Today Current Affairs: 28th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Garib Nawaz Employment Scheme:

The Union Minister for Minority Affairs replied in the Parliament that a total number of 371 training centers under Gharib Nawaz Employment Scheme were opened across the country.
About Gharib Nawaz Employment Scheme:
- It was launched by the Ministry of Minority Affairs in 2017.
- Maulana Azad Education Foundation, an autonomous body under the aegis of Ministry of Minority Affairs, implements the Scheme.
- The main aim of this scheme is to provide short term job oriented skill development courses to minorities’ youth in order to enable them for skill based employment.
- This scheme is implemented as per common norms of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSD&E) through the empanelled Program Implementation Agencies (PIAs).
- The PIA is mandated to place minimum 70% trainees out of total trained trainees.
- The monthly stipend for maximum of three months and post placement support for maximum of two months after getting employment are also being paid to the beneficiaries directly into their account.
Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) Programme:

Under the Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) programme, the government has given approval for establishing two additional facilities.
- In 2020, India filled its strategic petroleum reserves in view of the slump in crude prices.
- The new facilities will be commercial-cum-strategic facilities with a total storage capacity of 6.5 MMT (Million Metric Ton) underground storages at:
- Chandikhol, Odisha (4 MMT)
- Padur, Karnataka (2.5 MMT)
- They will be built in Public Private Partnership mode under phase II of the SPR Programme.
- Existing Facilities:
- Under Phase I of the Programme, Government of India has established petroleum storage facilities with total capacity of 5.33 MMT at 3 locations:
- Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh (1.33 MMT).
- Mangaluru, Karnataka (1.5 MMT).
- Padur, Karnataka (2.5 MMT).
- Under Phase I of the Programme, Government of India has established petroleum storage facilities with total capacity of 5.33 MMT at 3 locations:
- The petroleum reserves established under Phase I are strategic in nature and the crude oil stored in these reserves will be used during an oil shortage event, as and when declared so by the Government of India.
About Strategic Petroleum Reserves:
- Strategic petroleum reserves are huge stockpiles of crude oil to deal with any crude oil-related crisis like the risk of supply disruption from natural disasters, war or other calamities.
- According to the agreement on an International Energy Programme (I.E.P.), each International Energy Agency (IEA) country has an obligation to hold emergency oil stocks equivalent to at least 90 days of net oil imports.
- In case of a severe oil supply disruption, IEA members may decide to release these stocks to the market as part of a collective action.
- India became an associate member of the IEA in 2017.
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) Certificate:

The Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative (CHRI) has challenged the suspension of its Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) certificate for 180 days.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) suspended CHRI’s certificate in violation of various provisions of the FCRA Act.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010:
- Foreign funding of persons in India is regulated under FCRA act and is implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Individuals are permitted to accept foreign contributions without permission of MHA.
- However, the monetary limit for acceptance of such foreign contributions shall be less than Rs. 25,000.
- The Act ensures that the recipients of foreign contributions adhere to the stated purpose for which such contribution has been obtained.
- Under the Act, organisations are required to register themselves every five years.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Act, 2020:
- Prohibition to accept foreign contribution: The Act bars public servants from receiving foreign contributions. Public servant includes any person who is in service or paid by the government, or remunerated by the government for the performance of any public duty.
- Transfer of foreign contribution: The Act prohibits the transfer of foreign contribution to any other person not registered to accept foreign contributions.
- Aadhaar for registration: The Act makes Aadhaar number mandatory for all office bearers, directors or key functionaries of a person receiving foreign contribution, as an identification document.
- FCRA account: The Act states that foreign contributions must be received only in an account designated by the bank as FCRA account in such branches of the State Bank of India, New Delhi.
- Reduction in use of foreign contribution for administrative purposes: The Act proposes that not more than 20% of the total foreign funds received could be defrayed for administrative expenses. In FCRA 2010, the limit was 50%.
- Surrender of certificate: The Act allows the central government to permit a person to surrender their registration certificate.
Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code (Amendment Bill), 2021:

The government introduced the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment Bill), 2021 in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill is set to replace the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code Amendment Ordinance 2021 promulgated in April 2021.
- It introduced an alternate insolvency resolution process for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) with defaults up to Rs 1 crore called the Pre-packaged Insolvency Resolution Process (PIRP).
- In March 2021 a sub-committee of the Insolvency Law Committee (ILC) recommended a pre-pack framework within the basic structure of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
Major Provisions:
- Distressed Corporate Debtors (CDs) are permitted to initiate a PIRP with the approval of two-thirds of their creditors to resolve their outstanding debt under the new mechanism.
- A corporate debtor is a corporate person who owes debt to any other person.
- The PIRP also allows for a Swiss challenge to the resolution plan submitted by a CD in case operational creditors are not paid 100 % of their outstanding dues.
- A Swiss Challenge is a method of bidding, often used in public projects, in which an interested party initiates a proposal for a contract or the bid for a project.
About PIRP:
- A pre-pack is the resolution of the debt of a distressed company through an agreement between secured creditors and investors instead of a public bidding process.
- This system of insolvency proceedings has become an increasingly popular mechanism for insolvency resolution in the UK and Europe over the past decade.
- Pre-packs are largely aimed at providing MSMEs with an opportunity to restructure their liabilities and start with a clean slate while still providing adequate protections so that the system is not misused by firms to avoid making payments to creditors.
- Unlike in the case of Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP), debtors remain in control of their distressed firm during the PIRP.
- Under the pre-pack system, financial creditors will agree to terms with a potential investor and seek approval of the resolution plan from the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
Central And South Asia: Regional Connectivity:

Uzbekistan hosted a high-level International Conference titled “Central and South Asia: Regional Connectivity. Challenges and Opportunities” at Tashkent, recently.
- The conference was an initiative of the President of Uzbekistan, Shavkat Mirziyoyev.
- Delegates from over 40 countries and about 30 international organizations, and heads of think tanks participated in the conference. It was attended by President of Afghanistan Ashraf Ghani, Ministers from Central Asian, West Asian and South Asian countries, including Minister of External Affairs of India Dr. S. Jaishankar.
- Jaishankar said that for Central Asian countries, Chabahar port in Iran provides a ‘secure, viable and unhindered access to the sea.
- The port has been proposed to be included in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- It may be added that an India-Uzbekistan-Iran-Afghanistan Quadrilateral Working Group has been formed on the joint use of Chabahar port.
Typhoon Fabian:
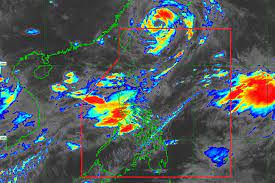
Typhoon In-fa, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Fabian, is an active and very large tropical cyclone inland over China.
- The system was first noted as an area of low pressure, located east of the Philippines on July 14.
- Favorable conditions helped the storm to intensify, becoming a tropical depression, two days later and a tropical storm on July 17.
- The storm has exacerbated and played a part in starting the 2021 Henan floods. Since 17 July 2021, China’s Henan province has been affected by severe flooding, caused by a period of prolonged heavy rainfall.
- According to projections, In-fa would beat Typhoon Fitow of 2013 as the costliest typhoon to strike China, and the third costliest typhoon on record (a total of $14.7 billion) when adjusted for inflation.
The National Mission For Clean Ganga (NMCG):

The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG), conceived as a ₹20,000-crore programme in 2014 to clean up the river, has so far been allocated ₹15,074 crore.
- Of this only ₹10,972 crore, or about two-thirds, has been released by the Finance Ministry to the NMCG, a body under the Jal Shakti Ministry. The NMCG further allocates the money to the riverine States.
- The planned outlay for the Ganga clean-up mission, accounting for future costs, is well over ₹20,000 crore.
- Overall, 346 projects had been taken up at a sanctioned cost of ₹30,235 crore, out of which, 158 projects are completed.
- Uttar Pradesh, at ₹3,535 crore, has received the most funds, followed by Bihar (₹2,631 crore), Bengal (₹1,030 cr) and Uttarakhand (₹1001 cr).
India’s Foreign Exchange Reserves:

India’s foreign exchange reserves rose by $835 million to touch a record high of $612.73 billion in the week ended July 16, 2021, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data showed.
- According to weekly data from the RBI, forex reserves rose to a record $612.73 billion in the reporting week, helped by a rise in Foreign Currency Assets (FCA), a major component of the overall reserves.
- India’s forex reserves cover Foreign Currency Assets (FCAs), Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), Gold Reserves and the country’s reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Currently, China has the largest reserves followed by Japan and Switzerland.
- India has overtaken Russia to become the fourth largest country with foreign exchange res
KANDLA SEZ (KASEZ): First Green SEZ In The Country.:

Kandla becomes first Green SEZ in the country.
- Kandla Special Economic Zone (KASEZ), the oldest export zone in the country, has become the “first green industrial city” in India to receive a platinum rating under IGBC Green Cities Rating for existing cities in the industrial cities category.
- Compared to the 25,000 trees in KASEZ in 2019, the 1000-odd acres has 3.5 lakh trees. Most of these trees have been planted post 2019, using the Miyawaki forestation method.
- Apart from this, KASEZ also used plastic waste to line the artificial water bodies created inside the area to prevent water seepage and mix with the saline water.
Kargil Vijay Diwas:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi on July 26, 2021, paid tributes to Kargil martyrs on the Vijay Diwas day.
- Kargil Vijay Diwas is commemorated every 26th July in India, to observe India’s victory over Pakistan in the War of 1999 for the ejecting the Pakistani Forces from the mountain tops of Northern Kargil District in Ladakh in 1999.
- Initially, the Pakistani army denied involvement in the war, claiming that it was caused by Kashmiri militants forces.
- However documents left behind by casualties, testimony of POWs and later statements by Pakistan’s Prime Minister and Chief of Army Staff showed the involvement of Pakistani paramilitary forces, led by General Ashraf Rashid.
- The infiltration was code named “Operation Badri”. The aim of the Pakistani incursion was to sever the link between Kashmir and Ladakh and cause Indian forces to withdraw from the Siachen Glacier, thus
Immigration Bill 2021:

The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) invited public inputs to the Immigration Bill 2021. The Bill presents a long overdue opportunity to reform the recruitment process for nationals seeking employment abroad.
Key Features of the Bill:
- The Bill intends to replace the Emigration Act of 1983.
- The Bill envisages comprehensive emigration management, institutes regulatory mechanisms governing overseas employment of Indian nationals and establishes a framework for protection and promotion of welfare of emigrants.
The bill proposes a three-tier institutional framework:
- It launches a new emigration policy division in (MEA) which will be referred to as the Central Emigration Management Authority.
- It proposes a Bureau of Emigration Policy and Planning, and a Bureau of Emigration Administration shall handle day-to-day operational matters and oversee the welfare of emigrants.
- It proposes nodal agencies under a Chief Emigration Officer to ensure the welfare and protection of the emigrants.
- It permits government authorities to punish workers by cancelling or suspending their passports and imposing fines up to Rs 50,000 for violating any of the Bill’s provisions.
- When enforced, it can be used as a tool to crackdown on workers who migrate through unregistered brokers or via irregular arrangements such as on tourist visas.
- The proposed legislation will also maintain registration of human resources agencies, validity and renewal and cancellation of a certificate.
- Besides, authorities will be empowered to have certain powers of the civil court.
Exercise Cutlass Express 2021:

Indian Naval Ship Talwar participated in a multinational training exercise Cutlass Express 2021, being conducted along the East Coast of Africa.
- The exercise is an annual maritime exercise conducted to promote national and regional maritime security in East Africa and the Western Indian Ocean.
- The 2021 edition of the exercise involves participation of 12 Eastern African countries, US, UK, India and various international organisations like International Maritime Organisation (IMO), United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Interpol, European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR), Critical Maritime Routes Indian Ocean (CRIMARIO).
- The exercise is designed to assess and improve combined maritime law enforcement capacity, promote national and regional security and increase interoperability between the regional navies.
- India’s Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) is also participating in the exercise.
- India’s participation is in accordance with India’s stated policy towards maritime cooperation in the Indian Ocean region and vision SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region).
Monkeypox:

The US started surveillance on people travelling from Nigeria, who may have had contact with the individuals infected with Monkeypox.
- It is a viral zoonotic disease (transmission from animals to humans) and is identified as a pox-like disease among monkeys hence it is named Monkeypox.
- It is endemic to Nigeria.
- It is caused by monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae.
- The natural host of the virus remains undefined. But the disease has been reported in many animals.
- Animals known to be sources of Monkeypox virus include monkeys and apes, a variety of rodents (including rats, mice, squirrels and prairie dogs) and rabbits.
- It was first reported in 1958, in monkeys in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and in humans in 1970, also in the DRC.
- In 2017, Nigeria experienced the largest documented outbreak, 40 years after the last confirmed case.
- Subsequently, the disease has been reported in many West and Central African countries.
- Symptoms:
- Infected people break out in a rash that looks a lot like chicken pox. But the fever, malaise, and headache from Monkeypox are usually more severe than in chicken pox infection.
- In the early stage of the disease, Monkeypox can be distinguished from smallpox because the lymph gland gets enlarged.
- Transmission:
- Primary infection is through direct contact with the blood, bodily fluids, or cutaneous or mucosal lesions of an infected animal. Eating inadequately cooked meat of infected animals is also a risk factor.
- Human-to-human transmission can result from close contact with infected respiratory tract secretions, skin lesions of an infected person or objects recently contaminated by patient fluids or lesion materials.
- Transmission can also occur by inoculation or via the placenta (congenital monkeypox)
Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakaram (PMJVK):

The Ministry of Minority Affairs is implementing the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakaram (PMJVK), in the identified Minority Concentration Areas (MCAs) of the country.
About the PMJVK:
- The erstwhile Multi-sectoral Development Programme (MsDP) has been restructured and renamed as Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram for effective implementation since 2018.
- It seeks to provide better socio-economic infrastructure facilities to the minority communities.
- 80% of the resources under the PMJVK would be earmarked for projects related to education, health and skill development.
- 33 to 40% of resources under the PMJVK would be specifically allocated for women centric projects.
What Is Nauka?:

Nauka was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on July 21 using a Proton rocket. It is scheduled to be integrated with the ISS on July 29.
- Nauka, meaning “science” in Russian, is the biggest space laboratory Russia has launched to date.
- It will replace Pirs, a Russian module on the International Space Station (ISS) used as a docking port for spacecraft and as a door for cosmonauts to go out on spacewalks.
- Now, Nauka will serve as the country’s main research facility on the space station.
- Nauka is 42 feet long and weighs 20 tonnes.
- It is also bringing to the ISS another oxygen generator, a spare bed, another toilet, and a robotic cargo crane built by the European Space Agency (ESA).
- On the ISS, Nauka will be attached to the critical Zvezda module, which provides all of the space station’s life support systems and serves as the structural and functional centre of the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) — the Russian part of ISS.
Assam-Mizoram Border Dispute:
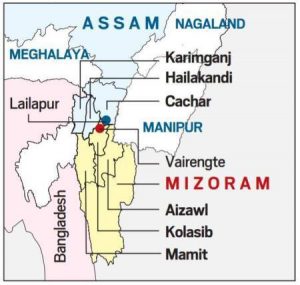
Earlier in June this year, two abandoned houses along the Mizoram-Assam border were burned down by unidentified persons, fuelling tension along the volatile inter-state border.
- Now, early a month after this incident, the border dispute between the two neighbouring states has cropped up again, with both accusing each other of encroaching on their respective territories.
- According to the Mizoram side, people from Assam have violated the status quo – as agreed upon between the two State governments a few years ago – in “no man’s land” to trigger the present crisis.
- Mizoram was carved out of Assam as a Union Territory in 1972 and by 1987, it became a full-fledged state.
- The two states have sparred over this 164.6 km long inter-state border over the past, sometimes leading to violent clashes.
- The dispute stems from two notifications passed under British era:
- First, notification of 1875, that differentiated Lushai Hills from the plains of Cachar.
- Second, notification of 1933, that demarcates a boundary between Lushai Hills and Manipur.
- Mizoram claims that the land is theirs is based on an 1875 notification, which came from the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act of 1873.
- Assam for its part, claims that the land is theirs. It goes by a 1933 notification by the state government that demarcated the Lushai Hills, which Mizoram was formerly known as, from the province of Manipur.
- During colonial times, Mizoram was known as Lushai Hills, a district of Assam.
- The border between the two neighbouring states is an imaginary line that changes with the natural obstacles of rivers, hills, valleys and forests.
- People of Assam and Mizoram have attributed the border conflicts to the differences over this not-so-clear boundary.
- Hence, often people living in the border areas cross over to the other side as they are not fully aware of the border demarcation.




