Today’s Current Affairs: 28th September 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
DF-41:

China says it successfully fired an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean on Wednesday, a rare public test that analysts said was meant to send a message to the United States and its allies amid heightened regional tensions.
- DF-41 Originate in 1980, China test-fired its first ICBM, the DF-5.
- Estimated range: 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers
- China held more than 500 operational nuclear warheads as of May 2023 and is likely to have more than 1,000 by 2030.
- Intercontinental Ballistic Missile have a range greater than 5,500 km and are primarily designed to deliver nuclear warheads.
- 8 nations have operational ICBMs—US, Russia, China, France, UK, India, Israel, and North Korea.
- India’s ICBM: Agni series
- Despite being nuclear-armed, Pakistan does not possess ICBMs
LAC Issue:
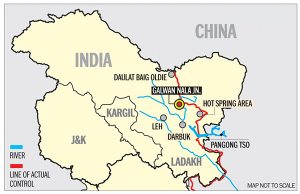
India and China are learnt to have made “significant progress” in narrowing their gap on pending issues along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in eastern Ladakh.
- The 31st WMCC talks and upcoming Corps Commanders’ meeting are key to finalizing troop redeployment and disengagement along the LAC.
- Both sides are discussing implementation details.
- Local commanders are holding regular meetings to prevent clashes, with both sides on alert but avoiding confrontation. Redeployment of troops will be gradual, continuing winter stocking efforts.
- India is planning to raise the 72 Division by mid-2024 for deployment in Ladakh, enhancing its military capabilities. Border infrastructure development continues to strengthen preparedness.
- Statements from both sides indicate that 75% of disengagement issues have been resolved, with disengagement completed at four points. Further talks aim to achieve complete disengagement.
- Long-standing disputes at Depsang Plains and Demchok persist, with Chinese troops blocking access to patrol points. Ongoing discussions are focused on resolving these legacy issues.
International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons:

The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons is celebrated on September 26th every year to raise awareness about the threat of nuclear weapons and to promote their elimination. It was declared by the UN General Assembly (UNGA) in 2013.
- The first Special Session of the UNGA devoted to disarmament, held in 1978, reaffirmed the preeminence of nuclear disarmament.
- The Atomic Energy Commission (1946) to propose measures for controlling nuclear energy and eliminating weapons of mass destruction.
- Other Initiatives of UNGA:
- Comprehensive disarmament in 1959
- Special Session on Disarmament in 1978
- Supported the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW)
Central Drugs Standards Control Organisation : In News

The Central Drugs Standards Control Organisation (CDSCO) flagged 53 drugs, including Paracetamol and Pan D, as ‘not of standard quality’ (NSQ), raising significant safety concerns regarding their consumption.
- The CDSCO has issued two lists, one with 48 drugs that failed quality tests and another with 5 drugs categorized as “Not of Standard Quality” (NSQ Alert), based on random monthly sampling by state drug officers.
- CDSCO under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government of India under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- Major functions of CDSCO include overseeing the regulatory control over drug imports, approving new drugs and clinical trials, and issuing certain licences as the Central License Approving Authority.
Minerals Security Finance Network:

India has officially joined the US-led Minerals Security Finance Network.
- It is a new initiative emerging from the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP).
- It is aimed at strengthening global cooperation in securing critical mineral supply chains.
- The network brings together institutions from the Indo-Pacific region and Europe, promoting cooperation, information exchange, and co-financing.
- The partnership includes 13 countries and the European Commission.
- These are the United States of America, Australia, Canada, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Norway, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and the European Union (represented by the European Commission).
- It helps India in diversifying and securing its supply of critical minerals from nations like Argentina, Chile, Australia, and select African countries. Kazakhstan, in Central Asia, is also being explored as a potential source for India’s mineral requirements.
- Minerals Security Partnership is a framework established by the US in 2022.
Women In Space Leadership Programme:

A Women in Space Leadership Programme (WiSLP) was launched by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in collaboration with the British Council as part of the UK-India Education and Research Initiative (UKIERI).
- This initiative aims to develop a women’s leadership framework to support institutions in strengthening their gender-inclusive practices and policies, specifically around space sciences and allied areas.
- It fosters women’s leadership in space sciences by developing a strategic leadership framework. Under this initiative Coventry University acts as the delivery partner.
- To promote a more equitable distribution of leadership opportunities and enable a workplace culture that recognises female leaders, this programme is underpinned by three foundational pillars:
- Intersectionality or understanding of different aspects of women’s identities
- Collaborative culturally sensitive approaches that respond to opportunities and challenges in India
- Using leadership theory from both social science and STEM to support female scientists to become more confident about their leadership abilities
Asia Power Index:

India ranked third in the annual Asia Power Index, released by an Australian think tank.
- Asia Power Index was launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018.
- It is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- It index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants
- The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection
- The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- The extent of a country’s diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
- A country’s overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators.
Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary:

A rarest of rare weather phenomenon- the collision of two cyclones- has been found to have caused flattening of thousands of trees in the Eturnagaram wildlife sanctuary in Mulugu district.
- Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary is located near the border of Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Telangana in the village of Eturnagaram, a tribal village in Mulugu district of Telangana.
- It is located 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- It was declared as a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by Hyderabad Nizam Government.
- It is spread over an area of around 806 sq. km.
- It has a water source called Dayyam Vagu, which separates the sanctuary into two parts.
- River Godavari also passes through it
- This sanctuary provides shelter to Tiger, Leopard, Panther, Wolf, Wild Dogs, Jackals, Sloth Bear, Chousingha, Black Buck, Nilgai, Sambar, Spotted Deer and Four Horned Antilope etc.
- The plethora of water in the sanctuary is attributed to the presence of reptiles like the famous Mugger crocodiles and snakes like the Cobra, Python and Krait.
- The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is situated inside the sanctuary.




