Today Current Affairs: 21st June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Hubble Space Telescope:

Nasa reports trouble with the Hubble Space Telescope. The telescope has been down for the past few days. The problem is a payload computer that has stopped working.
- The payload computer’s purpose is to control and coordinate the science instruments and monitor them for health and safety purposes.
About the Hubble Space Telescope:
- The Hubble Space Telescope is a large telescope in space. NASA launched Hubble in 1990.
- It was built by the United States space agency NASA, with contributions from the European Space Agency.
- Hubble is the only telescope designed to be serviced in space by astronauts.
- Expanding the frontiers of the visible Universe, the Hubble Space Telescope looks deep into space with cameras that can see across the entire optical spectrum from infrared to ultraviolet.
- The Hubble Space Telescope makes one orbit around Earth every 95 minutes.
Green Hydrogen Initiatives:

India is hosting a summit on Green Hydrogen initiatives involving the BRICS nations. The event offers a platform to share their respective Green Hydrogen initiatives and views on how to take it to the next level in their own countries.
- The event will be anchored by NTPC Ltd , a Maharatna CPSU under the Ministry of Power.
- Hydrogen when produced by electrolysis using renewable energy is known as Green Hydrogen which has no carbon footprint.
Significance of Green Hydrogen:
- Green hydrogen energy is vital for India to meet its Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) Targets and ensure regional and national energy security, access and availability.
- Green Hydrogen can act as an energy storage option, which would be essential to meet intermittencies (of renewable energy) in the future.
- In terms of mobility, for long distance mobilisations for either urban freight movement within cities and states or for passengers, Green Hydrogen can be used in railways, large ships, buses or trucks, etc.
- Green Chemicals like ammonia and methanol can directly be utilized in existing applications like fertilizers, mobility, power, chemicals, shipping etc.
- Green Hydrogen blending up to 10% may be adopted in CGD networks to gain widespread acceptance.
Farmers Protests:

According to the State of Environment in Figures 2021 report released by Centre for Science and Environment (CSE), there was a fivefold increase in major farmers’ protests since 2017.
- In 2017, there were 34 major protests across 15 States. The number has now shot up to 165 protests across 22 States and Union Territories.
- This was due to the three contentious Central farm laws, apart from procurement and agricultural market price-related failures.
- 12 of these are pan-India protests, including 11 agitations against the three farm reform laws introduced last year.
- Battles against acquisition of farm land for development projects, including highway and airport construction, are the prime cause of 17 agitations.
- At least seven agitations have been to demand loan waivers or to protest poor insurance coverage and delayed compensation.
- Although Punjab and Haryana farmers have caught the limelight for the recent protests outside Delhi, data shows that the largest number of recent protests have taken place in Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- The report notes that India now has more farm labourers than landowning farmers and cultivators. This is true in 52% of the country’s districts, as well as in all districts of Bihar and Kerala.
- More than 28 agricultural workers and cultivators end their lives every day. The latest data available shows that 5,957 farmers and an additional 4,324 farm labourers died by suicide in 2019.
Illegal adoption:

The Supreme Court agreed to intervene after the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) sounded the alarm on a spate of complaints about illegal adoption of COVID orphans through private individuals and organisations.
- Social media posts are circulating that children are up for adoption. This is plainly illegal and violates the Juvenile Justice Act.
- The adoption of orphaned/abandoned/ surrendered children is lawful only after the adoption procedure as given under the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015 is followed and the final adoption order is passed by the prescribed authority.
- Section 74 of the Juvenile Justice Act prohibits the disclosure of identity of children with regard to the name, school, age, address or any information which would reveal the essential details of the child.
- Placing any confidential information about children in the public domain which would make them susceptible to trafficking,
- NCPCR statistics shows that 3,621 children were orphaned, 26,176 children lost either parent and 274 children were abandoned between April 1, 2021 to June 5, 2021.
National Population Register (NPR):

Migrants belonging to six non-Muslim minority communities from Afghanistan, Pakistan and Bangladesh, while applying for long-term visas (LTVs), can also produce National Population Register (NPR) enrolment slips as proof of the duration of their stay in India, according to a Union Home Ministry manual.
- The NPR number is part of an illustrative list of more than 10 documents that could be provided to apply for an LTV, which is a precursor to acquiring Indian citizenship either by naturalisation or registration under Section 5 and 6 of the Citizenship Act, 1955, for the six communities — Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, Parsis, Christians and Buddhists — from the three countries.
- The special provision of LTVs for Hindus and Sikhs from Pakistan and Afghanistan was first made in 2011.
- Ministry officials assert that the awareness drive is not related to the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA), which is intended to benefit undocumented migrants from the six groups who entered India before the 2014 cut-off date.
- The CAA is yet to implemented.
- The NPR was first compiled in 2010 simultaneously with the decadal Census exercise and later updated in 2015.
- It already has a database of 119 crore residents.
- The NPR is a register of usual residents linked with location particulars down to the village level and is updated periodically “to incorporate the changes due to birth, death and migration”.
- The next phase of the NPR, expected to include contentious questions on date and place of birth of father and mother, last place of residence and mother tongue, was to be simultaneously updated with the 2021 House Listing and Housing Census that has been indefinitely postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
NFRA (National Financial Reporting Authority):

NFRA has invited suggestions from public on consultation paper on NFRA’s engagement with its stakeholders.
- NFRA is an independent regulatory body set up under Section 132 of the Companies Act.
- It was established by the Central Government in October 2018.
- After the Satyam scandal took place in 2009, the Standing Committee on Finance proposed the concept of the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) for the first time in its 21st report.
- It oversee compliance with Accounting and Auditing Standards by companies that can be described as Public Interest Entities (PIEs).
- This group includes all listed companies, and large unlisted companies.
- To discharge this mandate, NFRA is in the process of creating a verified and accurate database of companies and auditors that come under the regulatory ambit of NFRA.
- HQ: New Delhi
- Composition: NFRA consists of one chairman, three full-time members and one secretary. Former IAS officer Rangachari Sridharan was appointed as the first chairman of the body in October 2018.
The First CAR-T Cell Therapy:
The first CAR-T cell therapy (a type of gene therapy) in India was done at the Tata Memorial Hospital in Mumbai.
- The CAR-T cells were designed and manufactured at Bioscience and Bioengineering (BSBE) department of IIT Bombay with support from DBT/BIRAC, through National Biopharma Mission.
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) is a not-for-profit Section 8, Schedule B, Public Sector Enterprise, set up by Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology.
- The Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy has emerged as a breakthrough in cancer treatment especially in patients suffering from Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia.
- But, till now this technology was not available in India.
- Each patient’s CAR-T cell therapy costs 3-4 crore (INR).
Blue Water Operations With A Green Footprint:

Indian Navy has adopted a comprehensive ‘Indian Navy Environment Conservation Roadmap (INECR)’ for synergising the aim of ‘Blue Water Operations with a Green Footprint’
- Some of the noteworthy initiatives towards ‘Clean and Green Navy’ are
- Indian Navy commissioned one of its largest solar plant with a capacity of 3MW at Indian Naval Academy (INA), Ezhimala in July 2020.
- Another 2MW solar power plant was installed at Naval Station Karanja, Mumbai in July 2020. With this, the overall installed solar plant capacity at Naval Stations is 11 MW.
- The installation of SPVs are in line with Navy’s objective of fulfilling Govt of India’s ‘Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM)’ mission.
- Further, viability of setting up urban forests concepts such as Miyawaki forests is being emphasised to match the theme of World Environment Day 2021- ‘Ecosystem Restoration’
- Miyawaki is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki (born 1928), that helps build dense, native forests.
- The approach is supposed to ensure that plant growth is 10 times faster and the resulting plantation is 30 times denser than usual.
- It involves planting dozens of native species in the same area, and making them maintenance-free after the first three years.
- In July 2020, Union Environment Minister inaugurated a unique urban forest at the office of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) in New Delhi.
- This would be a dense urban forest with multiple tree layers including 12000 saplings of 59 indigenous species in another year or so.
- The Miyawaki method of forest creation is employed.
Vidabha Tiger Corridors:

In a first-of-its-kind project, radio telemetry has been deployed to identify corridors used by tigers in the Vidarbha landscape, tracking their actual movement.
- The study indicates that the animals are moving in a much wider swathe of area outside the protected areas than previously known.
- The investigators belonged the Maharashtra Forest Department and Wildlife Institute of India (WII),
- Vidarbha has 331 tigers in a forest area of around 26,775 sq km, dissected by 84,202 km of roads, apart from irrigation canals and other projects. There have been growing instances of man-tiger conflict in the region.
- The project, carried out between 2017 and 2020 using radio signals, identified 37,067 sq km, in all, of tiger corridors.
- They tracked the epic journey of Walker (as the tiger was dubbed) over 3,000 km from Tipeshwar Sanctuary in Yavatmal district to Dnyanganga Sanctuary in Buldhana district.
Indian Council Of Agricultural Research (ICAR):

Researchers from various institutes under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya found depleting trends in grain density of zinc and iron in rice and wheat cultivated in India.
- The researchers collected seeds of rice (16 varieties) and wheat (18 varieties) from the gene bank maintained at the ICAR’s Cultivar repositories.
Indian Council of Agricultural Research
- It is an autonomous organisation under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It is the apex body for coordinating, guiding and managing research and education in agriculture including horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences in the entire country.
- It was established on 16th July 1929 as a registered society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It is headquartered at New Delhi. With 102 ICAR institutes and 71 agricultural universities spread across the country this is one of the largest national agricultural systems in the world.
Cultivar repositories are nodal institutes that preserve and archive the old cultivars or varieties from our country. - Zinc and iron concentrations in grains of rice cultivars released within the 1960s were 27.1 mg/kg and 59.8 mg/kg. This depleted to 20.6 mg/kg and 43.1 mg/kg, respectively within the 2000s.
- Concentrations in Wheat: The concentrations of zinc and iron were 33.3 mg/kg and 57.6 mg/kg in cultivars of the 1960s, dropped to 23.5 mg/kg and 46.4 mg/kg, respectively in cultivars released during the 2010s.
Biofortification is the process by which the nutritional quality of food crops is improved through agronomic practices, conventional plant breeding, or modern biotechnology.
- Recently, the Prime Minister dedicated 17 biofortified varieties of 8 crops to the nation.
- Some examples:
- Rice- CR DHAN 315 has excess zinc.
- Wheat- HI 1633 rich in protein, iron and zinc.
- Maize- Hybrid varieties 1, 2 and 3 are enriched with lysine and tryptophan.
- Madhuban Gajar, a biofortified carrot variety, is benefitting more than 150 local farmers in Junagadh, Gujarat. It has higher β-carotene and iron content.
- ICAR has started Nutri-Sensitive Agricultural Resources and Innovations (NARI) programme for promoting family farming linking agriculture to nutrition, nutri-smart villages for enhancing nutritional security and location specific nutrition garden models are being developed to ensure access to locally available, healthy and diversified diet with adequate macro and micronutrients.
- The production of bio-fortified crop varieties will be upscaled and linked with government programmes of mid-day meal, Anganwadi etc. to reduce malnutrition.
Biotech-KISAN Programme:

The Ministry of Science and Technology has issued a Special Call for the NorthEast Region as a part of its Mission Programme “Biotech-Krishi Innovation Science Application Network (Biotech-KISAN)”.
- It is a scientist-farmer partnership scheme launched in 2017.
- It is a pan-India program, following a hub-and-spoke model and stimulates entrepreneurship and innovation in farmers and empowers women farmers.
- The Biotech-KISAN hubs are expected to fulfil the technology required to generate agriculture and bio-resource related jobs and better livelihood ensuring biotechnological benefits to small and marginal farmers.
- Farmers are also exposed to best global farm management and practices.
- This is a farmer-centric scheme developed by and with farmers under the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology.
- It was launched for agriculture innovation with an objective to connect science laboratories with the farmers to find out innovative solutions and technologies to be applied at farm level.
- 146 Biotech-KISAN Hubs have been established covering all 15 agroclimatic zones and 110 Aspirational Districts in the country.
- The scheme has benefitted over two lakhs farmers so far by increasing their agriculture output and income. Over 200 entrepreneurships have also been developed in rural areas.
- The present call specifically focuses on the North East Region (NER) as it is predominantly agrarian with 70% of its workforce engaged in agriculture and allied sector for livelihood.
- The region produces merely 1.5 % of the country’s food grain and continues to be a net importer of food grains even for its domestic consumption.
- The NER has untapped potential to enhance the income of the farming population by promotion of location specific crops, horticultural and plantation crops, fisheries and livestock production.
- The Biotech-KISAN Hubs in NER will collaborate with the top scientific institutions across the country as well as State Agricultural Universities (SAUs)/Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs)/existing state agriculture extension services/system in the NER for demonstrations of technologies and training of farmers.
Gain-Of-Function Research:
The Wuhan Institute of Virology was said to have conducted gain-of-function research on coronaviruses which may possibly have caused the lab-leak origin of the SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19 pandemic).
Gain-of-function Research:
- In virology, gain-of-function research involves deliberately altering an organism in the lab, altering a gene, or introducing a mutation in a pathogen to study its transmissibility, virulence and immunogenicity.
- This is done by genetically engineering the virus and by allowing them to grow in different growth mediums, a technique called serial passage.
- Serial Passage refers to the process of growing bacteria or a virus in iterations. For instance, a virus may be grown in one environment, and then a portion of that virus population can be removed, and put into a new environment.
- This would allow researchers to study potential therapies and ways to control the disease better in future.
- Gain-of-function studies, which enhance viral yield and immunogenicity (relating to immune response), are required for vaccine development.
Summer Solstice: 21st June:
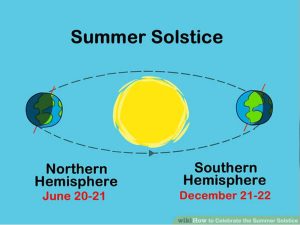
21st June is the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere, technically this day is referred to as Summer solstice. In Delhi, the day length is around 14 hours.
- The amount of light received by a specific area in the Northern Hemisphere during the summer solstice depends on the latitudinal location of the place.
- 21st June is also observed as the International Yoga Day.
About Summer Solstice:
- It is the longest day and shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
- During this, countries in the Northern Hemisphere are nearest to the Sun and the Sun shines overhead on the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° North).
- At latitudes of 23.5° are the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, north and south of the Equator.
- At 66.5° are the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, to the north and south.
- Latitudes are a measure of a location’s distance from the Equator.
- During the solstice, the Earth’s axis — around which the planet spins, completing one turn each day — is tilted in a way that the North Pole is tipped towards the sun and the South Pole is away from it.
- Typically, this imaginary axis passes right through the middle of the Earth from top to bottom and is always tilted at 23.5 degrees with respect to the sun.
- At the Arctic Circle, the sun never sets during the solstice.
Medical And Wellness Tourism (MWT):

The Ministry of Tourism has formulated three draft strategies with roadmaps for promoting Medical and Wellness Tourism, for development of Rural Tourism and for promotion of MICE Industry in India.
- India has been ranked 34th out of 140 countries on the World Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index 2019, released by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
Medical and Wellness Tourism (MWT):
- Describes the rapidly growing practice of travelling across international borders to obtain healthcare services.
- It may be broadly classified into three categories – Medical Treatment, Wellness & Rejuvenation and Alternative Cures.
- Now it is often referred to as Medical Value Travel (MVT).
Rural Tourism:
- Any form of tourism that showcases the rural life, art, culture, and heritage at rural locations, thereby benefiting the local community economically and socially.
- It offers an opportunity to promote sustainable and responsible tourism and fulfill the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Exhibitions):
- The main purpose is to create a networking platform for business, industry, government and Academic Community and engage in meaningful conversations.
- MICE is also known as ‘Meetings industry’ or ‘Events industry’.
Black Softshell Turtle:

The Assam forest department has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with two Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs) and adopted a Vision Document to raise at least 1,000 black softshell turtles by 2030.
About Black Softshell Turtle:
- Scientific Name: Nilssonia nigricans
- They look almost the same as the Indian peacock softshell turtle (Nilssonia hurum), which is classified as Endangered in the IUCN Red List.
- Habitat:
- A freshwater species and there are 29 species of freshwater turtles and tortoises found in India.
- They are found in ponds of temples in northeastern India and Bangladesh. Its distribution range also includes the Brahmaputra River and its tributaries.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: No legal protection
- Threats:
- Consumption of turtle meat and eggs, silt mining, encroachment of wetlands and change in flooding pattern.
7th International Day Of Yoga:

Seventh International Day of Yoga (21st June 2021) is being celebrated by the Ministry of Culture at 75 cultural heritage locations across the country.
- The idea of International Day of Yoga (IDY) was proposed by India during the opening of the 69th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), held in 2014.
- The UN proclaimed 21st June as IDY by passing a resolution in December, 2014.
- The first Yoga Day celebrations in 2015 at Rajpath in New Delhi created two Guinness World Records.
- It was the world’s largest yoga session with 35,985 people.
- 84 nationalities participated in it.
Theme 2021:
- This year’s theme is “Yoga for wellness”.
Ebola Outbreak:

An Ebola outbreak in Guinea that started in February, infecting 16 people and killing 12, has been declared over by WHO.
- The Ebola outbreak in 2014-2016 killed 11,300 people, mostly in Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia.
- In May 2021, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) officially declared the end of the 12th Ebola outbreak.
About Ebola:
- Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
- The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission.
- The average EVD case fatality rate is around 50%. Case fatality rates have varied from 25% to 90% in past outbreaks.
- Community engagement is key to successfully controlling outbreaks. Good outbreak control relies on case management, surveillance and contact tracing, a good laboratory service and social mobilisation.
- Early supportive care with rehydration, symptomatic treatment improves survival. There is yet no licensed treatment proven to neutralise the virus but a range of blood, immunological and drug therapies are under development.
Monoclonal antibodies:
An experimental monoclonal antibody cocktail, REGEN-COV2, has been found to be a life-saving treatment for some of the most severely affected Covid-19 patients, results of a clinical trial in the UK have shown.
- However, Such therapies are expensive because they are difficult to make and take a lot of time.
- They are artificially created antibodies that aim to aid the body’s natural immune system.
- They target a specific antigen — a protein from the pathogen that induces immune response.
- Monoclonal antibodies can be created in the lab by exposing white blood cells to a particular antigen.
- To increase the quantity of antibodies produced, a single white blood cell is cloned, which in turn is used to create identical copies of the antibodies.
- In the case of Covid-19, scientists usually work with the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which facilitates the entry of the virus into the host cell.
- In a healthy body, the immune system is able to create antibodies — tiny Y-shaped proteins in our blood that recognise microbial enemies and bind to them, signalling the immune system to then launch an attack on the pathogen.
- However, for people whose immune systems are unable to make sufficient amounts of these antibodies, scientists provide a helping hand- using monoclonal antibodies.




