Today’s Current Affairs: 28th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Kilauea Volcano : Released Lava Fountains

The Kilauea volcano on Hawaii’s Big Island released lava fountains reaching over 1,000 feet into the air recently.
- Kilauea Volcano is one of the world’s most active volcanoes.
- It is a shield-type volcano located in the southeastern part of the island of Hawaii, Hawaii state, United States.
- The volcano rises 4,190 feet (1,227 meters) above sea level.
- The summit caldera contains a lava lake known as Halema`uma`u that is said to be the home of the Hawaiian volcano goddess, Pele.
- Kilauea has been erupting on a continuous basis since 1983.
- Kilauea’s frequent eruptions are usually nonexplosive and are contained within Halema‘uma‘u, which sometimes rises and overflows along the floor and flanks of the caldera proper.
- They are the largest volcanoes on Earth that actually look like volcanoes (i.e., not counting flood basalt flows).
- The Hawaiian shield volcanoes are the most famous examples.
- Shield volcanoes are almost exclusively basalt, a type of lava that is very fluid when erupted. For this reason, these volcanoes are not steep.
- They are broad volcanoes with gentle slopes.
- Eruptions at shield volcanoes are only explosive if water somehow gets into the vent; otherwise they are characterized by low-explosivity fountaining that forms cinder cones and spatter cones at the vent; however, 90% of the volcano is lava rather than pyroclastic material.
Caliphaea sinuofurcata:

Scientists have identified a new species of damselfly, Caliphaea Sinuofurcata, from Arunachal Pradesh.
- Caliphaea sinuofurcata is a new species of damselfly.
- It was discovered during biodiversity surveys in the Upper Siang and Lower Dibang Valley districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Proposed to be called the “Bearded Bronzeback,” this stunning insect marks only the second species of the genus Caliphaea recorded in India.
- While the genus Caliphaea is known from parts of Southeast Asia and China, only one species — confusa — was previously recorded in India over 165 years ago.
- The species is visually captivating with the presence of dense, black, beard-like bristles around the mouthparts of both males and females.
- These hair-like setae on the labium and labrum inspired the proposed English name — the Bearded Bronzeback.
- The name sinuofurcata — from the Latin words sinuosus (wavy or sinuous) and furcatus (forked) — refers to the twisted, bifurcated shape of the paraproct, a tail structure used for mating and species recognition.
- The damselfly gleams in metallic copper-green hues, with slender wings faintly tinted in brown, and a body adorned with subtle yellow and olive markings.
- It inhabits small, rocky seasonal streams in broadleaf evergreen forests at elevations around 1200 to 1300 meters above sea level.
- Individuals were observed flying low and perching on vegetation near the water, in dappled sunlight.
Coastline Paradox:
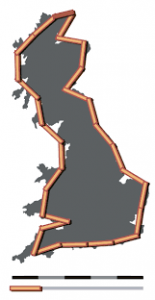
The coastline paradox reveals more than a peculiar measurement challenge: it underscores how science evolves with better tools.
- In December 2024, the Union Ministry of Home Affairs made an important announcement as part of its 2023-2024 annual report.
- It said the length of India’s coastline had increased from 7,516.6 km to 11,098.8 km, and that the length is also currently under review.
- The 7,516.6 km figure was first recorded in the 1970s based on measurement techniques available at the time.
- The new revised figure wasn’t prompted by any territorial expansion through new land/island annexation or geological upheaval, like tectonic activity stretching the shores.
- The root of the discrepancy lies in geometry, in a problem called the coastline paradox.
Bharat Forecasting System:

The India Meteorological Department (IMD) will soon adopt the Bharat Forecast System (BFS), which offers the highest resolution among weather models.
- Bharat Forecasting System (BFS) is an indigenously built advanced weather forecasting system.
- It was developed by the Pune-based Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM).
- It will provide forecasts with a 6 km resolution — the highest in the world — that would allow forecasters to predict small-scale weather features more accurately.
- This resolution is advanced in comparison to the previous 12-km Global Forecast System (GFS) used in India so far.
- This finer resolution will help in more precise predictions of localised weather events like heavy rainfall and cyclones.
- It is powered by the Arka supercomputer.
- This supercomputer has 11.77 petaflops (a unit to measure computer processing speed) and 33 petabytes (a petabyte is 1,000 terabytes (TB)) of storage.
- The supercomputer is located at IITM, Pune, and will massively reduce forecasting time compared to the older Pratyush
- Data from a network of 40 Doppler Weather Radars from across the country will be used to run the BFS model that would enable the weather office to issue more localised forecasts as well as nowcasts — weather forecasts for the next two hours.
- Gradually, the number of Doppler radars will increase to 100, which would allow the weather office to issue nowcasts across the country.
- The BFS can provide 6 km resolution forecasts for the tropical region that falls between 30 degrees South and 30 degrees North Latitudes.
- The Indian mainland extends between 8.4 degrees north and 37.6 degrees north latitudes.
- BFS is primarily a numerical weather prediction (NWP) model, but recently integrated AI and machine learning (ML) to enhance its working.
- Unlike most of the global models, BFS data will remain accessible to researchers worldwide, fostering collaborative advancements in meteorological science.
Kiru Hydropower Project:

The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) recently filed a chargesheet against the former Jammu and Kashmir Governor and five others over alleged irregularities in the Rs 2,200-crore civil works contract for the Kiru hydropower project.
- Kiru Hydropower Project is a 624 MW run-of-river scheme on the Chenab River in the Kishtwar district of Jammu & Kashmir.
- The project site lies approximately 1.5km downstream and 0.5km upstream at the convergence point of the Chenab River with the Singad and Bela streams.
- It is being constructed between the existing Kirthai II (upstream) and Kwar (downstream) hydel power projects, at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore.
- It will include the construction of a concrete gravity dam with a height of 135 m and an underground powerhouse located on the left bank of the river that will comprise four vertical Francis turbines with a capacity of 156 MW each.
- The project is being developed by Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPP), a joint venture between National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC, 49%), Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development Corporation (JKSPDC, 49%), and Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%).
- The project will provide much-needed power for the grid in northern India.
Mosura fentoni : New extinct species

Scientists recently identified a new extinct species, Mosura fentoni, an early marine predator from around 506 million years ago during the Cambrian period.
- Mosura fentoni is a newly discovered Cambrian marine organism found in the Burgess Shale, a globally significant fossil site in British Columbia, Canada.
- It belongs to the group Radiodonta, which are extinct stem-group arthropods, distant relatives of modern insects, spiders, and crustaceans.
- Despite being a small-sized species (ranging from 5 to 6 cm), M. fentoni displays highly specialised anatomical adaptations.
- The body of Mosura fentoni is unusually elongated, with a division into three distinct zones comprising a total of 26 segments:
- A short neck region that supports the head,
- A mesotrunk consisting of six paddle-shaped flaps that function as propulsive organs for swimming,
- A posterotrunk containing up to 16 segments dominated by rows of fine gills.
- The posterotrunk is proposed to be a specialised breathing tagma, drawing parallels to the oxygen-collecting tails of modern horseshoe crabs, suggesting a highly evolved respiratory mechanism in this ancient organism.
Maldives: Three-day official visit to India

Maldivian Foreign Minister is on a three-day official visit to India, accompanied by a high-level delegation, marking his third visit to India in 2025.
- Maldives is home to the 7th largest coral reef system in the world, contributing 14% of global reef area.
- The country has no rivers or streams and the average elevation is under 2 meters, making it highly vulnerable to sea-level rise.
- Barrier reefs provide natural protection against monsoon-related erosion and storm surges.
- The Maldives is an archipelagic state consisting of about 1,200 coral islands grouped in 26 atolls, located in the north-central Indian Ocean.
- It is strategically positioned astride major global sea lanes, making it vital for maritime trade and security in the IOR.
- The country lies south-southwest of India, separated from Lakshadweep by the Eight Degree Channel, a crucial sea route for India’s maritime movement.
IN-SPACe:

The Tamil Nadu Cabinet recently approved a Space Industrial Policy, making it the third Indian state, after Karnataka and Gujarat, to promote growth in the space ecosystem and attract investments.
- IN-SPACe is a single-window, independent, autonomous agency under the Department of Space (DoS) created as part of India’s space sector reforms.
- It aims to enable, promote, authorise, and supervise the participation of Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs) in various space activities.
- These include the development of launch vehicles and satellites, space-based services, and the utilisation or co-development of infrastructure controlled by ISRO and DoS.
- IN-SPACe functions as an interface between ISRO and private players, helping them access India’s space ecosystem and guiding their integration into national goals.
- It also assesses the requirements of private entities, educational institutions, and startups to facilitate research, design, and innovation in the space sector.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located at Bopal, Ahmedabad.
- Tamil Nadu already hosts major ISRO infrastructure, such as the ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) at Mahendragiri, Tirunelveli, where cryogenic and liquid propulsion systems are tested.
- ISRO is setting up India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Thoothukudi, which will significantly enhance satellite launch capabilities.
- The state is home to numerous space startups working in advanced areas like reusable launch vehicles, in-space manufacturing, in-orbit refuelling, and satellite data analytics.
- The Space Technology Incubation Centre (STIC) at NIT Trichy supports southern-region ISRO projects and innovation-led academic collaborations.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations:

Indonesia and China have reaffirmed their strategic partnership, with the Chinese Premier’s visit to Jakarta ahead of the ASEAN Summit reflecting growing diplomatic momentum.
- ASEAN is an inter-governmental regional organisation formed to promote political, economic, and security cooperation among Southeast Asian nations.
- Established in 1967 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration, its founding members were Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- ASEAN currently has 10 member countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, and Cambodia.
- The headquarters of ASEAN is located in Jakarta, Indonesia, underscoring Indonesia’s central role in the bloc.
- The ASEAN Summit is held annually, where member states discuss regional developments and set strategic policy directions.
- It is chaired by a rotating presidency.
- The ASEAN Coordinating Council (ACC) monitors the implementation of agreements and decisions, ensuring alignment across the member states.
- The ASEAN Secretariat, located in Jakarta, acts as the administrative body supporting and facilitating ASEAN’s initiatives, coordination, and documentation.
- The ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF) is a key platform for dialogue on political and security issues involving both member countries and external partners.
- India joined the ARF in 1996, marking its formal inclusion in ASEAN-led security dialogue mechanisms.
- ASEAN follows a decision-making process based on consultation and consensus, promoting unity while respecting national sovereignty.
Early Arrival of Monsoon:

The India Meteorological Department (IMD) declared the onset of the southwest monsoon over Kerala on May 24, 2025, eight days ahead of the usual June 1 date.
- This marks one of the earliest monsoon arrivals in over a decade, last seen in 2009.
- The Southwest Monsoon is a seasonal wind system that brings over 70% of India’s annual rainfall during June–September.
- It plays a critical role in agriculture, water availability, and overall economic activity.
Factors Behind Early Monsoon Onset 2025:
- Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO): Enhanced eastward-moving tropical disturbance boosted convection and rainfall over the Indian Ocean
- Mascarene High Intensification: Strong high-pressure system over the southern Indian Ocean aided in directing moist winds to Indian coastlines.
- Convection Surge: Rising heat and moisture movements increased vertical cloud build-up, bringing early rains.
- Somali Jet Strengthening: Cross-equatorial winds became stronger, accelerating the arrival of monsoon currents over Kerala and Karnataka.
- Heat Low Formation: Persistent low pressure over Pakistan and NW India created suction for moist monsoonal air.
- Monsoon Trough Activation: Elongated low-pressure zone stretching from Arabian Sea to Bay of Bengal activated rainfall over central India and NE India.
Madhubani and Gond Art:

Artists of Madhubani and Gond art met President Droupadi Murmu under the Artists-in-Residence Programme – Kala Utsav at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
Madhubani Art (Mithila Art):
- Originates from the Mithila region of Bihar; also referred to as Mithila painting.
- A folk-art form traditionally created by women on walls and floors of huts during auspicious occasions.
- Now practiced on cloth, canvas, and handmade paper.
- Uses plant-based pigments, cow dung-treated paper, and bamboo pens.
- Black lines made with cow dung and charcoal; filled with vibrant natural colors.
- Themes: Depictions of Hindu deities like Radha-Krishna, Shiva, Saraswati, etc.
- Social: Scenes from village life, weddings, and festivals.
- Nature: Birds, animals, trees (Tulsi, Banyan), sun, and moon.
- Cultural Identity: Symbol of female creativity and rural tradition passed down through generations.
Gond Art:
- Practiced by Pardhan Gond tribes of Madhya Pradesh and adjoining Central Indian states.
- Tribal art form with roots in oral storytelling and ritualistic practices.
- Initially drawn on walls of homes to depict folk tales and nature.
- Mythical Narratives: Depicts divine stories, village folklore, and animist beliefs.
- Pattern Work: Fills motifs with fine dots and lines to create visual rhythm.
- Nature Connection: Harmonious coexistence of humans, flora, and fauna.
- Colour Use: Bright, bold colour schemes with creative compositions.
- Global Reach: Popularized internationally through works like “The Night Life of Trees” by Tara Books.
Breakthrough Prize Physics 2025:
The 2025 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics has been awarded to major experimental teams at CERN—ATLAS, CMS, ALICE, and LHCb—based on their findings from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Run-2 data (2015–2024).Often dubbed the “Oscars of Science,” the Breakthrough Prize honors transformative achievements in fundamental physics.Awarded by: Given annually by the Breakthrough Prize Foundation. Awarded to: Teams behind ATLAS, CMS, ALICE, and LHCb experiments at CERN, comprising over 13,500 researchers. Prize Amount: $3 million awarded jointly to the four LHC experiments.
Biennial Election for Rajya Sabha:
The Election Commission has announced the schedule for the biennial elections for the eight Rajya Sabha seats including six seats from Tamil Nadu and two seats from Assam.Rajya Sabha is the Upper House of Parliament, representing the States and Union Territories. It is a permanent body, and elections are held periodically to fill the seats of retiring members.




