Today’s Current Affairs: 28th Feb 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
African Union Imposes Ban On Donkey Skin Trade:

African Union imposes historic ban on cruel donkey skin trade.
- Demand for the animals’ skins is fuelled by the popularity of an ancient Chinese medicine called Ejiao, traditionally made from donkey hides.
- About two-thirds of world’s estimated population of 53 million donkeys are in Africa.
- People in the poorest, rural communities use them for transport and to carry water, food and other goods.
- Donkey slaughter for its skin has eroded livelihoods in Africa, robbing the continent of its culture, biodiversity and identity.
African Union (AU):
- The African Union (AU), officially launched in 2002, is a continental body consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa.
- It serves as the successor to the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), which was established from 1963 to 1999.
- The AU’s primary goal is to propel a united continent toward peace and prosperity.
- It supports political and economic integration among its 54 member nations, aiming to boost development, eradicate poverty, and bring Africa into the global economy.
- The AU’s secretariat, known as the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa.
- The largest city within the AU is Lagos, Nigeria, while the largest urban agglomeration is Cairo, Egypt.
Indus Water Treaty : Update
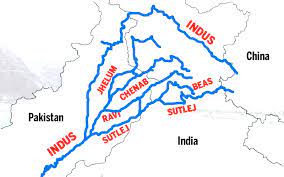
India completely stops Ravi River water flow to Pakistan.
- The completion of the Shahpur Kandi barrage diverts water from the Ravi River to benefit Jammu and Kashmir.
- This project, under the Indus Waters Treaty, aids irrigation and hydropower generation, contributing to agricultural and economic growth in the region.
INDUS WATER TREATY:
- The Indus Water Treaty is a water-sharing agreement between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank and signed in 1960.
- The treaty was signed by then Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and Pakistani President Ayub Khan.
- The treaty deals with the river Indus and its five tributaries, classified into two categories:
- Eastern rivers: Ravi, Beas, Sutlej
- Western rivers: Indus, Chenab, Jhelum
- India got control over the eastern rivers, while Pakistan got control over the western rivers.
- The treaty allows India to use the western river waters for limited irrigation use and unlimited non-consumptive use.
- A Permanent Indus Commission was set up by the United Nations for resolving any disputes that may arise in water sharing.
- India has undertaken several water management projects, including the construction of storage facilities such as the Bhakra Dam on the Sutlej, Pong and Pandoh Dam on the Beas, and Thein (Ranjit Sagar) on the Ravi.
- These initiatives, coupled with projects like the Beas-Sutlej link and the Indira Gandhi Nahar Project, have enabled India to utilize nearly its entire share (95%) of waters from the eastern rivers.
INDUS-X Summit 2024:

The United States Department of Defense (DoD) and the Indian Ministry of Defense (MoD) participated in the second India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem (INDUS-X) Summit in New Delhi, India.
- The summit was jointly organized by Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), MoD, and the DoD, and coordinated by the US-India Business Council (USIBC) and Society of India Defense Manufacturers (SIDM).
Key Highlights of the Second INDUS-X Summit:
- The summit emphasised the critical role India and the US play as key partners in ensuring a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
- Discussions centred on co-producing advanced military capabilities, strengthening defence supply chains, and enhancing interoperability to address shared security challenges.
- Emphasis was placed on fostering innovation in defence technologies through collaborative efforts between Indian and American industries.
- The summit provided a platform for startups and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the defence sector to engage with established players, facilitating knowledge exchange and partnerships.
- The summit highlighted the strong defence partnership between India and the US, citing initiatives like Initiatives on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) aimed at fostering innovation across key sectors, including defence.
- The Summit emphasised the crucial role of technological innovation in defence within the broader context of the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership, fostering collective progress for defence industries across borders.
- The Summit highlighted the introduction of Joint IMPACT Challenges, aiming to advance defence and aerospace co-development and co-production collaboratively, involving startups in pioneering solutions.
Amendments In FDI Policy Pertaining To The Space Industry:

The Union Cabinet approved amendments in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy pertaining to the space industry.
Recent Amendments in FDI Policy for the Space Sector:
- 100% FDI Allowed: Under the amended policy, 100% FDI is permitted in the space sector, aiming to attract potential investors to Indian space companies.
- Liberalised Entry Routes: The entry routes for various space activities are as follows:
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Satellites-Manufacturing & Operation, Satellite Data Products, Ground Segment & User Segment.
- Beyond 74%, the government route applies.
- Up to 49% under Automatic Route: Launch Vehicles, associated systems or subsystems, Creation of Spaceports.
- Beyond 49%, the government route applies.
- Up to 100% under Automatic Route: Manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems for satellites, ground segment, and user segment.
Parhyale Odian : New Species Of Marine Amphipod

Researchers from Odisha’s Berhampur University discovered a new species of marine amphipod in Chilika Lake. It has been named Parhyale Odian after Odisha’s native language, Odia.
- Amphipods are a diverse group of malacostracan crustaceans, meaning they share some features with crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
- They have a laterally compressed body, meaning they are flattened from side to side, and a curved body shape.
- The whale lice found on the bodies of whales and dolphins are actually a type of amphipod.
Parhyale Odian:
- It is a shrimp-like crustacean of the genus Parhyale.
- It is brown in colour, approximately 8 millimetres in length, and possesses 13 pairs of legs.
- The first pair of legs is specialized for capturing prey and feeding.
- Unlike the other 15 known species in the genus, Parhyale Odian stands out due to a stout robust seta- a spine-like structure on the surface of the male gnathopod (first pair of legs).
Aegis Graham Bell Awards:

The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT), the premier Telecom R&D centre of the Government of India, strikes a hat-trick by securing top position in three awards at 14th Annual Aegis Graham Bell Awards.
- Aegis Graham Bell Awards was initiated in 2010 by the Aegis School of Data Science.
- It is a tribute to the father of telephony and great innovator, Alexander Graham Bell.
- The Aegis School of Business, Data Science and Cyber Security has initiated this award to promote innovations and recognise the outstanding contributions by innovators in various fields including education, Information and Communications Technology (ICT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data science.
- This award in India is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Skill India and the National Informatics Centre.
- Projects of C-DOT which received this award:
- ASTR Project: ASTR (AI & Facial Recognition-powered Solution for Telecom SIM Subscriber Verification) is a game-changer in the fight against cybercrimes.
- Designed to analyse, identify, and eliminate fake/forged mobile connections, it’s a crucial step towards ensuring a secure telecom environment.
- CEIR (Central Equipment Identity Register) solution: CEIR helps revolutionise mobile security by detecting clone IMEIs, restricting the import of counterfeit mobile devices and also enabling the blocking and tracing of lost or stolen phones.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) product: India employs quantum mechanics to create an unbreakable cryptographic protocol even with Quantum computers.
Loss And Damage Board:

Developed countries have delayed nominating members to the Loss and Damage Board, hampering efforts to fully operationalise the fund to developing countries in time.
- Loss and Damage Board at the 27th Conference of Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP27) held in Egypt, Parties reached an agreement on providing loss and damage funding to nations most vulnerable and impacted by the effects of climate change.
- At COP28, the fund was formally established and a decision text stated that the fund would be governed and supervised by a board, a decision-making body.
- The board is tasked with setting up a strategic direction for the Fund as well as its governance and operational modalities, policies, frameworks and work programme, including relevant funding decisions.
- The Board will comprise 26 members, 12 members from developed countries and 14 from developing nations.
- Loss and Damage Fund is a global financial package to ensure the rescue and rehabilitation of countries facing the cascading effects of climate change.
- The term refers to the compensation that rich nations, whose industrial growth has resulted in global warming and driven the planet into a climate crisis, must pay to poor nations, whose carbon footprint is low but are facing the brunt of rising sea levels, floods, crippling droughts, and intense cyclones, among others.
SAMAR Assessment Certificates:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) handed over SAMAR assessment certificates to nine Industry Partners.
- System for Advance Manufacturing Assessment and Rating (SAMAR) certificateis a benchmark to measure the competency of defence manufacturing enterprises.
- It is an outcome of the collaboration between DRDO and the Quality Council of India (QCI) to strengthen the defence manufacturing ecosystem in the country to further the vision of making India self-reliant in defence manufacturing.
- Objective is:
- to provide an assessment of the manufacturing capability of Defence Manufacturing Enterprises
- Enable enterprises to benchmark their performance across a range of business capabilities to enhance quality, reliability and competitiveness
- Create a credible database of Defence manufacturers for ease in vendor selection and development
- Strengthen the Defence manufacturing ecosystem in the country with an objective to realise the vision of making India self-reliant in Defence manufacturing
- Eligibility: All defence manufacturing enterprises, both MSME and Large enterprises, are eligible to apply for this certification.
- Validity: It is valid for a period of 2 years from the date of issuance of the certificate.
- The certification is based on a maturity assessment model developed by QCI and is applicable to all defence manufacturing enterprises i.e., micro, small, medium and large enterprises.
Exercise Dharma Guardian 2024:

India and Japan kicked off a two-week military exercise ‘Dharma Guardian’ in Rajasthan’s Mahajan field firing range to foster deeper cooperation in confronting common security challenges.
- Exercise Dharma Guardian is an annual exercise and is conducted alternatively in India and Japan.
- It is the 5th edition of joint military exercise between India and Japan.
- The aim of the Exercise is to foster Military Cooperation and enhance combined capabilities to execute joint operations in the semi-urban environment under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- The Exercise would focus on a high degree of physical fitness, joint planning, joint tactical drills and basics of special arms skills.
- It will enable the two sides to share their best practices in Tactics, Techniques and Procedures for conducting tactical operations.
- The Exercise will also facilitate developing interoperability, bonhomie and camaraderie between troops of both sides.
- This will enhance the level of defence cooperation, further fostering bilateral relations between the two friendly nations.




