Today’s Current Affairs: 21st July 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Chikungunya:
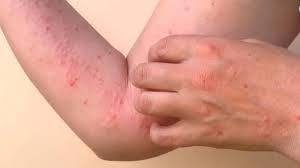
The Ministry of Health in China recently initiated an emergency campaign to safeguard those at risk of Chikungunya fever illness.
- It is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV).
- It causes fever and severe joint pain.
- The word comes from the African Makonde language and means “bent over in pain.”
- It was first described during an outbreak in southern Tanzania in 1952 and has now been reported in more than 110 countries in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Europe.
- It is transmitted to humans by the bites of infected female mosquitoes, most commonly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
- These two species can also transmit other viruses, including dengue and Zika viruses.
- An infected person cannot spread the infection directly to other persons (i.e., it is not a contagious disease).
- The symptoms of chikungunya are similar to those of dengue and Zika, making chikungunya easy to misdiagnose.
- The most common symptom is an abrupt onset of fever, often accompanied by joint pain.
- Other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash.
- Severe joint pain usually lasts a few days but can persist for months or even years.
- Serious complications are uncommon, but atypical severe cases can cause long-term symptoms and even death, especially in older people and in children under one year old.
- There is no vaccine or antiviral drug treatment for chikungunya.
- Treatment is focused on relieving the symptoms.
Pale-Capped Pigeon:

In a significant sighting for birdwatchers and conservationists alike, the elusive Pale-capped Pigeon was recently photographed in Dehing Patkai National Park in Assam.
- The pale-capped pigeon, also known as the purple wood pigeon, is a large, dark purplish-maroon bird that is found in parts of the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Scientific Name: Columba punicea
- It is very locally distributed across its broad range, which encompasses parts of northern and northeastern India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand,
- Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam.
- It largely inhabits forest habitats, chiefly, primary or secondary evergreen forests, and bamboo and agricultural fields in close proximity to forests.
- Its range extends from the lowlands up to 1,600 m.
- It is mainly brown above and chestnut below with a sheen of green or amethyst.
- Males have a whitish-grey-cap while females have a brownish-grey-cap and less gloss on the feathers.
- They are frugivores, foraging in small groups in the canopy of trees but sometimes descending to the ground for seeds and fallen fruit.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary:

The Karnataka government has violated Wildlife (Protection) Act as well as Supreme Court orders in clearing a proposal to reduce the extent of Shettihalli Wildlife Sanctuary,, while the National Board of Wildlife (NBWL) has failed to ensure that denotification of 300 sq km of sanctuary is compensated.
- It is located in the Shimoga District of Karnataka.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on 23rd November 1974.
- It spans an area of 395.6 square kilometres.
- Inside the sanctuary is located the Tunga Anicut Dam, which shelters otters and water birds.
- Mandagadde Natural Bird Sanctuary, present on a small island in the River Tunga, is also a part of this sanctuary.
- There are a large number of human settlements inside Shettihalli Sanctuary, mainly consisting of families that were displaced by the construction of the Sharavathi Dam in the 1960s.
- It houses mammals like Tiger, Leopard, Wild Dog, Jackal, Gaur, Elephant, Sloth Bear Sambar, Spotted Deer, Wild Pig, Common Langur, Bonnet Macaque, etc.
- Birds include Hornbills, Kingfishers, Bulbuls, Parakeets, Doves, Pigeons, Babblers, Flycatchers, Munias, Swallows, Woodpeckers, Peafowl, Jungle fowl and Partridges.
Tuvalu : In News

More than 5,000 people have applied for a first-of-its-kind migration visa that offers residents of Tuvalu an escape from the worst effects of climate change.
- Tuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is an island country located midway between Hawaii and Australia in the west-central Pacific Ocean.
- Its neighbours include Kiribati, to the north, and Fiji, to the south.
- It comprises nine islands (four reef islands and five coral atolls) scattered in a chain lying approximately northwest to southeast over a distance of some 420 miles (676 km).
- All islands are low-lying, with no point on Tuvalu being higher than 4.5 m above sea level. Thus, the islands are threatened by any future sea level rise.
- There are no rivers. Tuvalu’s climate is hot and rainy.
- With the exception of tiny Vatican City, Tuvalu has the fewest inhabitants of any other independent nation.
- Capital: Funafuti
- Most people speak a language called Tuvaluan. English is also common.
- Most people are subsistence farmers and are aided by remittances from relatives working overseas.
- A small quantity of copra is produced for export, the sale of stamps accounts for modest earnings, and fees are collected from foreign fishing fleets.
- Tuvalu became independent from the United Kingdom in October 1978.
- It operates as a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy.
- It is part of the Commonwealth Realm, with King Charles III recognized as King of Tuvalu. He is represented by a Governor-General, who is appointed upon the advice of the Prime Minister.
- There are no political parties: the prime minister is chosen by and from the legislature.
Lyriothemis abrahami : New species of dragonfly

- It is a new species of dragonfly discovered in Kerala.
- It breeds in small water pools in tree holes.
- It exhibits strong dimorphism, with males featuring uniquely shaped hamules and female displaying jet black bodies with yellow triangular spots.
- Its distribution spanned from lowland rainforests to mid-elevation evergreen and deciduous forests between 50 m and 1,100 m above sea level.
- The finding increased Kerala’s odonate species count to 191, including 78 endemic species,
- The dragonfly is an indicator of forest health, stressing habitat conservation’s broader ecological benefits.
- Dragonflies are among the apex predators of the insect world and are considered to be responsible for regulating the numbers of many other insect species.
- They are crucial insect predators that help regulate mosquito and pest populations in urban areas.
Kamchatka Peninsula : Five earthquakes struck

As many as five earthquakes struck near the coast of the Kamchatka peninsula region in the far east of Russia.
- It lies in far eastern Russia, between the Sea of Okhotsk on the west and the Pacific Ocean and Bering Sea on the east.
- It is one of the world’s most concentrated areas of geothermal activity.
- It is part of the Kamchatka Krai. Kamchatka, also known as a land of fire and ice, sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire and is home to over 150 volcanoes, including 29 active volcanoes.
- It is about 1,200 km long north-south and about 480 km across at its widest.
- Area: Approximately 370,000 square km.
- About 300,000 people live on the peninsula. The population density is one of the lowest in the world, at less than a person per square kilometre.
- Climate is Severe, with prolonged, cold, and snowy winters and wet, cool summers.
- The Klyuchevskaya Sopka in the Eastern Range is the highest point on the Kamchatka Peninsula.
- Regional Capital: Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
- The Kuril island chain runs from the southern tip of the peninsula to a short distance from Japan’s northern Hokkaido Island.
INVICTUS Research Programme:

It is a research programme with the goal of developing hypersonic technologies applicable to future reusable vehicles capable of horizontal launch.
- It is funded through ESA’s General Support Technology Programme(GSTP) and Technology Development Element (TDE)
- It is a fully reusable experimental aerospace vehicle capable of flying at Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound).
- The vehicle will demonstrate key technologies for sustained hypersonic flight in the atmosphere and will be upgradable, allowing for the exchange of materials, software and propulsion systems between flight test campaigns.
- INVICTUS builds on previous technology developments managed by ESA and will offer industry, agencies and academia an opportunity to test future hypersonic technologies in a relevant environment.
- The INVICTUS programme will prove the suitability of a hydrogen-fuelled precooled air-breathing propulsion system for horizontal take-off and hypersonic flight.
OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2025-2034:

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Agricultural Outlook 2025-2034 report, offers a 10-year outlook on global agricultural and fish markets to guide evidence-based policymaking.
- Global cereal production is expected to grow at 1.1% annually, driven largely by yield increases (0.9% per year). However, the expansion of harvested area will slow to 0.14% annually through 2034.
- By 2034, 40% of cereal production will be consumed directly by humans, while 33% will be used for animal feed and 27% will be diverted to biofuels and industrial uses.
- By 2034, India and Southeast Asia will drive 39% of global cereal consumption growth, while China’s share will fall to 13% from 32%, reflecting changing consumption trends.
- Biofuel demand is projected to grow at 0.9% annually, primarily due to increases in countries like Brazil, India, and Indonesia.
- Global agricultural and fish production is projected to grow by 14% through 2034, primarily driven by productivity gains in middle-income nations.
- However, this growth will also lead to a 6% increase in agricultural greenhouse gas emissions.
- Global per capita calorie intake from livestock and fish products is expected to increase by 6% over the next decade, driven by growth in lower-middle-income countries, where intake is anticipated to rise by 24% nearly four times the global average.
- This increase will raise daily intake in lower-middle-income countries to 364 kcal, but low-income countries will remain far behind, with an intake of just 143 kcal, well below the 300 kcal/day target for a healthy diet.
India Becomes Global Leader In Fast Payments : IMF Report:

India has become the global leader in real-time payments as UPI processed 18.39 billion transactions in June 2025, according to an IMF-supported report.
- It is Jointly developed by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and FIS Global, this Fast Payments Report 2025 analyses global public digital infrastructure.
- It uses a new metric: Faster Payment Adoption Score (FPAS) to benchmark digital payment adoption.
- Top Global Rank (FPAS: 87.5%): India leads 30 countries, surpassing Brazil, Singapore, UK, and USA.
- UPI Scale: Processes over 640 million transactions daily, serving 491 million individuals and 65 million merchants via 675 banks.
- Speed and Cost: Delivers payments within 5 seconds, with near-zero cost per transaction.
- Global Reach: UPI is now operational in 7 countries, including France, UAE, and Singapore.
- BRICS Integration: India is advocating UPI as a cross-border payment standard among BRICS+ nations.
Codex Alimentarius:

India’s millet standard and leadership in Codex committees were appreciated at the 88th Codex Executive Committee (CCEXEC88) in Rome.
- Codex Alimentarius is a collection of internationally recognized food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. It promotes food safety, consumer protection, and fair-trade practices in international food commerce.
- Established in: 1963 by FAO and WHO.
- Headquarters: Rome, Italy.
- Objectives is To ensure consumer health protection and promote fair practices in food trade, to assist countries in harmonizing food regulations to reduce non-tariff barriers.
Marungur Excavation:
The Tamil Nadu State Department of Archaeology (TNSDA) has completed the Marungur excavation in Cuddalore district, unearthing a habitation-cum-burial site dating from the Iron Age to Early Historic Period.A multidisciplinary archaeological excavation aimed at uncovering prehistoric settlements and burial systems spanning the Iron Age to Early Historic period, led by the TNSDA.Located in Panruti taluk, Cuddalore district, Tamil Nadu, between the Thenpennai and Vada Vellar rivers, part of the ancient Naduvil Mandalam
Cy-TB Skin Test:
Kerala has introduced the Cy-TB skin test as a simplified tool for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) detection under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).Cy-TB is a new-generation intradermal skin test developed to detect latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in individuals. Unlike traditional tests like the Mantoux test or IGRA blood test, Cy-TB uses specific antigens (ESAT-6 and CFP-10) derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.It is a Intradermal skin test to detect latent TB infection. Introduced under India’s NTEP, supported by state TB units and ICMR. Objective: Early detection of dormant TB to prevent progression to active disease. Target Group: Adults (18+), especially those in high-risk or contact groups.
Kashi Declaration:
The Youth Spiritual Summit concluded in Varanasi with the adoption of the Kashi Declaration, setting a national roadmap for youth-led action against drug abuse. The Kashi Declaration is a national action plan adopted at the Youth Spiritual Summit to combat substance abuse through youth and spiritual leadership. It emphasizes a multi-dimensional, culturally rooted framework to eliminate drug addiction from Indian society. Declared By: Initiated by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports during the Youth Spiritual Summit 2025.
Objectives of the Declaration:
- Eradicate Drug Abuse: Create a Nasha Mukt Yuva as the foundation of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
- Spiritual Mobilisation: Use India’s spiritual capital as a catalyst for healing and transformation.
- Whole-of-Society Approach: Integrate families, communities, and institutions into prevention and recovery.
- Institutional Coordination: Facilitate action through a Joint National Committee and regular reporting.
- Empower Youth Volunteers: Enable youth clubs under the MY Bharat platform to lead awareness and de-addiction campaigns.
Guryul Ravine Fossil Site:
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has warned of severe threats to the Guryul Ravine fossil site in Kashmir due to ongoing quarrying and land diversion.Guryul Ravine is a 260-million-year-old geological fossil site, capturing Earth’s greatest mass extinction—the Permian–Triassic boundary (PTB). It offers unmatched insight into ancient climate change and evolutionary events. Situated in Khonmoh, on the outskirts of Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir.
Geologically part of the Vihi District. It is Formed during the Permian–Triassic transition, when volcanic activity, oxygen decline, and climate disruption triggered global die-offs. Over time, marine and terrestrial sediments preserved fossil-rich strata.
Inauguration of IICT’s First Campus in Mumbai:
Inauguration of the first campus of the Indian Institute of Creative Technology (IICT) in Mumbai. This initiative aims to elevate India’s presence in the global AVGC-XR (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, Comic & Extended Reality) ecosystem by nurturing industry-ready talent through world-class training and collaborations. The launch aligns with the government’s broader vision to enhance India’s digital and creative economy while integrating emerging technologies into skill development.The AVGC-XR sector in India is growing rapidly, with increasing global demand for content creation and immersive experiences. Recognizing this, the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, in collaboration with the Maharashtra government, initiated the establishment of IICT under a public-private partnership framework.
2025 MRF National Racing Championship:
India’s premier motorsport event, the MRF MMSC FMSCI Indian National Car Racing Championship 2025, kicked off its first round at Kari Motor Speedway, Coimbatore, showcasing emerging young talent in top racing categories like MRF F2000, Formula 1600, and Touring Cars. The event saw intense competition and remarkable performances by teen racers, underlining the future of Indian motorsports.The MRF MMSC FMSCI National Championship is India’s flagship racing series, conducted annually across key racetracks. Organized by the Madras Motor Sports Club (MMSC) under the aegis of FMSCI, the event provides a platform for professional and amateur racers to compete in various categories, including open-wheel formula racing, touring cars, and Volkswagen Polo Cup.
PM Modi Launches ₹7,200 Crore Infrastructure Projects in Bihar:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated infrastructure projects worth ₹7,200 crore in Motihari, Bihar, aiming to accelerate the state’s transformation into a hub of growth and opportunity. These projects are part of the broader Viksit Bharat Mission, which envisions balanced regional development and integration of Eastern India into the national growth narrative.Bihar, despite its cultural and historical importance, has faced long-standing developmental challenges. PM Modi highlighted that during the UPA regime, Bihar received only ₹2 lakh crore over ten years, reflecting limited central support. In contrast, the NDA government claims to have significantly increased investments in the state, aiming for urban renewal, connectivity, and housing development.
Birth Anniversary of Shaheed Mangal Pandey:
The Prime Minister paid tribute to the great freedom fighter Mangal Pandey on his birth anniversary on 19th July.Mangal Pandey was born on 19th July, 1827, in the Ballia district of Uttar Pradesh. He joined the 34th Bengal Native Infantry of the East India Company’s army at the age of 22.
Mutiny: He refused to use the newly introduced Enfield Pattern 1853 rifle-musket, as sepoys believed its cartridges were greased with beef and pork fat, which offended Hindu and Muslim religious sentiments. On 29th March, 1857, he mutinied and fired at his Senior Sergeant Major. The movement of protest and rebellion came to be known as the Sepoy Mutiny of 1857, also known as the First War of Independence. Soldiers of the 7th Awadh Regiment revolted but were suppressed, while discontent spread to Ambala, Lucknow, and Meerut. He was hanged on 8th April, 1857, at Barrackpore, and his regiment was disbanded for showing resentment.
US President Donald Trump signed the GENIUS Act:
US President Donald Trump signed the GENIUS Act (Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for US Stablecoins), establishing a formal regulatory framework for payment stablecoins, marking a new phase of government engagement with digital assets. The law boosts user confidence with consumer protections and aims to make the US a global crypto leader.The Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that aim to maintain a stable value by being pegged to traditional assets like the USD or gold.The definition excludes digital national currencies, deposits (including tokenized deposits), and securities. Stablecoins are designed for everyday use, offering price stability unlike volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. They enable easy value transfer, support financial services, and maintain stability through collateral reserves or algorithmic supply control. Popular stablecoins like Tether and USD Coin are backed by the US dollar. India does not currently recognise stablecoins, treating all cryptocurrencies as Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) under Section 2(47A) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. In 2023, VDAs were brought under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, to curb misuse and enhance oversight.
Floods in Godavari River:
Floods in Godavari River have displaced many people in Eluru district, Andhra Pradesh, leading to large-scale evacuations and the establishment of relief camps. Godaveri River Known as Dakshin Ganga (Ganges of the South), the Godavari is India’s second-longest (1465 km) river (after Ganga) and the largest river system in Peninsular India.It originates from Trimbakeshwar near Nasik in Maharashtra and flows eastward before draining into the Bay of Bengal. Its basin spans Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha, with minor parts in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and the Union Territory of Puducherry. The Godavari basin is roughly triangular in shape, with the Godavari River flowing near the base of the triangle. It is bounded by the Satmala Hills, Ajanta Range, and Mahadeo Hills in the North, the Eastern Ghats in the South and East, and the Western Ghats in the West. Major Tributaries: Purna, Pranhita, Indravati, and Sabari, Wainganga, Wardha, Penganga (Left-Bank) and Pravara, Manjira, and Manair (Right Bank).




