Today’s Current Affairs: 14th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Leopard Cat : Spotted

A leopard cat has been spotted in Maharashtra’s Pench Tiger Reserve for the first time, a senior forest official said recently.
- Leopard Cat is a species of forest-dwelling cat, of the family Felidae. It is noted for its leopard-like colouring.
- They are the most widely distributed Asian small cats.
- Their range extends from the Amur region in the Russian Far East over the Korean Peninsula, China, Indochina, the Indian Subcontinent, to the West in northern Pakistan, and to the south in the Philippines and the Sunda Islands of Indonesia.
- They are found in agriculturally used areas but prefer forested habitats.
- They live in tropical evergreen rainforests and plantations at sea level, in subtropical deciduous and coniferous forests in the foothills of the Himalayas at altitudes above 1000 m.
- They vary widely in size and appearance across their range. The colouration ranges from pale tawny, to yellow, red or grey above, with the underparts white and spotted.
- There are usually four black stripes running down the forehead to the nape, breaking up into short bands and elongate spots on the shoulders.
- They are solitary, nocturnal carnivores.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concern
Peregrine Falcon:

Project Raptor Watch (PRW) of the Madras Naturalist’s Society, who have been tracking peregrines, aims to document, study and monitor raptor species in Tamil Nadu.
- Peregrine Falcon is one of the most widespread birds in the world.
- It is found on all continents except Antarctica and on many oceanic islands
- They prefer open habitats, such as grasslands, tundra, and meadows.
- They are most common in tundra and coastal areas and rare in sub-tropical and tropical habitats.
- They nest on cliff faces and crevices.
- They are active during the day. When not breeding they are primarily solitary and establish and defend territories.
- They are high level predators, peregrine falcons play an important role in regulating populations of their prey, particularly pigeons and doves.
- Conservation status :IUCN Red List status: Least Concern.
4th Joint Committee Meeting For The Review Of AITIGA:

The 4th Joint Committee meeting for the review of AITIGA (ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement) was held in Putrajaya, Malaysia from 7-9 May 2024
- ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- It was signed at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products; it does not apply to trade in services.
- ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
Vibrant Village Programme : Data

The Home Ministry recently sanctioned 113 roads under the Vibrant Village Programme in Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
- Vibrant Village Programme is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented over the financial years 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- Objective is comprehensive development of villages and blocks on the northern border, thus improving the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- This will help in encouraging people to stay in their native locations in border areas and reversing the outmigration from these villages, adding to improved security of the border.
- It will provide funds for the development of essential infrastructure and the creation of livelihood opportunities in 2967 villages in 19 Districts and 46 Border blocks of 4 states and 1 UT along the northern land border of the country: Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and the UT of Ladakh.
- It envisages focused areas of intervention in the select villages for the creation of opportunities for livelihood generation through promotion of tourism and cultural heritage, skill development and entrepreneurship, and development of cooperative societies, including agriculture/horticulture, cultivation of medicinal plants/herbs etc.
- Interventions also include providing road connectivity to unconnected villages, housing and village infrastructures, energy including renewable energy, television and telecom connectivity.
- Vibrant Village Action Plans will be created by the district administration with the help of Gram Panchayats, and 100 % saturation of Central and state schemes will be ensured.
- There will be no overlap with the Border Area Development Programme.
Zero-Day Vulnerability:
Google Chrome has been hit with another zero-day vulnerability, which has set the alarm bells ringing among users and cyber experts.
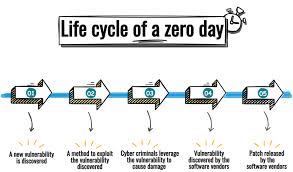
- Zero-Day Vulnerability is a system or software vulnerability unknown to the vendor and for which no patch or means of mitigation are available at the time it is discovered.
- The term ZDV refers to the flaw itself, while zero-day attack refers to an attack that has zero days between the time the vulnerability is discovered and the first attack.
- Zero-day exploit refers to the method or technique hackers use to take advantage of a ZDV, often via malware, and execute the attack.
- Thus, a zero-day attack occurs when threat actors develop and release malware that targets the ZDV.
- Because they were discovered before security researchers and software developers became aware of them—and before they can issue a patch— ZDVs pose a higher risk to users for the following reasons:
- Cybercriminals race to exploit these vulnerabilities to cash in on their schemes.
- Vulnerable systems are exposed until a patch is issued by the vendor.
- Once a ZDV has been made public, it is known as an n-day or one-day vulnerability.
Caenorhabditis elegans:
Researchers found that once C. elegans worms eat a disease-causing strain of bacteria, its children inherited the ‘knowledge’ to avoid making the same mistake — up to four generations.
- Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode worm which is a small, relatively simple, and precisely structured organism.
- It grows within 3-5 days from a fertilised egg to a millimetre-long adult, and it has informed profound insights into the human body, as well as biology.
- It is widely used in research to understand neuronal and molecular biology. It was the first multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced and neural wiring mapped.
- It has two sexes—a hermaphrodite and a male.
- The hermaphrodite can be viewed most simply as a female that produces a limited number of sperm: she can reproduce either by self-fertilization, using her own sperm, or by cross-fertilization after transfer of male sperm by mating.
- Self-fertilization allows a single heterozygous worm to produce homozygous progeny.
Freshwater Under The Ocean Bed:
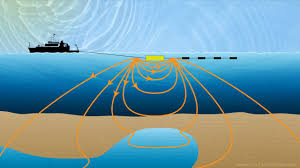
Freshwater exploration from under the ocean bed is gaining attention as a potential solution to depleting freshwater resources. Recent discoveries have revealed significant freshwater reservoirs under the ocean.
- Rainwater and surface water can seep into the ground and percolate deep into the Earth’s crust.
- Some of this water can accumulate in underground reservoirs or aquifers beneath the ocean floor.
- Geological activities such as tectonic movements and volcanic eruptions can create fractures, faults, and cavities in the
- These geological features can trap freshwater, preventing it from mixing with seawater.
- Submarine springs are underwater vents that release freshwater into the ocean.
- These springs can occur where groundwater from aquifers beneath the ocean floor discharges through openings in the seafloor.
- During periods of glaciation, large ice sheets store vast amounts of freshwater.
- As glaciers melt, freshwater can be released into the ocean, forming layers of less dense water that float on the denser seawater below.
Himalayan Magpies : Study

The enchanting Himalayan magpies have garnered increased attention as researchers delve deeper into their habitats and behaviours.
- These captivating birds adorn the mountainous landscapes from Kashmir to Myanmar, adding vibrancy to the region.
- Corvidae Family and Magpies: Magpies belong to the Corvidae family of birds, which includes crows, jays, and ravens.
- Corvids are generally considered to be noisy, inquisitive birds that are often associated with omens, both good and bad, in folklore from around the world.
- Despite their folklore associations, magpies are striking in appearance, and some of the most noticeable species are found in the Himalayas.
- Himalayan magpies are classified as “least concern” on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Indian Space Situational Assessment Report 2023:

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the Indian Space Situational Assessment Report (ISSAR) for 2023, which provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of India’s space assets and their vulnerability to potential collisions in space.
ISSAR 2023 Report Highlight:
- Globally, 3,143 objects were added in 2023 from 212 launches and on-orbit breakup events.
- India contributed to this with the launch of 127 satellites by the end of December 2023.
- In the year 2023, all seven launches of ISRO, namely SSLV-D2/EOS7, LVM3-M3/ONEWEB 2, PSLV-C55/ TeLEOS-2, LVM3-M4/ Chandrayaan-3, and PSLV-C57/Aditya L-1, were successful.
- A total of 5 Indian satellites, 46 foreign satellites, and 8 rocket bodies (including POEM-2) were placed in their intended orbits.
- As of 31st December 2023, India has 22 operational satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 29 in Geostationary Orbit (GEO).
- There are three active Indian deep space missions, Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter, Aditya-L1, and Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module.
- ISRO regularly carries out analyses to predict close approaches by other space objects to Indian space assets.
- In case of critical close approaches, ISRO carries out Collision Avoidance Maneuvers (CAMs) to safeguard its operational spacecraft.
- About 1 lakh close approach alerts were received from USSPACECOM (US Space Command), and over 3,000 alerts for close approaches within a distance of 1 km were detected for ISRO satellites.
- No close approaches with other space objects were detected for the Chandrayaan-3 mission throughout its mission phases, and also for Aditya-L1 during its Earth-bound phase.
- The report highlights a significant increase in the number of CAMs conducted by ISRO in 2023.
- ISRO conducts Collision Avoidance Analysis (COLA) to assess and prevent potential collisions.
- A total of 23 Collision Avoidance Maneuvers (CAMs) were carried out during 2023 to protect Indian space assets, compared to 21 in 2022 and 19 in 2021.
- The report details the successful re-entry of 8 Indian satellites in 2023. This includes the controlled de-orbiting of Megha-Tropiques-1, showcasing ISRO’s commitment to responsible space debris management.
PM-EAC Report:

According to a new analysis by the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (PM-EAC), the percentage of Hindus in India has decreased by 7.82% between 1950 and 2015, while the percentages of Muslims, Christians, and Sikhs have increased.
Key Findings of this PM-EAC Report:
- From 1950 to 2015, as per the data collected on the religious demographics of 38 OECD countries, 30 of these countries experienced a significant decrease in the proportion of Roman Catholics, the predominant religious group.
- In 167 surveyed countries, the average reduction of majority populations globally during the period 1950-2015 was 22%.
- The decline of the majority religious population was steeper in OECD countries, with an average decline of 29%.
- In Africa, animism or native religion was the dominant religion in 24 countries in 1950.
- By 2015, they are no longer a majority in any of these 24 countries in Africa.
- In the South Asian region, the majority religious group is increasing while minority populations have significantly declined in countries such as Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, and Afghanistan.
Findings for India: - The population of Hindus has declined by 7.82%.
- As per 2011 census, Hindu population in India as of 2011 is approximately 79.8%.
- The share of Muslim population rose from 9.84% to 14.095% and Christian population rose from 2.24% to 2.36%.
- Sikh population increased from 1.24% to 1.85% and the share of the Buddhist population rose from 0.05%to 0.81%.
- The Jain and Parsi community populations decreased. The share of Jains dropped from 0.45% to 0.36%, and the share of the Parsi population decreased by 85% from 0.03% to 0.0004%.
- As per the data from National Family Health Survey, India’s Total Fertility Rate (TFR) is currently around 2, which is close to the preferred TFR of 2.19.
- TFR is a reliable indicator for projecting population growth.
- For Hindus, it declined from 3.3 in 1991 to 2.1 in 2015, and further to 1.9 in 2024
- In Muslims, it declined from 4.4 in 1991 to 2.6 in 2015, and further to 2.4 in 2024.
- Equality for Minorities: In India, minorities experience equal benefits and live a comfortable life, while global demographic shifts remain a cause for concern.
Lancet Kamikaze Drone:

In the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, Russia’s utilization of the Lancet Kamikaze drone, which incorporates American AI technology, highlights complex global supply chain issues.
- Kamikaze drone are small unmanned aircraft packed with explosives that can be flown directly at a tank or a group of troops that are destroyed when it hits the target and explodes.
- These are also called as Switchblade drones.
- The name comes from the World War 2 era’s feared Japanese kamikaze pilots, who conducted suicide attacks by intentionally crashing their explosive filled aircraft into enemy targets.
- The modern drone versions have the capability of surpassing traditional defences to strike their targets and are also cheaper than their larger counterparts.
- The small lethal drones are difficult to detect on radar, and through the use of facial recognition, can be programmed to hit targets without human intervention.
- Although the US Kamikaze might be the most advanced in this class of drones, Russia, China, Israel, Iran and Turkey all have some versions of it.
Indian Ocean Basin-Wide (IOBW) Index:

According to a study, Indian Ocean basin-wide (IOBW) index exhibits a close association with dengue outbreaks in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
- Indian Ocean basin-wide (IOBW) Index represents the average sea-surface temperature variations across the tropical Indian Ocean.
- It has emerged as a key indicator for predicting the magnitude and timing of dengue epidemics in each country.
- Its association with the Southern Hemisphere is stronger than that with the Northern Hemisphere.
- It has a more pronounced impact on temperatures in tropical regions. Brazil, for example, bears a higher burden of dengue in the Southern Hemisphere.
- The Northern Hemisphere witnesses a peak dengue epidemic period between July and October and the Southern Hemisphere in February and April, both in the summers.
- Further, the amplitude of dengue incidence was high when the index was positive and low when it was negative.
- The link between the Indian Ocean’s temperature and dengue incidence is likely due to its influence on regional temperatures through teleconnections, large-scale atmospheric patterns that can transfer heat and moisture across vast distances.
Mammoth Carbon Capture Plant:

The world’s largest facility designed to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere started operations in Iceland.
- Mammoth carbon capture Plant is the largest carbon dioxide capture and storage facility of its kind situated on a dormant volcano in Iceland.
- It is dubbed as “Mammoth,” this plant is Climeworks’ second commercial direct air capture (DAC) facility in the nation and is significantly larger than its predecessor, Orca, which began in 2021.
- This cutting-edge technology draws in air and chemically extracts carbon dioxide, which can then be stored underground, converted into stone, or reused.
- The Swiss company Climeworks, in partnership with Icelandic company Carbfix, plans to sequester the captured carbon by turning it into stone beneath the earth’s surface, utilizing Iceland’s abundant geothermal energy to power the process.




