Today’s Current Affairs: 28th April 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
World Malaria Day 2025:

World Malaria Day is observed every year on April 25, as endorsed by WHO member states in 2007.
- The theme for 2025 is “Malaria Ends With Us: Reinvest, Reimagine, Reignite”, which urges renewed global action against malaria through innovation, collaboration, and sustained commitment.
- Malaria is a life-threatening febrile illness caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- The disease is not contagious, but can be spread through infected blood or contaminated needles.
- The most dangerous species are Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax.
- Symptoms appear 10–15 days after infection and include fever, chills, and headache.
- Severe symptoms can include seizures, difficulty breathing, jaundice, dark urine, and death if untreated.
- Partial immunity can develop in endemic regions, making diagnosis difficult in some patients.
- Prevention includes vector control, use of mosquito nets, repellents (DEET, IR3535, Icaridin), long clothing, and chemoprophylaxis for travelers.
- Early diagnosis and treatment using microscopy or rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) is critical.
- Treatments include:
- ACTs (Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies) for falciparum.
- Chloroquine for vivax where effective.
- Primaquine to prevent relapses in vivax and P. ovale infections.
- Severe malaria cases require injectable treatments in clinical settings.
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India:

The JCoR meeting, held at TRAI headquarters, New Delhi, emphasised the need for a unified and collaborative approach to combat spam and fraudulent calls, especially targeting senior citizens.
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) established under the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997, passed by Parliament.
- Primary mandate is to regulate telecom services in India including tariff fixation/revision, which was earlier the domain of the Central Government.
- Covers areas like tariffs, quality of service, interconnection, spectrum management, and consumer protection in the telecom sector.
- Issues regulations, recommendations, and orders that guide telecom policy-making and market practices.
- Composition of TRAI
- Consists of a Chairperson, a maximum of two full-time members, and two part-time members.
- Appointments are made by the Central Government.
- Tenure: Members serve for three years or until the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
World Social Report 2025:

The United Nations released the World Social Report 2025, highlighting the urgent need for a new global policy consensus focused on equity, economic security, and solidarity amid rising insecurity, inequality, and declining trust worldwide.
World Social Report 2025:
- 60% of the global population experiences economic insecurity, with over 690 million people still in extreme poverty.
- Despite poverty reduction gains, income inequality widened in two-thirds of countries; the richest 1% hold more wealth than 95% of humanity.
- Informal and precarious employment remains dominant, especially in Africa and South Asia, leading to unstable incomes and vulnerability.
- More than 50% of people globally report low or no trust in governments, driven by economic distress, misinformation, and governance failures.
- One in five people faced climate shocks and one in seven endured conflicts in 2024, reversing development gains and fuelling insecurity.
- Over 1 billion people lifted out of extreme poverty since 1995; improvements noted in literacy, life expectancy, and access to basic services.
- Weak social protection, unfair taxation, and underinvestment in public goods continue to widen the gap between rich and poor nations.
- The report urges building inclusive, equitable, and resilient societies through fair taxation, universal social protection, and renewed multilateralism
Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit in Paris:

At the Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit in Paris, world leaders stressed the urgent need to integrate food literacy into school education to tackle global malnutrition challenges.
- Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit is a global summit aimed at mobilizing commitments to tackle malnutrition in all its forms.
- Objective is to accelerate progress towards ending malnutrition by aligning nutrition goals with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development ,to emphasize a shift beyond food availability to improving food literacy and healthy eating habits, especially among children.
- Extension of the UN Decade of Action on Nutrition from 2025 to 2030.
- Global endorsement to embed nutrition education in school curricula.
- Renewed commitment to promote bio-diverse and sustainable diets.
Lanjia Saora Tribe:

The women of the Lanjia Saora tribal group in the Gunupur region of Rayagada district, Odisha, celebrate the mango harvest through traditional dance.
- The Lanjia Saora, a culturally rich and isolated subgroup of the Saora tribe, inhabit the forested hills of Gajapati and Rayagada districts in Odisha, they speak Saora, a Mundari language of the Austroasiatic family.
- The Lanjia Saora perform vibrant dances with spontaneous songs, using brass pipes, cymbals, and gongs.
- Men wear turbans adorned with crane feathers, while both men and women carry umbrellas, swords, and peacock plumes during the dance.
- The Saora are one of the oldest tribes of Odisha, mentioned in the Ramayana and Mahabharata, and also found in parts of Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Assam.
Mycetoma : Study
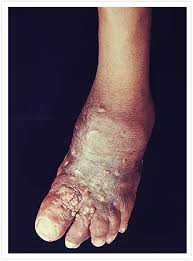
The world’s only research centre on mycetoma, a neglected tropical disease common among farmers, has been destroyed in Sudan’s two-year war, its director and another expert say.
- Mycetoma is a chronic, progressively destructive infectious disease of the subcutaneous tissues, that spreads to affect the skin, deep tissues and bone.
- It was first reported in the mid-19th century in Madurai, India, and hence was initially called Madura foot.
- It is a unique neglected tropical disease caused by a substantial number of microorganisms of fungal or bacterial origins.
- The disease commonly affects young adults, mostly males aged between 15 and 30 years in developing countries.
- Mycetoma occurs in tropical and subtropical environments characterized by short rainy seasons and prolonged dry seasons that favour the growth of thorny bushes.
- The causative organisms of mycetoma are distributed worldwide but are endemic in tropical and subtropical areas in the so called ‘Mycetoma belt’, which includes, among others, Venezuela, Chad, Ethiopia, India, Mauritania, Mexico, Senegal, Somalia, Sudan, Thailand, and Yemen.
- Transmission occurs when the causative organism enters the body through minor trauma or a penetrating injury, commonly thorn pricks.
- There is a clear association between mycetoma and individuals who walk barefooted and are manual workers.
- Symptoms are similar for bacterial and fungal mycetoma.
- Both appear as firm, painless masses under the skin. These masses usually appear on a person’s foot but can form anywhere on the body.
- Mycetoma masses start small, but over time they can grow larger and develop oozing sores.
- The affected limb can become deformed or unusable.
- The discharge from the oozing sores can contain sand-like particles called “grains,” that can be white, yellow, red, brown, or black.
- If left untreated or treatment fails, it can spread to other areas of the body and even result in blood infections.
- Long-term mycetoma can eventually destroy the underlying muscle and bone.
- For bacterial mycetoma, treatment consists of a combination of antibiotics, whereas for fungal mycetoma, treatment consists of a combination of antifungal drugs and surgery.
Yellowstone Supervolcano:

A “breathing” cap of magma has been discovered inside the Yellowstone supervolcano, and it might help determine when the volcano will next erupt, a new study has found.
- Yellowstone Supervolcano lies beneath Yellowstone National Park, in the western United States.
- It is one of the largest active volcanic systems in the world.
- It’s a caldera (a large crater formed by a major eruption) and an active supervolcanic system.
- The caldera formed when pyroclastic material exploded out of the volcano, partly emptying the magma chamber causing the roof to collapse.
- When the roof collapsed over the magma chamber, it created a bowl shaped depression in the ground.
- Three enormous eruptions occurred at the Yellowstone hotspot 2.1 million, 1.3 million, and 640,000 years ago.
- Two of these released so much material that the area is often referred to as a supervolcano.
- A supervolcano is a volcano that at one point in time erupted more than 1,000 cubic kilometers of deposits.
- One recent study estimates that another supervolcanic eruption at Yellowstone would blanket North America in ash, and some areas close to the hotspot could be covered by more than a meter of debris.
- Supervolcanoes can also have pronounced cooling effects on the climate for several years after an eruption because of the sulfur dioxide that is released to the atmosphere.
- The sulfur dioxide forms aerosols that block incoming sunlight.
- Eventually, the sulfur dioxide from the eruption will wash out of the atmosphere, and the climate cooling effect will subside.
Dhubri-Phulbari Bridge:

59 percent work completed on 19.28 Km Dhubri-Phulbari Brahmaputra Bridge, according to reports.
- Dhubri-Phulbari Bridge is an under-construction 4-lane bridge project over the Brahmaputra River connecting Dhubri in Assam and Phulbari in Meghalaya on NH 127 B.
- The length of the bridge is 3 km, which would make it the longest river bridge in the country.
- It comprises a navigation bridge stretching approximately 1625 kilometers, complemented by approach viaducts on both sides, with 3.5 kilometers on the Dhubri end and 2.2 kilometers on the Phulbari side.
- The project’s civil construction work is being done by Larsen & Toubro (L&T) for the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corp Ltd. (NHIDCL) and funded by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
- The project is estimated to cost Rs 3165.99 crore.
- The bridge will significantly reduce travel distances, especially between Phulbari in Meghalaya and Dhubri in Assam.
- It will shorten travel by more than 200 km, improving the connectivity of India’s northeastern states with the rest of the country.
Zero Shadow Day: Recently Observed

The Cosmology Education and Research Training Center (COSMOS), Mysuru, of the Indian Institute of Astrophysics recently observed ‘Zero Shadow Day’.
- Zero Shadow Day (ZSD) is an interesting celestial phenomenon that occurs twice in a year when the Sun is directly overhead and thus no shadow of any vertical object can be seen.
- This event happens for locations situated between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The ZSD phenomenon transpires when the Sun’s declination becomes equal to the latitude of the location.
- On this day, as the sun crosses the local meridian, its rays fall exactly vertically relative to an object on the ground, making it impossible to observe any shadow of that object.
- This is due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis and its rotation around the sun, causing the angle of the sun’s rays to change throughout the year, which in turn affects the lengths and directions of shadows.
- There are two zero shadow days every year, observed in places that lie between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- One falls during the Uttarayan (when the Sun moves northwards), and the other is during Dakshinayan (when the Sun moves southwards).
- It will clearly be different for different places on earth.
- It lasts for a small part of a second, but the effect can be seen for a minute to a minute-and-a-half.
- The southern part of India, roughly below the latitude of Bhopal, will experience the ZSD.
- The states that can see this event are Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Goa, Maharashtra, Odisha, Daman & Diu, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, most of Gujarat and Chhattisgarh, and the southern parts of Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, and Mizoram.
Scramjet Engine Test:

The Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), under DRDO, successfully conducted a ground test of a Scramjet Engine for over 1,000 seconds at Hyderabad.
- A Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) is an air-breathing engine designed to operate efficiently at hypersonic speeds (Mach 5 and above).
- Unlike traditional jet engines, it does not use rotating compressors, relying instead on the vehicle’s high speed to compress air.
- Scramjets enable supersonic combustion, making them suitable for Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs).
- Scramjet Engine Working Principle:
- Air intake: Vehicle must already be flying at supersonic speeds (Mach 3+).
- Compression: High-speed movement compresses the incoming air.
- Combustion: Hydrogen fuel is injected and ignited while air remains supersonic.
- Thrust Generation: Expanding gases create thrust (based on Newton’s Third Law).
- Scramjets need rocket-assisted takeoff as they can’t generate thrust at zero speed.
RBI Cancels Licence of Ajantha Urban Co-op Bank Maryadit:
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced the cancellation of the banking license of Ajantha Urban Co-operative Bank Maryadit, based in Aurangabad, Maharashtra. The action was taken due to the bank’s inadequate capital, poor earnings outlook, and inability to protect depositors’ interests. The RBI directed the Registrar of Cooperative Societies, Maharashtra, to initiate liquidation proceedings, ensuring depositor protection through the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC).
RBI’s Directive To Banks:
In a significant move aimed at enhancing the security of digital banking and combating growing cybersecurity threats, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has mandated all banks to transition their existing web domains to the new ‘.bank.in’ domain by October 31, 2025. This directive comes in response to the increasing number of frauds in digital payment systems and aims to create a more secure and trusted online banking environment. By adopting this exclusive domain, banks will be able to mitigate cybersecurity risks, such as phishing attacks, and ensure the safety of digital transactions.
Kumar Mangalam Birla to Receive Lata Deenanath Mangeshkar Award 2024:
Kumar Mangalam Birla, the 57-year-old Chairman of the Aditya Birla Group, will be conferred with the prestigious Lata Deenanath Mangeshkar Award on April 24, 2024, in a grand ceremony to be held at the Deenanath Mangeshkar Auditorium in Vile Parle East, Mumbai.A Padma Bhushan awardee, Kumar Mangalam Birla is being recognized for his visionary leadership and significant contributions to India’s economic development.
Exercise ‘Aakraman’ Indian Air Force Drills with Rafales and Su-30s:
Indian Air Force (IAF) conducted major military drills, named Exercise ‘Aakraman,’ simulating attacks on both mountain and ground targets. The exercise, which involved India’s most advanced fighter jets, including the Rafale and Su-30MKI aircraft, aimed to test and enhance the IAF’s capabilities in complex combat scenarios. With rising tensions between India and Pakistan, particularly after the Pahalgam terror attack, this exercise demonstrates the IAF’s readiness to defend India’s airspace and respond to any potential threats. The drills also emphasize the strategic advantage gained by the Indian Air Force through the induction of cutting-edge technologies like the Rafale jets and the S-400 air defense system.
India’s Record Cargo Movement on Inland Waterways In FY 2024–25:
India has achieved a significant milestone in its inland water transport (IWT) sector by recording 145.5 million tonnes (MMT) of cargo movement during the fiscal year 2024–25. This marks a dramatic rise from just 18.1 MMT in FY 2013–14, driven by massive infrastructure development, policy reforms, and technological innovations. The country has also expanded its National Waterways from 5 to 111 and increased the operational length to nearly 4,900 km, reflecting a strong commitment to multimodal logistics and sustainable development.
Dr. K. Kasturirangan :Passed Away
Prime Minister of India condoled the passing of Dr. K. Kasturirangan, a towering figure in India’s space and education sectors, who passed away at the age of 84.Dr. K. Kasturirangan Eminent astrophysicist and former Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Served as Secretary to the Government of India and Member of Parliament (Rajya Sabha, 2003–09). Awarded Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Vibhushan for his contributions.




