Today’s Current Affairs: 27th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Semi-transparent Perovskite Solar Cell:
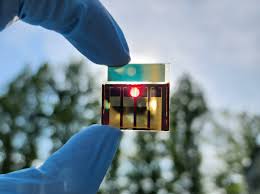
The IIT Bombay researchers have developed a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell (PSC).
- It is layered over a traditional silicon-based solar cell, forming a 4-terminal (4T) tandem structure.
- The bottom sub-cell uses well-established silicon technology, while the top sub-cell features an indigenously developed halide perovskite semiconductor, enabling high light absorption and efficient energy conversion.
- This helps in power conversion efficiency of approximately 30 per cent compared with around 20 per cent now.
- Halide perovskite is among the most efficient light-absorbing materials known today.
- Apart from being highly efficient in converting light into electricity, it is affordable as electronic grade perovskite semiconductors can be produced locally with available chemical resources.
- Perovskite Solar Cells are a type of photovoltaic (PV) technology that uses crystal structures called perovskites for converting sunlight into electricity.
- These crystals share the structure of the mineral calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO₃)and can be engineered to possess a wide range of optical, electrical, and semiconducting properties.
- The general chemical formula of a perovskite compound is ABX₃, where ‘A’ and ‘B’ are cations, and ‘X’ is an anion.
- They offer high power conversion efficiencies at a lower cost than traditional silicon-based PVs, but they suffer from shorter lifespan and stability issues.
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme:

The 38th Meeting of the Central Apprenticeship Council (CAC), chaired by the Minister of State (Independent Charge), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), recommended a 36% increase in stipend provided under the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS).
- The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) was launched on19th August 2016 by the Government of India.
- The scheme entails financial support to establishments undertaking apprenticeship programs.
- It is an initiative by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship aimed at promoting apprenticeship training across India.
- NAPS registration is essential for candidates and establishments to benefit from this program.
- Objectives
- To develop skilled manpower for the industry by promotion of on-the-job experiential training.
- To encourage establishments to enrol apprentices by sharing partial stipend support to the apprentices.
- To provide up-skilling opportunities for candidates who have undergone short-term skill training.
- To encourage enrolment of apprentices in small establishments (MSMEs), and those located in underserved areas like in aspirational districts and in the North-East
- This scheme provides financial incentives to establishments engaging apprentices under the Apprentices Act, 1961.
- By offering partial stipend support and advocacy, the scheme encourages industries to train a skilled workforce andbridge the gap between education and employment.
- The scheme not only promotes skill development but also focuses on building a trained workforce that aligns with industry needs. Candidates who complete their training receive a NAPS certificate, which enhances their employability.
- National Apprenticeship Training Scheme is one of the flagship programmes of Government of India for Skilling Indian Youth in Trade disciplines.
- It is under the provisions of the Apprentices Act, 1961 amended in 1973.
- It offers Graduate, Diploma students and Vocational certificateholders; a practical, hands-on On-the-Job-Training (OJT) based skilling opportunities.
- Ranging from 6 months to 1 year.
- During the period of apprenticeship, the apprentices are paid a stipend amount, 50% of which is reimbursable to the employer from the Government of India.
- At the end of the training period the apprentices are issued a Certificate of Proficiency by the Government of India which can be registered at all employment exchanges across India as valid employment experience.
- There is no guarantee of employment after completion of training as an apprentice.
Moringa:

PKM1, a variety of Moringa oleifera, has had a global impact, especially in countries such as Senegal, Rwanda, and Madagascar on the African continent.
- Moringa is known as the “tree of life” or “miracle tree,”and is classified as an important herbal plant.
- Its botanical name is Moringa oleifera, and it is native to India, which was introduced from India to Africa, Southeast Africa, and the Philippines in ancient times.
- It requires tropical and subtropical regions and grows at a temperature of about 25–35 °C
- It is a deciduous type of tree typically grown in tropical and subtropical regions across the globe
- It grows best in indirect sunlight and without waterlogging, and the soil should be slightly acidic to alkaline.
- The tree begins to bear fruit at 6 to 8 months of age.
- With its high nutritional values, every part of the tree is suitable for either nutritional or commercial purposes.
- The leaves are rich in minerals, vitamins and other essential phytochemicals.
- Extracts from the leaves are used to treat malnutrition, augment breast milk in lactating mothers.
- It is widely distributed worldwide, but its indigenous origin is in India, Arabia and the East Indies.
- It is common in Asia, Africa, the Caribbean, Latin America, the Pacific Islands, Florida, Madagascar, Central America, Cuba, the Philippines, Ethiopia, and Nigeria
INS Brahmaputra: Likely To Regain Seaworthiness

The Indian Navy’s guided missile frigate INS Brahmaputra, which suffered extensive damage in a dockyard accident last year, is likely to regain seaworthiness by the end of 2025 and be fully combat-ready by mid-2026, senior officials said recently.
- INS Brahmaputra is the first indigenously built Brahmaputra-class guided missile frigate.
- It was built by Kolkata-based Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
- It was commissioned into the Indian Navy on April 14, 2000.
- It takes on various roles such as coastal and offshore patrolling, monitoring sea routes, conducting maritime diplomacy, and carrying out counter-terrorism and anti-piracy missions.
- Its crest features a grey, one-horned Indian rhinoceros, which is native to the Brahmaputra valley, set against a brown background with white and blue sea waves.
- The ship has a displacement of 5,300 tonnes, is 125 meters long, and is 14.4 meters wide.
- It can reach speeds over 27 knots (about 50 km/h).
- It is equipped with medium- and close-range guns, anti-aircraft weapons, surface-to-surface and surface-to-air missiles, and torpedo launchers.
- It is equipped with a range of sensors for all aspects of maritime warfare and can operate Sea King and Chetak helicopters.
- It is crewed by 40 officers and 330 sailors.
Charaka and Sushruta Legacy:

The Vice-President commissioned the statues of Charaka and Sushruta at Raj Bhavan, Goa and recalled their contributions.
- Charaka (around 2nd century BCE and the 2nd century CE), known as the father of medicine, served as the royal physician of Kanishka (Kushan Kingdom).
- He authored the Charaka Samhita, a foundational text of Ayurveda.
- The Agnivesha Samhita, written by Agnivesa in the 7th century BCE under the guidance of Atreya, was revised and renamed the Charaka Samhita by Charaka, and divided it into eight sections known as Ashtanga Sthanas.
- Dhabala (scholar of Ayurveda) later added 17 chapters to the Charaka Samhita.
- Sushruta (7th–6th century BCE), an ancient Indian physician, is called the “Father of Surgery” and “Father of Plastic Surgery.”
- Sushruta was a disciple of Dhanvantari, one of the Navratnas of King Vikramaditya (Chandragupta II).
- He authored the Sushruta Samhita, one of the earliest texts on plastic surgery.
- The Sushruta Samhita is a part of Ayurveda’s Great Trilogy alongside Charaka Samhita and Astanga Hridaya.
- He performed and documented over 300 surgical procedures, including plastic surgery (e.g., rhinoplasty i.e., rebuilding of the nose), gutter removal, fracture management, and even caesarean delivery.
- He treated numerous cases of Oshtha Sandhan (lobuloplasty) and Karna Sandhan (otoplasty) as well.
Karni Mata Temple:

The Prime Minister recently visited the Karni Mata temple in Deshnok, a small town about 30 km from Bikaner, Rajasthan.
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Karni Mata at Deshnoke, 30 km from Bikaner, in Rajasthan.
- Karni Mata was a Hindu warrior sage who lived in the fourteenth century.
- Living the life of an ascetic, Karni Mata was highly revered by the locals and earned many followers too.
- Having received requests from the Maharajas of Jodhpur and Bikaner, she even laid the foundation stones of the Mehrangarh and Bikaner Forts.
- Locals believe that she is an incarnation of Goddess Durga.
- Although there are many temples dedicated to her, this temple in the town of Deshnoke is the most widely recognized.
- It is also known as the Temple of Rats.
- The temple is famous for the approximately 25,000 rats that live and are revered in the temple.
- These holy rats are called kabbas, and many people travel great distances to pay their respects.
- Out of all the rats, white rats are held specifically sacred as they are believed to be the incarnations of Karni Mata and her sons.
- The temple was built by Maharaja Ganga Singh in the early 20th century.
- It has been built in a typical Rajputana style.
- There are a few shades of Mughal architecture with arched doorways.
- The temple facade is largely made of marble, while the main temple doors, which are a recent addition, are solid silver.
Jinchuanloong niedu:

A new genus and species of eusauropod dinosaur named Jinchuanloong niedu has been recently identified from a fossilized partial skeleton with a nearly complete skull found in the Chinese province of Gansu.
- It is an early-diverging member of a group of long-necked, strictly herbivorous, quadrupedal dinosaurs called Eusauropoda.
- The fossilized remains of Jinchuanloong niedu were collected from the lower part of the Xinhe Formation near Jinchang city, Gansu province, northwestern China.
- Jinchuanloong niedu roamed our planet during the Middle Jurassic period, some 165 million years ago.
- Sauropods are any member of the dinosaur subgroup Sauropoda, marked by large size, a long neck and tail, a four-legged stance, and a herbivorous diet.
- These were the largest of all dinosaurs and the largest land animals that ever lived.
- They lived from the Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous, and have been found on all continents.
- Due to the global warming event in the late Early Jurassic, eusauropods were the only surviving sauropod lineage subsequently.
- In the Middle and Late Jurassic, the non-neosauropod, eusauropod became dominant, represented by Shunosaurus, Omeisaurus, and ‘core Mamenchisaurus-like taxa’.
Rising Northeast: The Investor Summit
The Prime Minister at the “Rising Northeast: The Investor Summit” declared that the Northeast Region (NER) of India is no longer a “frontier” but a “frontrunner” in India’s growth journey. Highlighting its strategic importance and economic potential, he emphasized the region’s evolving role as a gateway for trade with Southeast Asia. The NER, referred to as ‘Ashta Lakshmis’, highlights the region’s vast potential in renewable energy, agro-based industries, eco-tourism, and strategic manufacturing.
The region’s biodiversity is being leveraged for green growth. Assam is a major hub for tea production, while Arunachal Pradesh leads in bamboo-based industries. The region holds 40% of India’s hydropower potential (~62,000 MW), yet only 6.9% is harnessed. Solar potential is estimated at 57,360 MW with only 17% installed capacity.
ICMR Launches First Stigma Scale for Sickle Cell Disease:
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has developed the ICMR-SCD Stigma Scale for India (ISSSI), the country’s first tool to measure and address stigma faced by sickle cell disease (SCD) patients and their caregivers. The scale includes two components: ISSSI-Pt for patients and ISSSI-Cg for caregivers. Assesses stigma in 5 areas- familial/reproductive stigma, disclosure issues, illness burden, discrimination, and healthcare stigma.Developed in 6 SCD-endemic districts to reflect India’s tribal, regional, and linguistic diversity.Existing 3 SCD stigma scales from Africa and America were unsuitable for India due to phenotypic, socio-cultural, and contextual differences, necessitating a locally relevant tool.Psychometrically robust, suitable for clinical use, research, and policy evaluation. Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a genetic mutation in the haemoglobin gene, leading to abnormal, crescent- or sickle-shaped red blood cells (RBC) instead of the usual round shape.
Oil Spills:
A Liberian-flagged cargo vessel carrying hazardous materials, including calcium carbide and diesel, sank off the Kerala coast, raising serious concerns over oil spills. Calcium carbide (CaC2) is a chemical that reacts with seawater to release acetylene gas, which is highly flammable and hazardous.Oil Spills refer to the release of liquid petroleum hydrocarbons into the environment, particularly into oceans, rivers, or coastal waters as a result of human activities. Diesel, petroleum, crude oil, and other hydrocarbons may be released from sources such as tankers, offshore platforms, drilling rigs, or wells which have harmful effects on marine ecosystems, coastal livelihoods, and human health.
India Becomes World’s 4th Largest Economy:
At the 10th NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) Governing Council Meeting, NITI Aayog CEO announced that India has overtaken Japan to become the world’s 4th largest economy, with its GDP crossing USD 4 trillion.India remains the world’s fastest-growing major economy and is the only country projected to grow over 6% annually for the next two years.
This sustained growth is expected to raise India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to USD 5.58 trillion by 2028, enabling it to surpass Germany and become the third-largest economy globally. Earlier, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in its 2025 World Economic Outlook Report projected that India would become the fourth-largest economy in 2025 with a nominal GDP of USD 4.187 trillion, overtaking Japan’s USD 4.186 trillion.
Strengthening Urban Biodiversity:
Urban biodiversity is vital for a healthy planet and human well-being but faces severe threats, from habitat loss and climate change. On International Day for Biological Diversity (22nd May), the theme “Harmony with nature and sustainable development” stresses the urgent need to integrate ecological conservation into urban growth. Urban Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms (plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms) found within cities and urban areas. It includes all life forms in human-dominated environments, such as parks, gardens, green roofs, wetlands, and built structures.




