Today Current Affairs: 24th August 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
The Kanal Istanbul:
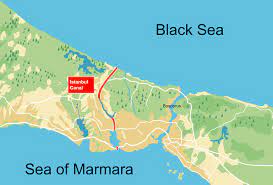
The Kanal Istanbul, an under-construction shipping route running parallel to the strategically critical Bosphorus Strait, is fast gaining prominence as a major divisive issue in Turkey.
- President Recep Tayyib Erdogan wants to dig up a new route through Istanbul connecting the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara.
- The planned canal will run parallel to the Bosphorus Strait, a natural waterway that separates Europe and Asia, which for centuries has served as a key outlet for Russian ships entering the Mediterranean Sea.
- Since 1936, passage through the Strait has been governed by the Montreux Convention, a multilateral treaty that allows ships to go across almost free of cost during peacetime, and which tightly restricts the movement of naval vessels.
- Turkish leaders say that the new canal, which will run on the European side of Bosphorus, will be safer and faster to navigate compared to the Bosphorus, making it a more attractive option for commercial ships, who will pay to pass through.
- Analysts also believe that Erdogan would use the canal to circumvent Montreux Convention, by marketing the mega project to NATO allies as a legally kosher way of sending their warships into the Black Sea to counter Russia, their major geopolitical rival, all while attracting Chinese investment.
Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY):

As part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav (AKAM) celebrations, around 1183 ‘mobilisation camps’ were organised across the country under the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) programme between 13th and 19th August, 2021.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) launched on the 25th September, 2014, is a nationwide placement-linked skill training program funded by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), Government of India (GoI).
- DDUGKY seeks to build the placement-linked skills of the poor rural youth and place them in wage employment across various sectors of the economy.
- The programme has an outcome led design with guaranteed placements for at least 70% trained candidates.
- The DDU-GKY programme is being implemented in 27 states and 3 UTs for rural poor youth with an emphasis on placements. More than 871 Project Implementation Agencies (PIAs) are training rural poor youth in close to 611- job roles through more than 2381 training centers.
National Monetisation Pipeline:

Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, will launch the National Monetisation Pipeline.
- The National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) comprises a four-year pipeline of the Central Government’s brownfield infrastructure assets.
- Besides providing visibility to investors, NMP will also serve as a medium-term roadmap for the Asset Monetisation initiative of the Government.
- The Union Budget 2021-22 laid a lot of emphasis on Asset Monetisation as a means to raise innovative and alternative financing for infrastructure, and included a number of key announcements.
- The National Monetisation Pipeline book will be released in the presence of Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog, Dr Rajiv Kumar, CEO, Shri Amitabh Kant, and Secretaries of relevant line ministries whose assets constitute the monetisation pipeline.
Ubharte Sitaare Alternative Investment Fund:

The Ministry of Finance has launched ‘Ubharte Sitaare’ Alternative Investment Fund to facilitate debt and equity funding to export-oriented MSMEs (Micro Small and medium Enterprises).
- The fund is expected to identify Indian enterprises with potential advantages, but which are currently underperforming or unable to tap their latent potential to grow.
- Under the scheme, an identified company is supported even if it is currently underperforming or may be unable to tap its latent potential to grow.
- The scheme diagnoses such challenges and provides support through a mix of structured support covering equity, debt and technical assistance.
- It will also have a Greenshoe Option of Rs 250 crore.
- A greenshoe option is an over-allotment option, which is a term that is commonly used to describe a special arrangement in a share offering for example an IPO (Initial Public Offering) that will enable the investment bank to support the share price after the offering without putting their own capital at risk.
- The fund has been set up jointly by Exim Bank and SIDBI (Small Industries Development Bank of India) which will invest in the fund by way of equity and equity-like products in export-oriented units, in both manufacturing and services sectors.
Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS):

The Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) has brought high-speed internet to some of the remotest tribal hamlets deep inside the Nilambur jungle in Kerala.
- The Scheme of JSS formerly known as Shramik Vidyapeeth was a unique creation of the Government of India and has been implemented through Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs) in the country since 1967.
- The scheme was renamed as JSS in 2000.
- It was transferred from the Ministry of Education (erstwhile Ministry of Human Resource Development) to the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship in July, 2018.
- The JSSs are imparting vocational skill training programmes at the door step of the beneficiaries with a minimum cost and infrastructure.
- JSSs are unique in the sense that they do not provide only vocational skills but also include an element of life skills which can help the beneficiary in day to day life.
- They are not working in isolation but also conduct convergence programmes with different departments.
- At present, 233 JSSs in 25 States and 3 Union Territories are functional.
- The annual coverage of the beneficiaries is around 4 lakh, out of which 85% are women.
Mandate:
- To provide vocational skills in non-formal mode to non-literate, neo-literates, persons with rudimentary level of education upto 8th and school drop-outs upto 12th standard in the age group of 15-45 years.
- The priority groups are women, Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribe, minorities and other backward sections of the society.
Implementation:
- It is implemented through NGOs with 100% grants from the Government of India. JSSs are registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- The affairs of Jan Shikshan Sansthan are managed by the respective Board of Management approved by the Government of India.
Geo-Heritage Sites:

The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has identified certain geological sites across the Northeast for promotion of geo-tourism.
- 12 locations in the Northeast have been included in the 32 approved geo-tourism or geo-heritage sites in the country.
Geo-heritage Sites:
- Geo-heritage refers to the geological features which are inherently or culturally significant offering insight to earth’s evolution or history to earth science or that can be utilized for education.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) is the parent body which is making efforts towards identification and protection of geo-heritage sites/national geological monuments in the country.
- Some of these sites are: Marine Gondwana fossil park in Chhattisgarh; Siwalik vertebrate fossil park in Himachal Pradesh; Stromatolite park in Rajasthan; Pillow lava in Karnataka, Eparchaean unconformity and Tirumala hills in Andhra Pradesh, Lonar Lake in Maharashtra, etc.
Geo Tourism:
- Geotourism is defined as “tourism that sustains or enhances the geographical character of a place – its environment, culture, aesthetics, heritage, and the well-being of its residents.”
- It will foster community involvement, improve the local economy and create respect for local culture and tradition.
- India is a country with diverse physical attributes, rich cultural heritage and eventful ancient history and its subcontinent exhibits imprints of varied geological processes through ages and is a storehouse of interesting geological features.
Geo-heritage sites in Northeast:
- Majuli (Assam):
- A river “island”, among the world’s largest, in Brahmaputra river.
- The island is also the hub of spiritualism in Assam because of a number of ‘satras’ or Vaishnav monasteries established by the 15th-16th century saint-reformer Srimanta Sankaradeva and his disciples.
- Sangetsar Tso (Arunachal Pradesh):
- It is popularly known as Madhuri Lake.
- It is close to the border with Tibet and was formed due to the damming of a river during a major earthquake in 1950.
- Loktak Lake (Manipur):
- It is the largest freshwater lake in the Northeast.
- The attractions of this lake are the ‘phumdis’ or floating biomass and the ‘phumsangs’ or huts of fishermen on them.
- The Keibul Lamjao National Park, the only floating wildlife habitat on earth, is on the southwestern part of the lake and is the last natural habitat of the sangai or brow-antlered dancing deer.
Exercise Konkan 2021:

Indo-UK Naval Exercise, ‘Konkan 2021’ was recently held between INS Tabar and HMS Westminster in the English Channel.
- The English Channel is located between the Isle of Great Britain’s southern coast and France’s northern coast and separated from the North Sea on the north by the Strait of Dover.
- The Bilateral Konkan exercise is a naval exercise conducted between India and the United Kingdom.
- The Konkan series of exercises was started in 2004. Since then, the exercise is hosted in rotation by both the Navies and has grown in complexity, scale, and intensity.
Other Exercises between India and UK:
- Exercise ‘Indradhanush’ (Air Force Exercise)
- Ajeya Warrior (Joint Military Exercise)
Arunachal Pradesh Draft Inheritance Bill:

Experts have asked the Arunachal Pradesh State Commission for Women (APSCW) to scrap certain provisions from the proposed Arunachal Pradesh marriage and inheritance bill, keeping in view the public sentiment and the state’s interest.
Overview of the draft Bill:
- Essential conditions of marriage, registration of marriage: The bill is made applicable to any person who belongs to any indigenous scheduled tribe of Arunachal Pradesh. It provides that a marriage between parties may be solemnized according to local customary rites and rituals of the either party.
- Restitution of conjugal rights, void and voidable marriage: The bill also provides for restitution of conjugal rights stating when either of the party has, without reasonable excuse, withdrawn from the society of the other, the aggrieved party may apply by petition to the district court for restitution of conjugal rights.
- Grounds for dissolution of marriage (divorce): Marriage solemnized after the commencement of the act can be dissolved on various grounds.
- Permanent alimony and maintenance: A wife who is unable to maintain herself can file application to the court for maintenance. The court may order that the husband shall pay to her an appropriate lump sum of permanent alimony.
- Bill’s status on polygamy: Every person who, being at the time married, procures a marriage of himself or herself to be solemnized under this act shall be deemed to have committed an offence under Section 494 or Section 495 of the Indian Penal Code (45 of 1860), as the case may be, and the marriage so solemnized shall be void.
Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA):

A ban under the stringent Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act may be imposed on both factions of the secessionist conglomerate Hurriyat Conference which has been spearheading the separatist movement in Jammu & Kashmir for over two decades.
- The proposal was mooted in accordance with the Union government’s policy of zero tolerance against terrorism.
- The factions of the Hurriyat are likely to be banned under Section 3(1) of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), under which “if the Central government is of opinion that any association is, or has become, an unlawful association, it may, by notification in the Official Gazette, declare such association to be unlawful.”
Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act:
- Passed in 1967, the law aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may, by way of an Official Gazette, declare it so.
- It has death penalty and life imprisonment as highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged.
- It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if crime is committed on a foreign land, outside India.
- Under the UAPA, the investigating agency can file a charge sheet in maximum 180 days after the arrests and the duration can be extended further after intimating the court.
As per amendments of 2019:
- The Act empowers the Director General of National Investigation Agency (NIA) to grant approval of seizure or attachment of property when the case is investigated by the said agency.
- The Act empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases of terrorism in addition to those conducted by the DSP or ACP or above rank officer in the state.
- It also included the provision of designating an individual as a terrorist.




