Today’s Current Affairs: 11th February 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Graphene: Study
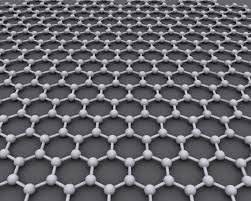
Researchers recently discovered a strange new state of matter in the dynamics of currents flowing through layers of graphene.
- It is an allotrope of carbon, along with diamond and graphite.
- It is a two-dimensional material consisting of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb structure.
- The stacked form of graphene is graphite.
- Graphene was first isolated in 2004.
- Since then, it has utilised in various innovative applications, from sensors and electronics to energy storage and healthcare.
- Graphene is the world’s thinnest material – it is only one atom thick, one million times thinner than a human hair.
- It is 200 times stronger than steel but six times lighter.
- It is extremely flexible and stretchable.
- It is an excellent electrical and thermal conductor.
- It is almost perfectly transparent since it only absorbs 2% of light.
- It is impermeable to gases, even those as light as hydrogen or helium.
Civil Liability for Nuclear Damages Act (CLNDA), 2010:

Union government’s recent announcement that it would amend the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damages Act (CLNDA), 2010, and the Atomic Energy Act, 1962, is likely to enthuse American and French nuclear power companies, whose projects have been deadlocked due to legal concerns for more than 15 years.
Civil Liability for Nuclear Damages Act (CLNDA), 2010:
- It is the legal foundation that influences India’s response to nuclear incidents. It was adopted by Parliament of India in 2010.
- It is based on the international principles of civil nuclear liability laid down in the Vienna Convention, Paris Convention and Brussels Supplementary Convention.
- It created a mechanism for compensating victims from damage caused by a nuclear accident, allocating liability and specifying procedures for compensation.
- The CLNDA provides for strict and no-fault liability on the operator of the nuclear plant, where it will be held liable for damage regardless of any fault on its part.
- This Act establishes the operator’s liability for nuclear catastrophes up to 1,500 crores, which requires insurance or financial security.
- In case the damage claims exceed ₹1,500 crore, the CLNDA expects the government to step in.
- The Act has limited the government liability amount to the rupee equivalent of 300 million Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) or about ₹2,100 to ₹2,300 crore.
- In addition to establishing a timeline for compensation claims, the act authorises the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board to report incidents within 15 days.
- In addition, the Act establishes a Nuclear Damage Claims Commission to facilitate equitable compensation and conflict resolution.
Neutrinos:

Chinese scientists recently placed special detectors deep in the South China Sea to explore the possibility of building a huge underwater observatory to find neutrinos.
- Also called ghost particles, neutrinos are nearly massless, electrically neutral subatomic particles that interact extremely weakly with matter.
- Their tendency not to interact very often with other particles makes detecting them very difficult.
- First predicted in 1930, they weren’t discovered in experiments until 1956, and scientists thought they were massless until recently.
- They belong to the family of particles called leptons, which are not subject to the strong force. Rather, neutrinos are subject to the weak force that underlies certain processes of radioactive decay.
- Neutrinos come from all kinds of different sources and are often the product of heavy particles turning into lighter ones, a process called “decay.”
- They are the most common particles in the universe.
- Approximately 100 trillion neutrinos pass completely harmlessly through your body every second.
- Neutrinos play crucial roles in the standard model of particle physics, in stellar physics and black holes, and even in cosmology and the nature of the Big Bang.
Satkosia Tiger Reserve:

Odisha’s first captive breeding of sambar will be undertaken at the Satkosia division of Satkosia Tiger Reserve.
- Satkosia Tiger Reserve is located in the heartland of Odisha and spread over four districts viz. Angul, Cuttack, Boudh and Nayagarh.
- It comprises two adjoining sanctuaries, namely Baisipalli Sanctuary and Satkosia Gorge Sanctuary.
- The reserve has an area of 963.87sq km with 523.61sq km as core area.
- The area is also a part of the Mahanadi elephant reserve. The river Mahanadi flows through the valleys in the middle of the reserve.
- Satkosia is the meeting point of two biogeographic regions of India; the Deccan Peninsula and the Eastern Ghats.
- The terrain is hilly, with moderate to steep slopes and narrow valleys. The average elevation of the terrain varies between 37 m and 932 m, with the lowest point being at Katrang and the highest point being at Sunakhania.
- The forest vegetation comprises North Indian tropical moist deciduous forests and Moist peninsular low-level Sal.
- The reserve has a low population of tiger, leopard, elephant, spotted deer, sambar, chowsingha, barking deer, bison, wild dog, sloth bear, jackal, giant squirrel, and porcupine.
- It is the natural habitat of two endangered species, viz., the fresh water crocodile and the gharial.
Salamander:

Researchers discovered that wandering salamanders can rapidly fill, trap, and drain the blood in their toe tips to optimise attachment, detachment and general locomotion through their arboreal environment.
- The researchers have uncovered that the wandering salamanders can finely control and regulate blood flow to each side of their toe tips.
- This allows them to adjust pressure asymmetrically, improving grip on irregular surfaces like tree bark.
- The blood rushing in before “toe off” appears to help salamanders detach rather than attach.
- By slightly inflating the toe tip, the salamanders reduce the surface area in contact with the surface they are on, minimising the energy required to let go.
- Salamander is an amphibian with a slender body and a long tail.
- Their size varies with different species, ranging from 2.5 cm to 20 cm. The largest salamander in the world is the Chinese Giant Salamander, which can grow up to a length of 5 feet.
- Most salamanders look like a cross between a lizard and a frog.
- They have moist, smooth skin, like frogs, and long tails, like lizards.
- They are nocturnal and cold-blooded species and their temperature changes with their habitat.
- Some salamander species can be poisonous, and some even have teeth.
- They are capable of regenerating lost limbs within a few weeks, including tails and toes, allowing them to survive attacks from predators.
- They live in or near water or find shelter on moist ground and are typically found in brooks, creeks, ponds, and other moist locations, such as under rocks.
- They are mainly found in North America, Europe, Asia, the northern parts of South America and North Africa.
Cook Islands: In News

The New Zealand’s Foreign Minister voiced “significant concern” as close Pacific partner the Cook Islands prepared to sign a cooperation deal with China.
- Cook Islands is a small, self-governing Pacific nation that has a “free association” pact with New Zealand.
- It is located in the South Pacific Ocean, between Tonga to the west and French Polynesia to the east.
- It consists of 15 islands divided into a northern group of six islands and a southern group of nine islands.
- Northern Islands:They are mostly low-lying and sparsely populated coral atolls; and include the islands of Manihiki, Nassau, Penrhyn, Pukapuka, Rakahanga, and Suwarrow. They are covered in light vegetation and equipped with stunning white sand beaches.
- Southern islands: They generally consists of much larger higher islands that are volcanic in origin and more densely populated. The southern island group includes Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Atiu, Mangaia, Manuae, Mauke, Mitiaro, Palmerston, and Takutea.
- The highest point is Te Mangawhich rises to 652m on the Rarotonga island.
- Most of the population is found on the island of Rarotonga.
- Capital city:Avarua, which is on Rarotonga island.
Algorithmic Trading:

The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has mandated stock exchanges to empanel algorithmic trading providers and has also defined rules for using application programming interfaces (APIs).
- Algorithmic Trading is a method of executing trading orders by providing a predefined set of rules to a computer program.
- This helps in placing share orders at a speed and frequency not possible for human traders.
- Algo trading is already prevalent in India among both institutional as well as retail investors.
- New Algo Trading Framework by SEBI is aimed at spelling out the rights and responsibilities of the main stakeholders of the trading ecosystem such as investors, brokers, algo providers/vendors and Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs) so that the retail investors can avail algo facilities with requisite safeguards.
- Under the framework, retail investors will get access to the approved algos only from the registered brokers.
- The facility of algo trading would be provided by the stock broker only after obtaining requisite permission from the stock exchange for each algo.
- All algo orders shall be tagged with a unique identifier provided by the exchange in order to establish audit trail and the broker shall seek approval from the exchange for any modification or change to the approved algos,”
- Brokers will be solely responsible for handling investor grievances related to algo trading and the monitoring of APIs for prohibited activities.
- Algos will be categorised into two categories:
- White box algos, where logic is disclosed and replicable i.e. execution algos.
- Black box algos, where the logic is not known to the user and is not replicable.
Bombay Blood Group:
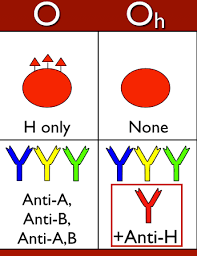
In a rare and complex medical procedure, a 30-year-old woman with the extremely rare ‘Bombay’ (hh) blood group underwent a successful kidney transplant in India.
- The Bombay, also known as HH, blood group is a rare blood group first discovered in Mumbai in 1952 by Y.M. Bhende.
- The Bombay blood group lacks A, B and H antigens, which are found in the common ABO blood groups.
- In normal individuals, the H antigen serves as the base structure for building A and B antigens. In Bombay blood group individuals, the gene responsible for producing the H antigen is mutated or absent, so neither A nor B antigens can be formed.
- Consequently, the people with Bombay Blood Group are incompatible with all standard blood types, including O-negative, complicating both transfusions and organ transplants.
- They can only receive blood from another Bombay blood group donor. Its prevalence is about 0.0004% (one in 4 million) of the total human population.
- While it drops to one in a million in the European population and one in 10,000 in Mumbai, the act of finding a donor is still daunting.
India has introduced new Harmonized System (HS) codes to facilitate the export of GI-recognized rice varieties:
India has introduced new Harmonized System (HS) codes to facilitate the export of GI-recognized rice varieties like Red Rice, Black Rice, and Kalanamak Rice. This move aims to differentiate these premium varieties from general non-basmati rice, ensuring they are not affected by export restrictions.
2025 Chennai Open Title:
French tennis player Kyrian Jacquet secured his maiden ATP title by winning the 2025 Chennai Open men’s singles championship. He triumphed over Elias Ymer of Sweden in the final, held on 9 February 2025 at the SDAT Tennis Stadium, Nungambakkam, Tamil Nadu.
IRS Officer Maimun Alam Appointed as Director in Ministry of Steel:
The 2025 Henley Passport Index ranks 199 passports based on visa-free or visa-on-arrival access, using IATA data. Singapore tops the list, while India ranks 80th alongside Algeria, Equatorial Guinea, and Tajikistan. The report also tracks changes in global mobility trends.
Nokia Names Intel’s AI Chief Hotard as New CEO:
Nokia has announced a leadership transition, with Justin Hotard set to take over as CEO on April 1, 2025, replacing Pekka Lundmark. Hotard, currently Intel’s Executive Vice President and General Manager of Data Center & AI Group, brings vast expertise in artificial intelligence (AI) and data centers, crucial for Nokia’s future growth.
RBI Defers Liquidity Coverage Ratio and Project Financing Norms to 2026:
The RBI has deferred the implementation of Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) and project financing norms by a year, now set for March 31, 2026. Originally planned for April 1, 2025, these norms required banks to maintain higher liquid assets, potentially impacting ₹4 lakh crore in lending.
Government Initiatives to Support Women Employees and Entrepreneurs in India:
The Government of India has launched several initiatives aimed at promoting gender equality in the workplace and supporting women entrepreneurs. These initiatives focus on creating a safe, secure, and non-discriminatory environment for women employees while also fostering women-owned enterprises. Through legislative measures and various programs, the government seeks to ensure that women have equal opportunities for career growth, business development, and social security.
India-EFTA Strengthen Economic Ties with the Inauguration of the India-EFTA Desk:
India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) – which comprises Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein – have taken a major step towards deeper economic collaboration with the inauguration of the India-EFTA Desk. This initiative follows the successful conclusion of the India-EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA), which positions EFTA as the first European bloc to formalize a trade pact with India. The desk will act as a critical link to ensure transparency, trust, and ease of doing business between the two regions, further enhancing their growing economic ties.
Operation Devil Hunt : Bangladesh
Bangladesh has launched a large-scale security operation, “Operation Devil Hunt,” targeting loyalists of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina. The move comes after protesters were attacked by gangs allegedly linked to Hasina’s regime. The interim government, led by Muhammad Yunus, has vowed to restore order and uphold democratic values. The unrest was sparked by reports of Hasina’s possible address from exile in India, leading to violent protests, including the destruction of buildings linked to her family.




