Today Current Affairs: 2nd April 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Demand Of President’s Rule In West Bengal:

Imposition of President’s rule in West Bengal is being demanded, following the gruesome incidents in Birbhum in which 10 people, including two children, were burnt alive.
- Article 356 of the Constitution of India gives the President of India the power to suspend state government and impose President’s rule of any state in the country if “if he is satisfied that a situation has arisen in which the government of the state cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution”.
- It is also known as ‘State Emergency’ or ‘Constitutional Emergency
- Upon the imposition of this rule, there would be no Council of Ministers.
- The state will fall under the direct control of the Union government, and the Governor will continue to be head the proceedings, representing the President of India.
- A proclamation imposing President’s Rule must be approved by both the Houses of Parliament within two months from the date of its issue.
- The approval takes place through simple majority in either House, that is, a majority of the members of the House present and voting.
- Initially valid for six months, the President’s Rule can be extended for a maximum period of three years with the approval of the Parliament, every six months.
- Under Article 356, President’s Rule is imposed if the President, upon receipt of the report from the Governor of the State or otherwise, is satisfied that a situation has arisen in which the government of the State cannot be carried on in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution.
World’s Biggest Electric Cruise Ship:

The largest electric cruise ship in the world has returned back to port in Yichang in central Hubei province, China after traveling up and down the Yangtze River for its maiden voyage.
- This cruise ship has been powered by a 7,500-kilowatt-hour massive-sized marine battery.
- This battery has been provided by Contemporary Amperex Technology, the No. 1 battery manufacturer for electric cars in the world.
- From the month of April 2022 this ship will be beginning commercial operations.
- This ship will mainly be used for the purpose of conducting sightseeing trips.
- The developer of this ship, China Yangtze Power has plans to use this electric ship as the starting point for expanding the marine electric vehicle market in China.
- The name of the ship is Yangtze River Three Gorges 1 and it is a 100 percent electric cruise ship that has been developed and built in China.
- Its main purpose will be to ferry passengers who will be going on sightseeing trips on the River Yangtze.
Bilateral Exercise ‘VARUNA-2022’:

The 20th edition of the Indian and French Navy bilateral exercise ‘VARUNA-2022’ is being conducted in the Arabian Sea.
- It has become a vital part of the India-France strategic bilateral relationship.
- The Indian and French Navies have been conducting bilateral maritime exercises since 1993. Since 2001, these exercises have been called ‘VARUNA’. This is an annual event.
- These interactions further underscore the shared values as partner navies, in ensuring freedom of seas and commitment to an open, inclusive Indo-Pacific and a rules-based international order.
- Other Indo-French Joint Exercises:
- Desert Knight-21 and Garuda (Air exercise)
- Shakti (Army exercise)
Digital Platform: FASTER

Chief Justice of India (CJI) launched the digital platform FASTER (Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records).
- The Supreme Court has also launched other programmes involving technology like Artificial Intelligence (AI) based portal ‘SUPACE’ in the judicial system aimed at assisting judges with legal research.
- eCourts Mission Mode Project is a pan-India Project, monitored and funded by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice, for the District Courts across the country.
- The objective of the project is to provide designated services to litigants, lawyers and the judiciary through ICT enablement of courts.
- FASTER Digital Platform is a digital platform to communicate interim orders, stay orders, bail orders etc., of the Supreme Court to authorities concerned through a secured electronic communication channel.
- There have been cases where jail inmates are not released despite bail orders passed by the Supreme Court due to delay in communication of such orders.
- So, it was needed to utilise information and communication technology tools for efficient transmission of court’s orders.
- It will help in preventing unnecessary arrests and custody of people even after the court had already granted them its protection.
- Ensure fundamental rights of personal liberty, life and dignity of the prisoners which is given under Article 21 of Constitution of India.
Two New Geological Heritage Sites:

Geological Survey of India (GSI) has identified two geological heritage sites in the Indian Himalayan Region of India.
- The sites identified are Siwalik Fossil Park, Himachal Pradesh and Stromatolite bearing Dolomite / Limestone of Buxa Formation of Buxa Formation, Sikkim.
- With inclusion of these two sites, there are 34 Geological Heritage Sites in India.
- Earlier, the GSI identified certain geological sites across the Northeast for promotion of geo-tourism.
Siwalik Fossil Park (Himachal Pradesh):
- The Siwalik Fossil park displays a rich collection of vertebrate fossils recovered from the Siwalik rocks of the area of Plio-Pleistocene age (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago).
- The deposition of Siwalik sediments took place in the narrow linear depression, called the ‘fore deep’, which started developing in front of the Himalayas since the inception of its uplift in the middle Miocene (23 million years to 2.6 million years ago).
Stromatolite bearing Dolomite / Limestone of Buxa Formation of Buxa Formation (Sikkim):
- This Geoheritage site at Mamley exposes lithounits of Buxa Formation, Daling Group of Proterozoic age (2.5 billion years to 541 million years ago).
- The dolostones (sedimentary rock) are profusely stromatolitic (Precambrian algal structures). This site provides one of the rare examples of early life in Sikkim Himalaya.
- The Precambrian is the earliest of the geologic ages, which are marked by different layers of sedimentary rock.
Geo-heritage Sites:
- Geo-heritage refers to the geological features which are inherently or culturally significant offering insight to earth’s evolution or history to earth science or that can be utilized for education.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) is the parent body which is making efforts towards identification and protection of geo-heritage sites/national geological monuments in the country.
Government Permitted Genome-Edited Plants:

The Government has allowed genome-edited plants without the cumbersome GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms) regulation at the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
- The government has exempted Site Directed Nuclease (SDN) 1 and 2 genomes from Rules 7-11 of the Environment Protection Act, thus allowing it to avoid a long process for approval of GM crops through the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC).
- The Institutional BioSafety Committee (IBSC) under the Environment Protection Act would now be entrusted to certify that the genome edited crop is devoid of any foreign DNA.
Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee:
- It functions under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- It is responsible for the appraisal of activities involving large-scale use of hazardous microorganisms and recombinants in research and industrial production from the environmental angle.
- The committee is also responsible for the appraisal of proposals relating to the release of genetically engineered organisms and products into the environment including experimental field trials.
- GEAC is chaired by the Special Secretary/Additional Secretary of MoEF&CC and co-chaired by a representative from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
Genome Editing:
- Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism’s Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA).
- These technologies allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome.
- Advanced research has allowed scientists to develop the highly effective Clustered Regularly Interspaced Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR) -associated proteins based systems. This system allows for targeted intervention at the genome sequence.
- This tool has opened up various possibilities in plant breeding. Using this tool, agricultural scientists can now edit the genome to insert specific traits in the gene sequence.
- Depending on the nature of the edit that is carried out, the process is divided into three categories — SDN 1, SDN 2 and SDN 3.
- Site Directed Nuclease (SDN) 1 introduces changes in the host genome’s DNA through small insertions/deletions without introduction of foreign genetic material.
- In SDN 2, the edit involves using a small DNA template to generate specific changes. Both these processes do not involve alien genetic material and the end result is indistinguishable from conventionally bred crop varieties.
- The SDN3 process involves larger DNA elements or full length genes of foreign origin which makes it similar to Genetically modified organisms (GMO) development.
AFSPA Withdrawn From Parts Of Three Northeast States:
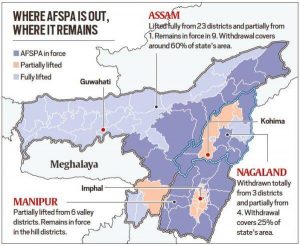
The Union Government has partially withdrawn the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA), 1958 from parts of three Northeast states— Assam, Nagaland and Manipur.
- Currently, AFSPA remains in force in parts of these three states as well as in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir.
- AFSPA gives sweeping powers to the armed forces.
- It allows them to open fire, even causing death, against any person in contravention to the law or carrying arms and ammunition.
- Also, it gives them powers to arrest individuals without warrants, on the basis of “reasonable suspicion”, and search premises without warrants.
- It can be imposed by the Centre or the Governor of a state, on the state or parts of it, after these areas are declared “disturbed’’ under Section 3.
- The Act was amended in 1972 and the powers to declare an area as “disturbed” were conferred concurrently upon the Central government along with the States.
- Currently, the Union Home Ministry issues periodic “disturbed area” notification to extend AFSPA only for Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The notification for Manipur and Assam is issued by the State governments.
- Tripura revoked the Act in 2015 and Meghalaya was under AFSPA for 27 years, until it was revoked by the MHA from 1st April 2018.
New India Literacy Programme:

The Union of India has approved a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, namely, “New India Literacy Programme (NILP)”.
- The NILP has been approved for the next five financial years (2022-27) in order to integrate all the aspects of adult education with the National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP).
- The Education ministry has chosen to use ‘Education for All’ rather than ‘Adult Education,’ since the previous terminology was not applicable to non-literates aged 15 and above.
- It aims to support the States and Union Territories in promoting literacy among non-literates in the age group of 15 and above.
- It will cover across the country covering 5 crore non-literates during the implementation period from 2022-23 to 2026-27.
- The scheme has been approved with a financial outlay of Rs.1037.90 crore including Central share of Rs.700.00 crore and State share of Rs.337.90 crore.
Features of the NILP are:
- Involvement of school students, pre-service students of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs), school teachers, Anganwadi and ASHA workers.
- School to be unit for implementation of the scheme.
- Use of ICT and online implementation of the scheme through ‘Online Teaching Learning and Assessment System’ (OTLAS) material and resources through digital modes, viz, TV, radio, cell phone-based free/open-source Apps/portals, etc.
The scheme will be implemented through volunteerism through online mode.
- The training, orientation, workshops of volunteers, may be organized through face-to-face mode. All material and resources shall be provided digitally.
- School will be Unit for implementation of the scheme.
- Schools to be used for conducting surveys of beneficiaries and Voluntary Teachers.
PM Gati Shakti Entails The Geospatial Mapping:

PM Gati Shakti entails the geospatial mapping of everything in the country, different layers of maps which talk to each other, leading to integrated planning, with better optimization of time and cost.
- Geospatial technology uses tools like GIS (Geographic Information System), GPS (Global Positioning System) and Remote Sensing for geographic mapping and analysis.
- These tools capture spatial information about objects, events and phenomena (indexed to their geographical location on earth, geotag).
- The location data may be Static or Dynamic.
- Static location data include position of a road, an earthquake event or malnutrition among children in a particular region while dynamic location data include data related to a moving vehicle or pedestrian, the spread of an infectious disease etc.
- The technology may be used to create intelligent maps to help identify spatial patterns in large volumes of data.
- The technology facilitates decision making based on the importance and priority of scarce resources.
PM GatiShakti:
- It is a digital platform that connects 16 ministries — including Roads and Highways, Railways, Shipping, Petroleum and Gas, Power, Telecom, Shipping, and Aviation.
- It aims to ensure holistic planning and execution of infrastructure projects.
- The portal will offer 200 layers of geospatial data, including on existing infrastructure such as roads, highways, railways, and toll plazas, as well as geographic information about forests, rivers and district boundaries to aid in planning and obtaining clearances.
- The portal will also allow various government departments to track, in real time and at one centralised place, the progress of various projects, especially those with multi-sectoral and multi-regional impact.
MSP For Raw Jute For 2022-23 Season:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for Raw Jute for 2022-23 season.
- The approval is based on recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices.
- The announced MSP of raw jute for 2022-23 season is in line with the principle of fixing the MSP at a level of at least 1.5 times all India weighted average cost of production as announced by the Government in the Budget 2018-19.
- It assures a minimum of 50 percent as margin of profit.
- It is one of the important and progressive steps towards ensuring better remunerative returns to the jute growers and to incentivize quality jute fibre.
- MSP is the rate at which the government buys grains from farmers.
- The MSP is the rate at which the government purchases crops from farmers, and is based on a calculation of at least one-and-a-half times the cost of production incurred by the farmers.
- The Union Budget for 2018-19 had announced that MSP would be kept at levels of 1.5 the cost of production.
- The MSP is fixed twice a year on the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which is a statutory body and submits separate reports recommending prices for kharif and rabi seasons.
RAMP Scheme:

The Union Cabinet approved a USD 808 million or Rs 6,062.45 crore, World Bank assisted programme on “Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance” (RAMP).
- RAMP is a new scheme and would commence in FY 2022-23.
- “Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance” (RAMP) is a World Bank assisted Central Sector Scheme.
- It has been launched to support various Resilience and Recovery Interventions of the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME).
- In addition to building the MoMSME’s capacity at the national level, the RAMP program will seek to scale up implementation capacity and MSME coverage in States.
- The programme aims at improving access to market and credit, strengthening institutions and governance at the Centre and State, improving Centre-State linkages and partnerships, addressing issues of delayed payments and greening of MSMEs.
- RAMP will function as a:
- ’Policy Provider’’ through the enhanced capacity for evidence-based policy and program design, to enable the delivery of more effective and cost-efficient MSME interventions to improve competitiveness and business sustainability.
- “Knowledge Provider” through bench-marking, sharing and demonstrating best practices/success stories by leveraging international experiences.
- “Technology Provider” by providing access to high-end technology resulting in the digital and technological transformation of MSMEs through state of art Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics, Internet of things (IoT), Machine Learning etc.
- RAMP was formulated and proposed by the Government of India, for strengthening MSMEs in line with the recommendations made by U K Sinha Committee, KV Kamath Committee and Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (PMEAC).




