Today’s Current Affairs: 31st March 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Carriage of Goods by Sea Bill, 2024 : Passed In Lok Sabha

The Lok Sabha recently passed the Carriage of Goods by Sea Bill, 2024, paving the way for the enactment of modern maritime law in the country.
- Carriage of Goods by Sea Bill, 2024 will replace the colonial-era Indian Carriage of Goods by Sea Act, 1925.
- The Act establishes the responsibilities, liabilities, rights, and immunities in case of goods carried from a port in India to another port in India or any other port in the world.
- The Act is in conformance with the International Convention for the Unification of Certain Rules of Law relating to Bills of Lading of August 1924 (Hague Rules) and subsequent amendments to it.
- The bill retains all provisions of the act.
- The bill is aimed at consolidating laws related to port management, promoting integrated port development, and enhancing the ease of doing business in the maritime sector.
- It seeks to optimize the utilisation of India’s vast coastline by establishing and empowering State Maritime Boards to ensure effective management of ports other than major ports.
- It also proposes the formation of the Maritime State Development Council to foster structured growth and development of the port sector.
- It also addresses critical aspects such as pollution control, disaster management, emergency response, security, safety, navigation and data management at ports.
- It seeks to ensure India’s compliance with international obligations and maritime conventions.
- This bill includes provisions for port conservation and introduces adjudicatory mechanisms for resolving port-related disputes efficiently.
Protests Against Pollution In The Ulhas River : Maharashtra

Taking serious note of citizen activists’ protests against pollution in the Ulhas River, the Maharashtra State Government during a special meeting recently, decided to remove water hyacinth from the Ulhas River within the next 15 days.
- Ulhas River is one of the west flowing Rivers in Maharashtra falling into the Arabian Sea.
- It rises from the Sahyadri hill ranges in the Raigad district of Maharashtra at an elevation of 600 meters above M.S.L.
- The total length of this west-flowing river from its origin to its outfall into the Arabian Sea is 122 km.
- The boundary of the basin consists of the main Sahyadri hills on the east, westerly offshoots on the north and south and on the west, a narrow opening at the end leading to the sea.
- The Ulhas drains an area of 4,637 sq km, which lies completely in Maharashtra. The Thane, Raigad, and Pune districts fall in the basin.
- The important tributaries of the Ulhas River are Pej, Barvi, Bhivapuri, Murbari, Kalu, Shari, Bhasta, Salpe, Poshir and Shilar.
- The Kalu and Bhasta are the major right bank tributaries, which together account for 7% of the total catchment area of Ulhas.
- The estuary of Ulhas houses several historical ports of Kalyan, Kopri, and Shurparaka.
Chicken’s Neck Corridor:
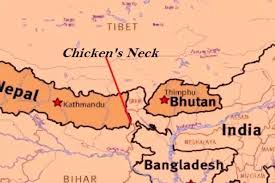
Bangladesh has invited China to invest in a river conservation project close to the ‘Chicken’s Neck’ corridor – the link between India’s mainland and its seven northeastern States.
- ‘Chicken’s Neck’, also known as the Siliguri Corridor, a narrow strip of land in West Bengal that connects India’s northeastern states to the rest of the country.
- The corridor is situated in the northern part of West Bengal, spanning approximately 22 kilometres at its narrowest point.
- It is flanked by Nepal to the west, Bhutan to the north, and Bangladesh to the south.
- It links the North-eastern Region (NER), comprising eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura—to mainland India.
Operation Brahma:

After a devastating earthquake ravaged Myanmar recently, India initiated its relief and rescue efforts in the country under the banner ‘Operation Brahma’.It is India’s humanitarian mission launched in response to the devastating 7.7-magnitude earthquake that struck Myanmar on March 28, 2025.
- The massive earthquake that devastated Myanmar and neighbouring Thailand killed over 1,600 people and caused widespread destruction.
- The large-scale humanitarian mission includes rescue teams, medical aid, and relief supplies.
- The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) deployed an 80-member team equipped with concrete cutters, drill machines, plasma cutters, and other rescue tools.
- The Indian Army has mobilised a specialised medical task force to provide urgent humanitarian assistance.
- The Indian Army dispatched a specialized 118-member medical team from the elite Shatrujeet Brigade Medical Responders.
- As part of the mission, the Indian Army will set up a 60-bed Medical Treatment Centre to provide immediate care to those injured in the disaster.
- The facility will be equipped to handle trauma cases, emergency surgeries, and essential medical services to support Myanmar’s strained healthcare system.
- Two Indian naval ships, INS Satpura and INS Savitri, were dispatched carrying 40 tonnes of humanitarian aid to the port of Yangon.
Kasampatty Sacred Grove:

The Tamil Nadu government recently notified Kasampatty (Veera Kovil) sacred grove as a Biodiversity Heritage Site.
- The Kasampatti Sacred Grove, also known as Veera Kovil Sacred Grove, is a revered ecological and cultural site located in Kasampatti village, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu.
- Spanning 4.97 hectares near the Alagarmalai Reserve Forest, this grove is enveloped by lush mango plantations, enhancing its natural beauty and fertility.
- It hosts an impressive variety of species – 48 plant species, 22 shrubs, 21 lianas (woody vines), and 29 herbs.
- It also shelters more than 12 species of birds, along with small mammals, reptiles, and numerous insects, highlighting the grove’s genetic richness.
- The Tamil Nadu government has notified Kasampatti Sacred Grove as the state’s second Biodiversity Heritage Site under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
Future Circular Collider:
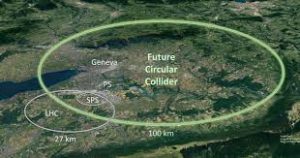
Plans for the Future Circular Collider (FCC), a proposed $30 billion project by CERN, have led to significant divisions within the scientific community.
- Project scope is a 91 km circular tunnel beneath the Swiss-French border, designed to accelerate and collide particles at unprecedented energies.
- Purpose is to generate Higgs bosons in large numbers (Phase 1, ~2040) and later to collide protons at extreme energies (Phase 2, ~2070).
- Estimated cost: $30 billion (initial), with long-term funding implications for the next decades.
- Supporters: CERN leadership, senior physicists like Fabiola Gianotti and Mark Thomson, claim it will be the most powerful instrument to study nature.
- Many physicists fear the project will drain funds, limiting investment in other scientific advancements.
Amur Tigers:

A recent study published in Oryx highlights the alarming rise in tiger roadkill incidents, which could impact their long-term survival.
- Scientific name: Panthera tigris altaica
- Common name: Amur Tiger / Siberian Tiger
- IUCN red list status: Endangered
- Estimated 265–486 (2022) in Russia, with a small number in China & possibly North Korea
- Primarily in eastern Russia’s birch forests, with some presence in China and North Korea
- Diet: Carnivore – Preys on elk, wild boar, and other ungulates
- Size: 10.75 feet in length, weighing up to 660 pounds
- Lifespan: 10-15 years in the wild, up to 20 years in captivity
- Unique adaptations: Thick fur, large size and a lighter coat color for cold climates
Frankincense-Producing Trees : Risk Of Extinction

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has issued a warning that Frankincense-producing trees (Boswellia species) are at risk of extinction.
- Five species on Socotra Island (Yemen) have moved from Vulnerable to Endangered, one species is now Critically Endangered and three others have been assessed as Critically Endangered for the first time.
- Frankincense is an aromatic resin derived from trees of the Boswellia genus.
- It has been historically valued for use in incense, perfumes, and traditional medicine.
- It was one of the three gifts (Gold, Frankincense, and Myrrh) presented to Jesus by the Magi, as mentioned in the Bible.
- Goats graze on young saplings, preventing tree regeneration.
- Frequent cyclones, flash floods, and landslides (2015, 2018) have damaged and uprooted trees.
- Prolonged droughts hinder sapling growth.
- Excessive tapping for resin extraction weakens trees and reduces seed production.
- Lack of effective protective measures like fencing and regulated harvesting has worsened the crisis.
Geostationary Transfer Orbit:

ISRO’s Breakthrough in Semi-Cryogenic Engine Development for LVM3
- ISRO has achieved a breakthrough in developing a semi-cryogenic engine (liquid oxygen/kerosene engine) with a high thrust of 2,000 kN (kilonewtons).
- The first successful hot test of the Engine Power Head Test Article (PHTA) was conducted at the ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
- This engine will be used in the semi-cryogenic booster stage of the Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3), enhancing India’s space launch capabilities.
- A Transfer Orbit is used to move a satellite from one circular orbit to another in a fuel-efficient manner.
- The Hohmann Transfer Orbit is a commonly used maneuver for such transfers.
- Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO is a highly elliptical orbit with:
- Perigee (closest point to Earth): 180-200 km above Earth’s surface.
- Apogee (farthest point from Earth): ~35,900 km (near geostationary orbit).
Gene Bank:

Government to set up second National Gene Bank to ensure future food security.
- The Government of India has announced the establishment of the Second National Gene Bank to conserve 10 lakh crop germplasm for ensuring future food and nutritional security.
- This initiative is part of the “Investing in Innovations” theme of the Union Budget 2025-26.
- A Gene Bank is a storage facility that preserves seeds, pollen, and plant tissues to protect plant species from extinction and ensure their availability for future use.
- These stored samples help in crop breeding, scientific research, and biodiversity conservation.
- Gene banks play a crucial role in maintaining genetic diversity, essential for climate resilience and food security.
- India’s First National Gene Bank was established in 1996 by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research – National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (ICAR-NBPGR) in New Delhi.
- Second-largest Gene Bank globally after the Svalbard Global Seed Vault in Norway.
- Houses 4,71,561 accessions of 2,157 species.
- Provides plant genetic resources for use by both the public and private sectors involved in crop improvement and genetic conservation.
BIMSTEC : Indian Prime Minister will visit for 6th BIMSTEC Summit
The Indian Prime Minister will visit Bangkok, Thailand, from April 3-4, 2025, to participate in the 6th BIMSTEC Summit and hold discussions with the Thai PM.BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) is a regional multilateral organization that connects South Asia and Southeast Asia. Established through the Bangkok Declaration in 1997, it promotes economic and social progress in the region.
Member Countries :
- South Asia: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka.
- Southeast Asia: Myanmar, Thailand.
IAEA Backs India’s NSG Bid via MECR:
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has backed India’s entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), a key body within the 4 major Multilateral Export Control Regimes (MECR).MECR are voluntary frameworks aimed at preventing the proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMDs) and restricting the transfer of sensitive technologies.India is a member of 3 out of the 4 MECRs, except the NSG.They function independently of the United Nations (UN). Their regulations apply only to members, and participation is voluntary
India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) Rises:
India’s current account deficit (CAD) widened to $11.5 billion (1.1% of GDP) in Q3 FY25 (Oct-Dec 2024) due to a higher merchandise trade deficit, according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). However, CAD moderated from $16.7 billion (1.8% of GDP) in Q2 FY25. Foreign exchange reserves have increased by $311 billion since December 2018, marking the largest jump under any RBI Governor. The balance of payments (BoP) saw a depletion of $37.7 billion, contrasting with an accretion of $6 billion in Q3 FY24. The full-year CAD for FY25 is expected to be around 0.8% of GDP.
Light Fishing:
Despite being banned in India’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) since 2017, light fishing continues unchecked, damaging marine biodiversity.Centre has banned light fishing in all coastal states in 2017.A fishing method using high-intensity artificial lights (often powered by generators) to attract fish to the water surface during night operations.Predominantly used by mechanised trawlers, especially for catching squid, sardines, and juvenile fish.LED light fishing usually takes place between December and February, a season which sees meagre catches.LED or halogen lights are suspended over the water or placed underwater. The bright light disturbs the fish’s natural orientation and attracts entire shoals. Fish, including juveniles, are easily netted, increasing bycatch and unsustainable harvest.
SBI Chief CS Setty Appointed as Chairman of Indian Banks Association:
The Indian Banks Association (IBA), the apex body representing the banking sector in India, has elected Challa Sreenivasalu Setty, the Chairman of State Bank of India (SBI), as its new chairman for the upcoming fiscal year. Setty will lead the association until the next Annual General Meeting (AGM). The appointment was announced after the IBA managing committee meeting held on March 28, 2025.
Steve Waugh Appointed to Centre for Australia-India Relations Advisory Board:
Former Australian cricket captain Steve Waugh has been appointed to the Centre for Australia-India Relations Advisory Board, as announced by Australian Minister for Foreign Affairs, Penny Wong. This appointment highlights Waugh’s long-standing contributions to fostering ties between Australia and India, particularly in the fields of sports, culture, and philanthropy.
UNESCO Releases ‘Education and Nutrition: Learn to Eat Well’ Report:
UNESCO released the report “Education and Nutrition: Learn to Eat Well” during the ‘Nutrition for Growth’ event hosted by France on March 27-28, 2025. The report highlights concerns regarding the nutritional quality of school meals worldwide and urges governments to improve food standards in schools.As of 2024, approximately 47% of primary school pupils worldwide received school meals. However, UNESCO’s findings indicate that many of these meals lack adequate nutrition. The organization stresses that improving the quality of school meals is crucial for reducing child undernourishment and enhancing academic performance. Studies suggest that nutritious meals can increase school enrolment and attendance rates
37th Kathak Mahotsav 2025:
The 37th Kathak Mahotsav 2025, organized by Kathak Kendra, New Delhi, a constituent unit of Sangeet Natak Akademi, concluded successfully in New Delhi. This six-day festival was a landmark event, featuring the world’s first-ever Kathak Literary Festival along with seminars, exhibitions, and captivating dance performances. The festival showcased all major Kathak gharanas—Lucknow, Jaipur, Banaras, and Raigarh—through performances by distinguished artists.
MGNREGS Wage Hike for 2025-26:
The Government of India has notified an increase in wage rates under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) for the financial year 2025-26. The hike ranges from 2.33% to 7.48%, with wages increasing by Rs 7 to Rs 26 per day depending on the state. This marks the first time NREGS wages have reached Rs 400 per day in any state, with Haryana recording the highest increase.
Gudi Padwa 2025:
Gudi Padwa is a popular festival celebrated in Maharashtra. It marks the beginning of the Marathi New Year. The festival also welcomes the harvest season and the arrival of spring. According to the Hindu lunisolar calendar, Gudi Padwa falls on the first of the Chaitra month. In 2025, Gudi Padwa will be celebrated on Sunday, 30 March.




