Today’s Current Affairs: 24th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Scheduled Caste And Scheduled Tribe (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989:

The Allahabad High Court recently said that an alleged act of intentional insult or intimidation causing humiliation would constitute an offence under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 only if it is committed in public view.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989:
- It is an Act to prevent the commission of offences of atrocities against the members of the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and the Scheduled Tribes (STs) by persons other than SCs and STs.
- It provides for punishment for offences of atrocities committed against SCs and STs.
- It authorizes the Central Government to frame rules for carrying out the purpose of the Act.
- The Act is implemented by the respective State Governments and Union Territory Administrations, which are provided due central assistance under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme for effective implementation of the provisions of the Act.
- This Act does not apply to crimes committed between SCs and STs or between STs and SCs.
- There are 37 offences included in the Act that involve patterns of behaviour inflicting criminal offences and breaking the self-respect and esteem of the SCs and STs community.
- Among these are the denial of economic, democratic and social rights, as well as the exploitation and abuse of the legal system.
- All offences listed in the Act are cognizable.
- An investigation of offence committed under the Act cannot be investigated by an officer not below the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP).
- The investigation should be completed within 30 days, and the report should be sent directly to the director of the state police.
Foreigners Tribunal:

The Supreme Court (SC) recently halted the deportation of a woman who was declared a foreigner by a Foreigners’ Tribunal in Assam
- Foreigners Tribunal (FT) came into existence through the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, to let state administration (District Collector/District Magistrate) to make a reference about a person suspected to be a foreigner to the Tribunals.
- The Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, was enacted by the Central government through the use of powers granted under Section 3 of the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- The Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, applies to the whole of India, yet, FTs exist only in Assam as of now.
- In other states, if an illegal immigrant is found, he is produced before a local court and dealt with as per the Foreigners Act, 1946.
- Prior to the 2019 amendment to the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964, only the Centre was empowered to establish FTs in states, but after this amendment, the power has been granted to states as well.
- The superintendents of police (SPs) and district commissioners were empowered to detect suspected foreigners.
- References for these “suspected persons” were required to be made before an authority which came into existence through the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order, 1964.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) can also refer cases of D or Doubtful voters to the local SP, who then refers them to a tribunal to verify their citizenship.
- The persons excluded from the final draft of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) as released in August 2019 can appeal before the FTs to prove their citizenship.
Bay Of Bengal Initiative For Multi-Sectoral Technical And Economic Cooperation:

BIMSTEC will now be open to new members and observers after a historic first charter of the grouping came into force recently.
- BIMSTEC is a multilateral regional organization comprising seven member states lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal, constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- Aim is Accelerating shared growth and cooperation between littoral and adjacent countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- It was founded as BIST-EC in June 1997, with the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration, with Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand as members.
- It became BIMST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation) with the entry of Myanmar in late 1997, and eventually, it was named in its current form when Nepal and Bhutan became members in 2004.
- Current Member States: Five deriving from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal and Sri Lanka and two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- Permanent Secretariat: Dhaka, Bangladesh
- It is a sector-driven cooperative organisation in which, initially, six sectors had been included:
- Trade, Technology, Energy, Transport, Tourism, and Fisheries
- As of now, BIMSTEC has 14 priority areas of cooperation. Climate change was added as the 14th priority area of cooperation in 2008.
- Among these priority areas, a member country chooses which of the 14 priority areas it is willing to take the lead.
- India is lead country for Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management, Counter-Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
eVTOL: To Launch e-flying Taxis In Bengaluru

Indian Institute of Technology, Madras-incubated ePlane Company is expected to launch its e-flying taxis in Bengaluru this year but the Indian government has yet to establish clear policies regarding eVTOL flying taxis.
- An electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft is one that uses electric power to hover, take off and land vertically.
- It is one of the newer technologies and developments in the aerospace industry.
- It is a low-altitude urban air mobility aircraft capable of carrying only a few passengers- six-seaters and eight-seaters.
- Most eVTOLs use distributed electric propulsion technology which means integrating a complex propulsion system with the airframe.
- There are multiple motors for various functions; to increase efficiency; and to also ensure safety.
- This is a technology that has grown on account of successes in electric propulsion based on progress in motor, battery, fuel cell and electronic controller technologies and also fuelled by the need for new vehicle technology that ensures Urban Air Mobility (UAM).
- Applications: Air Taxi, Delivery, Medical assistance (EMS), Cargo Transport, Recreation.
Ujani Dam:

Six persons, including two children, drowned after their boat capsized in the Ujani dam backwaters in Maharashtra’s Pune district recently.
- Ujani Dam is located on the Bhima Rivernear Ujjani village in the Solapur district of the state of Maharashtra.
- It is an earth-fill cum masonry gravity dam.
- It was constructed between 1977 and 1980 with the primary objective of providing irrigation water and hydroelectric power to the region.
- With a total length of 2,534 m, the Ujani Dam is founded on massive basaltic rock formations and comprises a central portion, which is the spillway dam of 602m in length.
- The dam has a height of 63 meters.
- With a storage capacity of 117 thousand million cubic feet (TMC), the dam has a live storage of 54 TMC and 63 TMC is dead storage.
- Power Generation Capacity: 12MW
- The water quality of the Ujani Dam is very bad as it contains hazardous pollutants from Pune and many other small cities located on the banks of the Bhima River or its tributaries.
Planetary Alignment:

On June 3, there will be planetary alignments that may actually allow people to witness six planets align in the sky.
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that’s Earth.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- Aligning planets: Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune will form a near-straight line.
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Eliminating Mercury-Containing Medical Devices:

The governments of Albania, Burkina Faso, India, Montenegro, and Uganda have united to combat chemical pollution by launching a USD 134-million project to eliminate the use of mercury in medical devices.
- The initiative is led by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), funded by Global Environment Facility (GEF), and executed by World Health Organisation (WHO), aiming to reduce the impact of healthcare on the environment and human health.
- It aims to support global efforts in improving the management of mercury waste and promote the use of alternatives.
- The project aims to phase out mercury-added thermometers and sphygmomanometers at a rate of 20% per year, improving the lives of over 1.8 million people.
- Medical thermometers and sphygmomanometers (devices that measure blood pressure) contain mercury and are harmless as long as they remain intact.
- Instances of breakages and improper disposal of medical devices release mercury vapour that contaminates surroundings both air and water.
- Inhalation of these mercury vapours can cause damage to the lungs, kidneys and nervous system.
RBI Surplus Transfer To Government:

The surplus calculation was based on the Economic Capital Framework (ECF) recommended by the Bimal Jalan committee, which advised the RBI to maintain a Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) between 5.5% and 6.5% of its balance sheet.
- This risk provisioning is made primarily from retained earnings and only then is the surplus income transferred to the government as dividends.
- This range includes provisions for monetary and financial stability risks as well as credit and operational risks.
- RBI transfers its surplus, which is the excess of income over expenditure, to the government as per Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Reasons for the Increase in RBI’s Surplus: As of March 2024, the RBI had USD 646 billion in foreign exchange reserves, with USD 409 billion parked in top-rated sovereign securities.
- The RBI’s gross dollar sales were lower in FY24 (USD 153bn) compared to FY23 (USD 213 bn).
- Despite lower dollar sales in FY24 compared to FY23, the RBI’s management of foreign currency assets ensured continued high revenue.
- Income from Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) operations also contributed to the overall surplus.
Buddha Purnima:

The President of India extends greetings on the occasion of Buddha Purnima, highlighting the significance of Lord Buddha’s teachings.
- Buddha Purnima also known as Vesak, commemorates the birth of Prince Siddhartha Gautama, who later became known as Gautama Buddha and founded Buddhism.
- Celebrated primarily in South, Southeast, and East Asia, it falls on the full moon day of the Hindu month of Vaisakha, typically in April or May.
- It is considered a ‘triple-blessed day’ as it marks Buddha’s birth, enlightenment, and Maha Parnirvana.
- It has been recognised by the United Nations as the ‘UN Day of Vesak’ since 1999.
Pre-eclampsia : Effect

Pre-eclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy that leads to multiorgan dysfunction in the mother.
- It typically manifests after 20 weeks of pregnancy, characterized by high blood pressure.
- Other symptoms include swelling in the face, hands, and feet, severe headaches, vision changes, upper abdominal pain, and trouble breathing.
- Studies show that pre-eclampsia significantly raises the risk of heart failure, coronary heart disease, stroke, and cardiovascular death in mothers.
- India accounts for nearly a quarter of the world’s adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Statistics show perinatal mortality at 32 per 1,000 pregnancies and neonatal mortality at 25 per 1,000 live births.
- Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy are a leading cause of maternal death
Ferroptosis : Recent Study
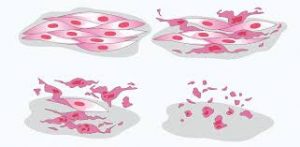
A recent study by researchers has identified ferroptosis, an unusual form of cell death, as a significant contributor to lung damage in COVID-19 patients.
- Ferroptosis occurs when the outer fat layers of cells collapse, leading to cell death.
- This differs from the more common type of cell death, where cells break down their internal molecules.
- The study analysed human tissues and autopsies of COVID-19 victims, along with samples from hamsters, revealing that ferroptosis was a primary mechanism behind the lung damage observed.
- Ferroptosis is a form of regulated cell death characterized by the iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxides to lethal levels.
- Unlike other forms of cell death such as apoptosis or necrosis, ferroptosis specifically involves the oxidative damage of lipids within cell membranes, leading to cell membrane destabilization and ultimately cell death.
First-Ever Patient Safety Rights Charter : WHO

World Health Organization (WHO) launched the first-ever Patient Safety Rights Charter at the Global Ministerial Summit on Patient Safety.
- Assuring patient safety in health care is a critical component in delivering the right to health.
- Patient safety can be compromised due to avoidable errors such as unsafe surgical procedures, medication errors, mis- or late diagnosis, poor injection practices, unsafe blood transfusion and the onset of life-threatening infections such as sepsis and other health care-associated infections.
- Patient Safety Rights Charter outlines the core rights of all patients in the context of the safety of health care and seeks to assist governments and other stakeholders to ensure that the voices of patients are heard and their right to safe health care is protected.
- The Charter covers 10 patient safety rights crucial to mitigate risks and prevent unintentional harm, which includes
- Timely, effective, and appropriate care
- Safe health care processes and practices
- Qualified and competent health workers
- Safe medical products and their safe and rational use
- Safe and secure healthcare facilities
- Dignity, respect, non-discrimination, privacy and confidentiality
- Information, education, and supported decision-making access to medical records
- To be heard and fair resolution
- Patient and family engagement.
Exercise Cyber Suraksha 2024:

Head of the Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan started Cyber Suraksha – 2024 on May 22, 2024.The Indian Armed Forces and other national groups are fully committed to protecting the country’s security in the very important area of cyberspace, as shown by Exercise Cyber Suraksha – 2024.
- Defence Cyber Agency of India is in charge of the event, which runs from May 20th to May 24th. To protect India from new cyber threats, General Chauhan stressed how important it was to improve the country’s cyber defence system.
- The main goal of Exercise Cyber Suraksha – 2024 is to improve the cyber defence skills of all cybersecurity organizations in the country.
- The goal is for the military and key government agencies involved in cybersecurity to work together better and come up with a more unified approach.
- The exercise is designed to further develop the cyber defence skills of participants.
- Encourage the sharing of best practices and techniques in cyber defence.
- Encourage a unified strategy approach to building a strong Cyber Defence Framework.
1st Human Case Of ‘Bird Flu’ Reported In Australia:

A child who came back to Victoria from India in March was the first person in Australia to get the H5N1 bird flu.
- The child had a serious sickness, but now fully better. Victoria’s chief health officer confirmed that there have been no more cases tied to this incident.
- This shows how rare it is for this strain to be passed from person to person.
- Avian influenza, also called “bird flu,” is a very contagious virus that affects many types of birds, both wild and tame.
- It mostly spreads through direct touch or places that are contaminated with germs.
- People can get infected with the H5N1 type and get very sick from it, but this doesn’t happen very often.
- Other strains, like H7N7, which is more common in Australia, have mostly harmed poultry.
- The H7N7 strain was found at an egg farm in Victoria, which is different from the H5N1 type found in the child.
- After this was found, Agriculture Victoria started checking right away and putting farms within 5 km of the affected farm under quarantine.
- As part of the quick reaction, animals that are infected with the virus will be killed to stop the outbreak from spreading.
Global Impact Of Land Squeeze:

A recent study conducted by the International Panel of Experts on Sustainable Food Systems (IPES-Food) focusses on the unprecedented ‘land squeeze’, threatening farmers and food production.
- The report warns of prevalent “land squeeze” due to rising land prices, land grabs, and carbon schemes, threatening farmers and food production.
- Globally, the top 1% of the world’s largest farms now control 70% of the world’s farmland.
- As land becomes scarce, it can be converted from productive agricultural land to other uses, impacting food production
Between 2008-2022, there has been a doubling of global land prices. - This increase has been particularly pronounced in Central-Eastern Europe, where prices have tripled.
- “Green grabs,” land acquisitions are evidently motivated by environmental concerns, now account for approximately 20% of large-scale land deals.
- Green grabbing refers to the large-scale acquisition or control of land and resources for environmental purposes, often with negative social and economic consequences. It’s essentially land grabs done under the guise of environmental protection.
- Over half of the land designated by governments for carbon removal projects presents a potential risk of interference with the livelihoods of small-scale farmers and Indigenous people.
- Carbon offset markets are expected to quadruple in the next 7 years




