of statehood.
- Puerto Rico is a Spanish-speaking island located in the Caribbean Sea.
- Since its discovery by the explorer Christopher Columbus in 1493, Puerto Rico was a part of the Spanish Empire for over 4 centuries until 1898, when it was annexed by the United States.
- In 1917, Puerto Ricans were granted US citizenship, but the island itself was never made a full state, and continues to remain a “US territory”, along with Guam, North Mariana Islands, American Samoa, and the US Virgin Islands.




