Today’s Current Affairs: 12th November 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Coronary Artery Disease:
New research from Seoul scientists reveals how gut microbes may influence the development of coronary artery disease, the world’s leading killer.
- It is a common type of heart disease. CAD also may be called coronary heart disease.
- It affects the main blood vessels that supply blood to the heart, called the coronary arteries.
- In CAD, there is reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
- A buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls, a condition called atherosclerosis, usually causes CAD.
- The buildup, called plaque, makes the arteries narrow.
- CAD often develops over many years.
- Symptoms are from the lack of blood flow to the heart.
- They may include chest pain and shortness of breath.
- A complete blockage of blood flow can cause a heart attack.
- Common heart attack symptoms include:
- Chest pain that may feel like pressure, tightness, squeezing or aching.
- Pain or discomfort that spreads to the shoulder, arm, back, neck, jaw, teeth or sometimes the upper belly.
- Cold sweats.
- Fatigue.
- Shortness of breath.
- Lightheadedness or sudden dizziness.
- Treatment:
- Treatment for CAD may include medicines and surgery.
- Eating a nutritious diet, getting regular exercise and not smoking can help prevent CAD and the conditions that can cause it.
Altermagnetism : Discovery
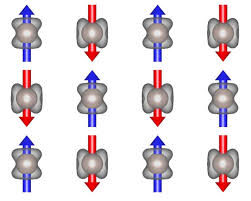
The discovery of altermagnetism represents a step forward in physicists’ understanding of the magnetic world.
- Magnetism has long been categorised into two primary types: ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism.
- Ferromagnetism is responsible for the behaviour of materials like iron and nickel, where all magnetic moments align in the same direction, producing strong magnetisation – such as the force that makes fridge magnets stick.
- Antiferromagnetism occurs when magnetic moments align in a regular pattern but point in opposite directions, cancelling each other out and resulting in no external magnetic field.
- Altermagnetism is a type of magnetism where magnetic moments (tiny magnetic fields created by electrons) align in opposite directions but follow a distinct rotated pattern.
- This unique arrangement creates properties that combine key elements of both ferromagnets and antiferromagnets.
- Like antiferromagnets, altermagnets have magnetic moments that align in opposite directions, cancelling out any overall magnetisation.
- However, like ferromagnets, altermagnets still allow spin-polarised currents. In ferromagnets, spin-polarised currents can only occur because all electron spins or moments align in one direction (producing a magnetic field).
- The key distinction in altermagnets is that the larger, crystal-like structures holding these magnetic moments are rotated relative to each other, creating distinct electronic behaviours.
- It is the rotation of these larger structures that allows for spin-polarised currents to still occur in altermagnets.
- This makes altermagnets potentially valuable for a variety of applications, particularly in electronics and data storage.
- They eliminate the possibility of stray magnetic fields while still allowing for a spin-polarised current – a highly useful combination for modern electronics.
Cornea : New Amend for Donar

The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare recently amended the Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues (Amendment) Rules, 2025, to boost cornea donation and transplant services across the country.
- The cornea is the clear outer layer at the front of the eye.
- It covers the pupil (the opening at the center of the eye), iris (the colored part of the eye), and anterior chamber (the fluid-filled inside of the eye).
- Viewed from the front of the eye, the cornea appears slightly wider than it is tall. This is because the sclera (the “white” of the eye) slightly overlaps the top and bottom of the anterior cornea.
- The cornea’s main function is to refract, or bend light. The cornea is responsible for focusing most of the light that enters the eye.
- As light passes through the cornea, it is partially refracted before reaching the lens.
- The curvature of the cornea, which is spherical in infancy but changes with age, gives it its focusing power.
- The cornea provides approximately 65 to 75 percent of the focusing power of the eye.
- The remainder of the focusing power of the eye is provided by the crystalline lens, located directly behind the pupil.
- Cornea’s specific shape plays a key role in how your eyesight works and filters some ultraviolet (UV) rays.
- Except at its margins, the cornea contains no blood vessels, but it does contain many nerves and is very sensitive to pain or touch.
- Since there are no nutrient-supplying blood vessels in the cornea, tears and the aqueous humor (a watery fluid) in the anterior chamber provide the cornea with nutrients.
- Most refractive errors — nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism — are due to a less-than-optimal curvature or symmetry of the cornea.
- The cornea is incredibly sensitive, helping you instinctively and immediately react to stop anything from harming your eyes further.
- Because corneas are the first line of defense for the surface of your eye, they’re also prone to injuries and damage.
- The cornea tends to repair itself quickly from minor abrasions.
- However, deeper abrasions may cause scars to form on the cornea, which causes the cornea to lose its transparency, leading to visual impairment.
Improvised Explosive Device:

J&K Police recently arrested seven locals linked to a terror module, seizing 2900 kg of IED-making materials and arms.
- An IED is a type of unconventional explosive weapon that can take any form and be activated in a variety of ways.
- IEDs are used by criminals, vandals, terrorists, suicide bombers, and insurgents.
- Because they are improvised, IEDs can come in many forms, ranging from a small pipe bomb to a sophisticated device capable of causing massive damage and loss of life.
- The extent of damage caused by an IED depends on its size, construction, and placement and whether it incorporates a high explosive or propellant.
- IEDs can be carried or delivered in a vehicle; carried, placed, or thrown by a person; delivered in a package; or concealed on the roadside.
- The term IED came into common usage during the Iraq War that began in 2003.
- IEDs are inexpensive and can be easily manufactured, concealed and detonated.
- Further, IEDs can be manufactured by using commonly available material or chemicals.
- It consists of a variety of components that include an initiator, switch, main charge, power source, and container.
- IEDs may be surrounded by or packed with additional materials or “enhancements” such as nails, glass, or metal fragments designed to increase the amount of shrapnel propelled by the explosion.
- An IED can be initiated by a variety of methods depending on the intended target.
- Many commonly available materials, such as fertilizer, gunpowder, and hydrogen peroxide, are used as explosive materials in IEDs.
- Explosives must contain a fuel and an oxidizer, which provides the oxygen needed to sustain the reaction.
- A common example is ANFO, a mixture of ammonium nitrate, which acts as the oxidizer, and fuel oil (the fuel source).
2025 Booker Prize:

David Szalay won the 2025 Booker Prize for his novel ‘Flesh’ becoming the first Hungarian-British author to win one of top awards in the English-speaking world.
- It is the world’s leading literary award for a single work of fiction.
- It was founded in the UK in 1969, the Booker Prize initially rewarded Commonwealth writers and now spans the globe: it is open to anyone regardless of origin.
- It aims to promote the finest in fiction by rewarding the best novel of the year written in English.
- The Booker Prize awards any novel originally written in English and published in the UK and Ireland in the year of the prize, regardless of the nationality of their author.
- The novel must be an original work in English (not a translation)
- It must be published by a registered UK or Irish imprint; self-published novels are not eligible.
- The winner receives £50,000 and each of the shortlisted authors will be given £2,500.
Indian Laburnum:

According to SeasonWatch -a citizen science project that monitors tree phenology observed that over the last few years, Indian laburnum trees flowers have been blooming earlier than usual.
- Indian laburnum (Cassia fistula) is called “amaltas” in northern India and “kanikonna” in south
- It is a species of flowering plant in the Fabaceae family.
- It is also known as Golden Shower Tree, Amaltas, Purging Fistula, Pudding-pipe tree.
- It is native to India and is the State tree of Kerala and Delhi.
- It is a medium to large deciduous tree that can reach heights of up to 10 to 20 meters (approximately 30 to 65 feet).
- It is native to the Indian subcontinent, but it is also found in other parts of Asia, including Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- It is a medium-sized deciduous tree that is leafless only for a brief time, between March and May.
- The new leaves are glossy, a trait that they lose on maturing, and are mostly bright green, though sometimes a rich copper too.
- It produces clusters of pendulous, cylindrical, yellow flowers that hang from the branches and bloom in abundance during the flowering season.
- It is commonly cultivated as an ornamental tree in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.
- Its extracts from the bark, leaves, flowers, and seeds have been used to treat a variety of ailments, including constipation, skin conditions, digestive issues, and respiratory problems.
- Its bark is used to make dye and the pulp in the fruit pod also serves as a strong purgative agent, which helps animals that feed on it.
Molasses:

The Central government has decided to allow export of 1.5 million tonnes (MT) of sugar for the 2025-26 and also remove 50 per cent export duty on molasses.
- It is a byproduct which comes from crushed sugar cane or sugar beets.
- It is a dense, viscous liquid of dark brown tint, rich in sugars, and containing a small percentage of water.
- It contains more vitamins and minerals than other sweeteners but is still high in sugar.
- The different types of molasses vary in color, consistency, flavor, and sugar content.
- Light molasses is the syrup that results from the first boiling of the sugar syrup. It has the lightest color and the sweetest taste. People commonly use it in baking.
- Dark molasses results from the second boiling. It is thicker, darker, and less sweet.
- Blackstrap molasses is the syrup that results from the third boiling. It is the thickest and darkest type of molasses and tends to have a bitter taste.
- It is traditionally used in animal feed and for the production of ethanol, yeast, and lactic acid.
- Molasses is also used in the production of ethyl alcohol and as an additive in livestock feed.
Exercise MITRA SHAKTI-2025:

The “Exercise MITRA SHAKTI-2025” is being conducted at Foreign Training Node, Belagavi, Karnataka.
- It is the eleventh edition of joint military exercise between India and Sri Lanka.
- Aim is to jointly rehearse conduct of Sub Conventional Operations under Chapter VII of United Nations Mandate.
- The Indian contingent is being represented mainly by troops from the RAJPUT Regiment and personnel from the Indian Air Force are also participating in the exercise.
- The scope of the exercise includes synergising joint responses during counter-terrorist operations.
- Both sides will practice tactical actions such as raid, search and destroy missions, heliborne operations, etc.
- It will also involve employment of Drones and Counter Unmanned Aerial Systems besides helicopters.
- It also involves drills to secure helipads and undertake casualty evacuation during counter-terrorist operations will also be rehearsed jointly by both sides.
- Both sides will exchange views and practices of joint drills on a wide spectrum of combat skills.
Rift Valley Fever:

The World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed an outbreak of Rift Valley Fever (RVF) affecting Mauritania and Senegal in Western Africa.
- It is caused by a Phlebovirus belonging to the Phenuiviridae family.
- It primarily affects animals such as sheep, goats, cattle, and camels.
- Humans become infected through close contact with infected animals or by the bite of infected mosquitoes.
- The virus has not been shown to spread from person to person.
- It derives its name from Kenya’s Rift Valley, where the disease was first recognised in the early 1930s.
- Since then, the infection has appeared across sub-Saharan Africa.
- In 1977, it spread northwards to Egypt, and by 2000, it had crossed the Red Sea into Saudi Arabia and Yemen, marking its first confirmed appearance outside the African continent.
- Multiple mosquito species can transmit the Rift Valley fever virus, and the predominant vector differs from one region to another.
- In about 90 % of cases, RVF presents as a mild, flu-like illness that begins two to six days after infection.
- The onset is marked by high fever, muscle and joint pain, headache, weakness, and backache, sometimes accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light.
- In a small proportion of patients, disease progresses to a severe form affecting the eyes, brain, or liver.
- Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment. Medical care is primarily supportive.
ICFT–UNESCO Gandhi Medal:

The 56th International Film Festival of India (IFFI), 2025, the ICFT-UNESCO Gandhi Medal continues to honour cinematic works that embody Mahatma Gandhi’s values of peace, non-violence, and inter-cultural dialogue.
- ICFT–UNESCO Gandhi Medal was instituted at 46th edition of IFFI (2015) in collaboration with International Council For Film, Television And Audiovisual Communication (ICFT)-Paris under UNESCO.
- This medal honours films that not only hold high artistic and cinematic standards but also encourage ethical reflection on society’s most pressing issues.
- The award was created to foster a deeper understanding of humanity’s shared values through the transformative power of cinema.
- ICFT was established at the General Conference of UNESCO held in New Delhi in 1956 to encourage intercultural dialogue and peace through film, television, and digital media.
Co-Op Kumbh 2025:

The Union Minister of Cooperation inaugurated ‘Co-Op Kumbh 2025’, an international conference on the future of India’s urban cooperative banking sector, and adopted the Delhi Declaration 2025.
Outcomes:
- Delhi Declaration 2025: It will serve as a roadmap for the expansion of Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs).
- Digital Initiatives: Launch of Sahkar Digi-Pay and Sahkar Digi-Loan apps to enable even the smallest UCBs to offer digital payment and loan facilities.
- Expansion Goal: A target to establish one UCB in every city with a population of over 2 lakhs within 5 years.
- Future Initiatives: National Federation of Urban Cooperative Banks and Credit Societies (NAFCUB) has been directed to onboard 1,500 banks onto Sahkar Digi-Pay within two years; encourage conversion of successful credit societies into UCBs.
- NAFCUB is an Apex Level promotional body for Urban Cooperative Banks and Credit Societies, registered as a Multi-State Cooperative Society in February 1977.
Digital Gold Risks: SEBI

The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has issued a strong advisory cautioning investors against investing in unregulated digital gold/e-gold products, highlighting their high risks and lack of investor protection.
- Digital gold is not classified or regulated as a security or commodity derivative and lacks the investor protection mechanisms available for SEBI-approved products.
- Investors rely entirely on the issuer, creating a high risk of default on physical gold or cash delivery.
- Market safeguards like insurance, grievance redressal, and guaranteed settlements do not apply, leaving investors without formal recourse.
- Digital gold refers to buying gold electronically without physical possession, with its price linked to physical gold. Created using blockchain technology, it allows investors to buy, sell, and store gold online.
- It is easy to access, can be sold quickly in emergencies, and allows investment with small amounts.
- It removes storage hassles and can be converted into physical gold like coins, bars, or jewellery when needed.
- SEBI advises investors to use regulated gold investment options such as Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs), Gold exchange-traded fund (ETF), Electronic Gold Receipts (EGRs), and commodity derivatives.
India-Bhutan Bilateral Relations:
Prime Minister of India is in Thimphu to join the seventieth birthday celebrations of former King Jigme Singye Wangchuck, widely called K Four, and to underline the strategic depth of India Bhutan ties.India is Bhutan’s largest trade and investment partner, absorbing over 90% of Bhutan’s exports, mainly hydropower.Bhutan remains India’s most reliable partner in South Asia, exemplifying the “Neighbourhood First” policy in practice.The 1949 Treaty of Friendship institutionalised India-Bhutan relations; the 2007 revision removed guidance clauses, marking a mature, sovereign partnership.
Watershed Mahotsav:
Union Minister of Agriculture will inaugurate the Watershed Mahotsav in Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, on November 11, 2025.The Watershed Mahotsav is a national festival celebrating community participation in sustainable watershed management. It focuses on integrating citizens, policymakers, and local bodies to promote holistic soil and water conservation in rural India.It is part of the National Watershed Conference 2025, organised by the Department of Land Resources (DoLR) under the Ministry of Rural Development. Aim is to foster Jan Bhagidari (public participation) in watershed development, restore degraded ecosystems, and strengthen rural livelihoods through efficient water management and soil conservation.
Integrity Matters Checklist:
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) has launched the UN-endorsed “Integrity Matters Checklist”, a new tool designed to help companies align their climate disclosures with UN standards for credible net-zero commitment.An UN-endorsed climate disclosure framework that helps companies and investors transparently report on net-zero targets, transition plans, and greenhouse gas reduction efforts. Developed by GRI in partnership with the United Nations, aligning with recommendations of the UN High-Level Expert Group (HLEG) on Net Zero Commitments.Aim is to operationalise the Integrity Matters report of the HLEG by ensuring corporate climate action is credible, science-based, and transparent, supporting both the Paris Agreement and 2030 Agenda goals.
Graded Response Action Plan III:
The Delhi government has implemented Stage III of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-III) as the city’s Air Quality Index (AQI) breached 400, entering the ‘severe’ category for the first time this season. The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) is a dynamic pollution control framework designed to combat deteriorating air quality in the National Capital Region (NCR) through stage-wise preventive and corrective actions based on AQI levels.
Organisation Involved: Implemented by the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in coordination with the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), Delhi Government, and state pollution control boards of NCR states. Established in: 2017, following the directions of the Supreme Court of India, based on recommendations by the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA).Aim is to reduce air pollution in Delhi-NCR through timely, coordinated, and graded interventions, thereby safeguarding public health and ensuring compliance with the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) objectives.
2nd WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit:
The 2nd WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit is set to take place from December 17–19, 2025, at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi. Co-hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and India’s Ministry of AYUSH, the summit is expected to bring together experts, policymakers, and practitioners from across the globe. The event will focus on the theme: “Restoring Balance: The Science and Practice of Health and Well-being.”The summit is designed to advance the goals of the WHO Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025–2034. According to AYUSH Minister Prataprao Jadhav, the summit will Promote dialogue between global health leaders on traditional and integrative medicine, Encourage evidence-based research to strengthen the role of traditional medicine in health systems, Foster policy actions supporting universal health coverage (UHC) and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium in Delhi to Be Redeveloped as Sports City:
Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium (JLN) in New Delhi is set to undergo a complete transformation into a modern Sports City. As announced by the Sports Ministry, the ambitious project proposes converting the existing stadium complex into a state-of-the-art facility that caters to multiple sports disciplines and includes dedicated lodging facilities for athletes. This marks a pivotal move in India’s journey toward creating world-class training environments and supporting long-term athletic development.
Britannia Industries has appointed Rakshit Hargave as its new CEO and Executive Director:
Britannia Industries, one of India’s leading FMCG and food companies, has named Rakshit Hargave as its Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Executive Director for a five-year term. The appointment will take effect from December 15, 2025, following approval from company members, according to a stock exchange filing. This move marks a significant leadership transition at Britannia, as Hargave brings with him decades of experience across global consumer brands and successful business transformations.Rakshit Hargave served as the CEO of Birla Opus, the paints division of the Aditya Birla Group
Assam Passes Bill to Ban Polygamy:
The government of Assam has taken a landmark step by approving the Assam Prohibition of Polygamy Bill 2025. This move aims to prohibit the practice of polygamy — entering into more than one marriage while a first marriage subsists — making it a punishable offence. The legislation reflects the state’s push toward legal uniformity in marriage practices and reinforcing women’s rights.
Key Provisions of the Bill
- The Bill seeks to make it illegal for an individual to marry another person if their first marriage still stands (i.e., they are not legally separated or divorced).
- Offenders could face imprisonment for up to 7 years for violating the law.
- A provision in the Bill allows for the establishment of a special compensation fund for women adversely affected by polygamous marriages.
- The Bill will be tabled in the Assembly (scheduled for 25 November 2025) for legislative approval.
Shaikha Nasser Al Nowais of the UAE has been appointed as the first woman to head UN Tourism:
Shaikha Nasser Al Nowais has become the first-ever woman to lead UN Tourism. Her appointment was confirmed during the 123rd UN Tourism Executive Council session in Segovia, Spain, and will be formally ratified by the UN General Assembly. She is set to assume office in January 2026 for a four-year term, breaking a 50-year precedent since the organisation’s founding in 1975.




