Today’s Current Affairs: 24th Apr 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Kamakhya Temple Corridor:

The government in Assam is planning to construct a corridor at the Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati on the lines of the Kashi-Vishwanath Temple Corridor in Varanasi.
- The project will transform the grandeur of this major ‘shakti peeth’ significantly while also improving the accessibility for differently abled and aged devotees and tourists manifold.
- Kamakhya Temple is Located on Nilachal Hill in Guwahati, Assam
- It is Considered one of the oldest and sacred places of worship.
- Millions of pilgrims and tourists visit the temple every year, especially during the Ambubachi Mela held in June every year.
- Ambubachi Mela, is a four-day fair to mark the annual menstruation of the goddess
- One of 51 shaktipeeths or seat of Shakti followers, each representing a body part of Sati, Lord Shiva’s companion. The temple’s sanctum sanctorum houses the yoni — female genital — symbolised by a rock.
- The attainment of womanhood of girls in Assam is celebrated with a ritual called ‘Tuloni Biya’, meaning small wedding.
- A centrepiece of Tantrik Shaktism cult in India
- The main temple is surrounded by individual temples dedicated to the ten Mahavidyas: Kali, Tara, Sodashi, Bhuvaneshwari, Bhairavi, Chhinnamasta, Dhumavati, Bagalamukhi, Matangi and Kamalatmika.
PSLV-C55 Mission:

Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is scheduled to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C55 (PSLV-C55) mission with Singapore’s TeLEOS-2 as primary satellite and Lumelite-4 as a co-passenger satellite.
- The PSLV-C55 mission has the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM), where the spent PS4 of the launch vehicle would be utilised as an orbital platform to carry out scientific experiments through non-separating payloads.
- This is the third time that PS4 will be used after satellite separation as a platform for experiments.
TeLEOS-2 satellite
- Primary Satellite Support the satellite imagery requirements of various agencies within the government of Singapore.
Carries a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload. - Provide all-weather day and night coverage, and be capable of imaging at 1m full-polarimetric resolution.
- Lumelite-4 satellite :A co-passenger satellite
- An advanced 12U satellite developed for the technological demonstration of the high-performance space-borne VHF Data Exchange System (VDES).
- It Aims to augment Singapore’s e-navigation maritime safety and benefit the global shipping community.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle(PSLV):
- PSLV is known as the ‘workhorse’ of ISRO.
- It is the third-generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is a four-staged launch vehicle with first and third stages using solid rocket motors and second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
SpaceX Starship: Exploded During First test-flight

SpaceX’s Starship, the world’s biggest rocket, exploded during its first test-flight to space.
- SpaceX’s Starship spacecraft and Super Heavy rocket – collectively referred to as Starship.
- It is the first stage, or booster, of the Starship launch system.
- Powered by 33 Raptor engines using sub-cooled liquid methane (CH4) and liquid oxygen (LOX).
- The Raptor engine is a reusable methane-oxygen staged-combustion engine that powers the Starship system
Super Heavy is fully reusable and will re-enter Earth’s atmosphere to land back at the launch site. - Starship spacecraft is the second stage of the Starship system.
- It is also capable of point-to-point transport on Earth, enabling travel to anywhere in the world in one hour or less.
- It is a fully reusable transportation system designed to carry both crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- It is the world’s most powerful launch vehicle ever developed, capable of carrying up to 150 metric tons fully reusable and 250 metric tons expendable.
4th India-CARICOM Ministerial Meeting:

India’s External Affairs Minister co-chaired the 4th India-CARICOM ministerial meeting with his Jamaican counterpart.
- CARICOM, which stands for Caribbean Community, is the oldest surviving integration movement in the developing world.
- It is an organization of Caribbean countries and dependencies originally established as the Caribbean Community and
- Commons Market in 1973 by the Treaty of Chaguaramas.
- Main Purposes is to Promote economic integration and cooperation among its members;
- To ensure that the benefits of integration are equitably shared;
- To coordinate foreign policy;
- It has 15 members; Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Haiti, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- Anguilla, Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, and the Turks and Caicos Islands have associate member status, and Aruba, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Venezuela maintain observer status.
- The Chairmanship of the Community is rotated every six months among the member countries’ Heads.
- The CARICOM Secretariat in Georgetown, Guyana, is the principal administrative organ of the Community and is headed by a Secretary General who is the Chief Executive Officer of the Community.
- In 2007, CARICOM officially inaugurated the Caribbean Court of Justice (CCJ), which serves as the final court of appeal for CARICOM members and also handles regional trade disputes.
Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga Project:
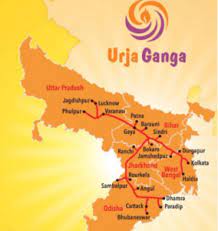
Prime Minister praised the completion of Bihar portion of Barauni- Guwahati pipeline under Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga Project.
- The project is also known as Jagdishpur – Haldia & Bokaro – Dhamra Pipeline Project (JHBDPL) project.
- It was launched in 2016 and will cater to the energy requirements of five states namely Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal.
- This pipeline will connect six districts in Bihar to the National Gas Grid. The project will provide access to clean natural gas for industries, CNG for vehicles and PNG for homes, promoting a sustainable lifestyle.
- Total length of pipeline under Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga Project is 3,384 km, out of which 766 km of pipeline is in Odisha state and the balance 2,618 km is in the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal & Assam.
- The seven main station cities include Varanasi, Patna, Bokaro, Jamshedpur, Kolkata, Ranchi, Bhubaneswar and Cuttack as the major beneficiaries of the project.
- The project is being implemented by GAIL.
Ballistic Missile Interceptor:

The DRDO and Indian Navy successfully conducted a maiden flight trial of sea-based endo-atmospheric interceptor missile off the coast of Odisha.
- India entered an elite club of nations with the capability to fire a Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) interceptor from a naval platform.
- Prior to this, DRDO has successfully demonstrated land-based ballistic missile defence system with capability to neutralize ballistic missile threats, emerging from adversaries.
India’s Ballistic Missile Defence Programme:
- India launched the BMD program after Kargil war in 1999 to counter the enemy nation’s widening spectrum of ballistic missiles that usually delivered both conventional and nuclear warheads.
- Two-tires of BMD system
- Prithvi Air Defence missile
- It was originally tested in 2006 and is capable of intercepting and destroying missiles at exo-atmospheric altitudes ranging from 50 to 180 kilometres.
- The Pradyumna interceptor has already replaced the Prithvi Air Defence BMD.
- Exo-atmospheric missiles are capable of completing missions in the Earth’s upper atmosphere.
- Advanced Air Defence Missile
- The second layer is Advanced Air Defence (AAD) Missile for lower altitude interception.
- It was first tested in 2007 and designed to knock down hostile missiles in the endo-atmosphere at altitudes of 15-40 KM.
- The endo-atmospheric missiles are the ones that operate within the earth’s atmosphere that covers an altitude below 100 KM.
- Prithvi Air Defence missile
Logistics Performance Index (LPI) 2023:

India’s rank in the recently released World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index 2023 has improved by six places.
- Logistics Performance Index (LPI) is released by World Bank.
- It is an interactive benchmarking tool created to help countries identify the challenges and opportunities they face in their performance on trade logistics and what they can do to improve their performance.
- It measures the ease of establishing reliable supply chain connections and structural factors that make it possible, such as the quality of logistics services, trade and transport-related infrastructure, as well as border controls.
Highlights of LPI 2023:
- The LPI 2023 allows for comparisons across 139 countries.
- The LPI 2023, for the first time, measures the speed of trade with indicators derived from big datasets tracking shipments.
- Singapore and Finland are the most efficient and highest-ranked LPI countries as per the 2023 LPI.
- India is ranked 38 out of 139 countries, climbing six places from the previous index.
- Two major factors for India’s jump in the index could be modernisation and digitalisation, which the report quotes as a reason for emerging economies like India to leapfrog advanced countries




