Today’s Current Affairs: 4th July 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Sawalkote Hydropower Project:

Months after India put the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) on hold, it is now moving to revive a long-stalled Sawalkote Hydropower Project on the Chenab, first envisioned six decades ago but held back by the treaty with Pakistan.
- Sawalkote Hydropower Project is a 2,185 megawatt (MW) run-of-the-river hydroelectric plant proposed on the Chenab River in the Ramban District of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It will be the largest hydroelectric project in the Union Territory and one of the biggest in North India.
- The project was first conceptualised in the 1980s and revised several times due to environmental and technical concerns.
- The project, to be executed by National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) Ltd in collaboration with Jammu and Kashmir State Power Development Corporation Limited (JKSPDC), is estimated to cost ₹22,704 crore
- The project would feature a 5-metre roller-compacted concrete gravity dam.
- It is expected to generate over 7,000 million units of electricity annually.
- It is expected to enhance power availability in the Union Territory, especially during winters when electricity shortages are frequent.
- It also has the potential to turn J-K into a power-surplus region, creating scope for exporting surplus energy to the national grid.
- By regulating the flow of the Chenab River, the Sawalkote project could contribute to flood mitigation downstream, while also ensuring better water management for agriculture and domestic use.
American singer Justin Timberlake Battling with Lyme Disease:
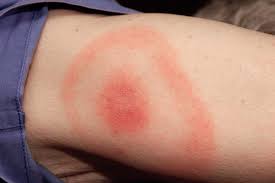
American singer Justin Timberlake has announced that he was battling Lyme disease during his recently wrapped up world tour.
- Lyme Disease is a bacterial infection that can be spread to humans by infected ticks.
- It is caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi.
- It primarily affects the skin, nervous system, heart and joints.
- It was named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, United States, where it was first identified in children in 1976.
- It is most commonly reported in North America, Europe and some parts of Asia.
- It’s also known as Lyme borreliosis.
- It’s transmitted (spread) to humans through a tick bite.
- Not all tick bites cause Lyme disease.
- Only deer ticks (also called black-legged ticks) can spread the bacteria that cause Lyme disease.
- These ticks are commonly found in wooded or grassy areas worldwide, particularly during warmer months.
- It cannot spread between humans, from pets to humans, through air, food, water, or lice, mosquitoes, fleas, and flies also do not transmit it.
- Lyme disease occurs in stages. The signs and symptoms of each stage can overlap.
- Typical symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash called erythema migrans.
- Untreated Lyme disease can cause severe arthritis and damage the heart and nervous system.
- Most cases are treatable with antibiotics although recovery can take time, especially for those who are left undiagnosed in the early stages.
- Even after treatment, some symptoms may linger.
HQ-16 Missile:

The United States military publicly unveiled a mockup of a Chinese HQ-16 surface-to-air missile system, drawing attention at this year’s Experimental Aircraft Association ‘AirVenture Show’ in Oshkosh, Wisconsin.
- The HQ-16, known by its NATO designation CH-SA 16, is a medium-range Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system developed by China and based heavily on Russia’s Buk missile family.
- It is designed to engage enemy aircraft, cruise missiles, helicopters, and unmanned aerial vehicles.
- HQ-16 features a vertical launch system, giving it 360-degree coverage and the capability to fire in a complicated geographical environment.\
- The missile system is mounted on a Chinese-designed 6×6 high mobility chassis instead of tracked platforms, providing ease of maintenance and better road mobility.
- Each launch vehicle carries up to 6 missiles.
- The missile weighs 650 kg, has a length of 5.2 m and a diameter of 0.34 m.
- It can intercept flying aerial targets at altitudes of 15 km to 18 km.
- The maximum interception range for aircraft is 40 km, between 3.5 km and 12 km for cruise missiles flying at 300 m/s.
- The missile guidance system comprises inertial guidance and semi-active radar homing at the terminal phase.
De-notified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Tribes:

There is a call for the establishment of a permanent national commission for Denotified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Tribes.
- Denotified Tribes (DNT) also known as Vimukta Jati, are the tribes that were listed originally under the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871 as criminal tribes.
- Once a tribe becomes “Notified” as a criminal, all its members were required to register with the local magistrates, failing which they would be charged with a ‘crime’ under the Indian Penal Code.
- After Independence, this Act was repealed in 1952, and the communities were “denotified”, hence the name.
- Nomadic Tribes are the communities who usually do not have land and move from one place to another for livelihood.
- The DNT/NT/SNTs are among the most neglected, marginalised, and economically deprived communities.
- Historically, these communities never had access to private land or home ownership and used forests and grazing lands for their livelihood and residential use.
- In India, roughly 10 percent of the population is Denotified and Nomadic.
- While the number of Denotified Tribes is about 150, the population of Nomadic Tribes consists of about 500 different communities.
- In 2014, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment constituted a National Commission for DNT/NT/SNTs under the chairmanship of Bhiku Ramji date for a period of three years-
- to prepare a State-wise list of castes belonging to DNT/NT/SNTs
- to suggest appropriate measures in respect of Denotified and Nomadic Tribes that may be undertaken by the Central Government or the State Government.
- In 2017, the commission prepared draft lists of DNT/NT/SNTs.
- Based on the Commission’s recommendations, the ministry constituted the Development and Welfare Board for Denotified, Nomadic and Semi-Nomadic Communities (DWBDNCs) in 2019.
- The Board has been mandated to formulate and implement welfare and development programmes for these communities.
- The Renke Commission (2008) was earlier commissioned to identify and list the DNT communities.
Krasheninnikov Volcano:

The eruption of the Krasheninnikov volcano was recently recorded for the first time.The Volcano erupted on 2 August 2025, three days after a nearby magnitude 8.8 earthquake. Ash emissions reached an altitude of 20,000 ft.
- Krasheninnikov Volcano is an active complex volcano located in the Eastern Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia.
- The Kamchatka Peninsula lies along the Pacific “Ring of Fire.”
- There are 114 volcanoes on the Kamchatka Peninsula that have erupted during the Holocene Epoch (approximately 12,000 years ago to the present).
- Krasheninnikov is a stratovolcano and reaches a height of 1,886 meters.
- The volcano is located in a collapsed caldera.
- It is made up of two eruptive cones in a 9 km wide caldera.
- The southern cone of Krasheninnikov contains a crater 800 m wide and 140 m deep.
- Its last eruption took place about 400 or 600 years ago.
Apna Ghar Initiative:

The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas recently launched an ambitious initiative named ‘Apna Ghar’ aimed at improving truckers’ long-haul journeys across the country.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India.
- It aims to provide comfortable and hygienic resting spaces for truckers across major highways in the country.
- As of July 1, 2025, a total of 368 ‘Apna Ghar’ units with 4,611 beds have been set up by Public Sector Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) at retail fuel outlets along national and state highways.
- The facilities at ‘Apna Ghar’ include:
- Dormitories (10-30) beds
- Restaurants/Dhabas
- Self-cooking areas
- Clean toilets
- Dedicated bathing areas (Houdas)
- Purified drinking water facilities
- Tech Integration: ‘Apna Ghar’ mobile application introduced for reservations, reviews, and driver interaction.
- Public-Private Execution: Developed and overseen by OMCs at retail fuel outlets.
- User-Focused Design: Tailored to the requirements of truckers, guided by their feedback and insights from mobile app data analysis.
PM National Dialysis Programme:

The Government of India has significantly expanded the reach of the Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme (PMNDP) and it is now operational across all 36 States and Union Territories, covering 751 districts.
- It was rolled out in 2016 to provide dialysis services free of cost to Below Poverty Line (BPL) beneficiaries at the district hospitals in the country.
- It is being implemented under the National Health Mission (NHM) to provide free dialysis services to patients suffering from end-stage kidney failure in Public Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- The programme supports both Haemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis services.
- Under this initiative the PMNDP portal was launched which will integrate all the dialysis centres operational in the state under NHM and facilitate building of renal registry and ensuring portability within the state (One State One Dialysis) and later throughout the country (One Nation-One Dialysis).
- The NHM provides financial assistance to States and UTs for establishing and operating dialysis centres to ensure equitable access to kidney care services for all, regardless of geography.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority:

The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) is in the final phase of testing its Integrated Portal, a unified digital platform designed to streamline claim processes and enhance accessibility for both investors and companies.
- The Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) was established in 2016 under the Companies Act, 2013.
- It manages the Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF) and promotes investor awareness and financial protection.
- It makes refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, matured deposits/debentures etc. to investors and promotes awareness among investors.
- It is dedicated to safeguarding investor interests by facilitating the return of unclaimed shares and dividends and advancing financial literacy nationwide.
- Through flagship initiatives such as Niveshak Didi, Niveshak Panchayat, and Niveshak Shivir, IEPFA empowers individuals to make informed financial choices and fosters a financially aware citizenry.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- The IEPF consists of amounts that remained unclaimed for 7 years, including:
- Unpaid dividends,
- Application money due for refund,
- Matured deposits and debentures,
- Interest on investments from the fund,
- Grants or donations received from the government or other entities
Alpine musk deer:

A Central Zoo Authority report reveals a mix-up in identifying the Alpine musk deer for conservation breeding, mistakenly initiating programs for the Himalayan musk deer instead.
- The Alpine musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster) is a musk deer species found only in Asia.
- It is not a true deer, but rather its family is closely related to Bovidae, the group that contains antelopes, bovines, sheep, and goats.
- It is generally solitary and a crepuscular animal.
- It inhabits coniferous and deciduous forestsin the mountain regions at elevations of 3,000–5,000 m.
- It is a ruminant herbivore, foremost a browser and feeds mainly on forbs, grasses, moss, lichens, and shoots, leaves and twigs of shrubs.
- It is mainly found in India, Nepal, Bhutan and China.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- Threats: The main threat to the Alpine musk deer is poaching for its musk, which is used in cosmetic products.
Mount Lewotobi Laki Laki:

Mount Lewotobi Laki Laki, one of Indonesia’s most active volcanoes erupted, spewing ash up to 18 km high and covering nearby villages with volcanic debris.
- Mount Lewotobi is located on the Indonesian island of Flores. It lies along the Pacific “Ring of Fire,” known for intense seismic activity.
- The volcano is part of a twin-peaked system called Lewotobi, meaning “husband and wife.” It consists of the Lewotobi Lakilaki (man) and Lewotobi Perempuan (woman) stratovolcanoes, whose summit craters are located less than 2 km apart on Flores Island.
- The Ring of Fire, or Circum-Pacific Belt, is a 40,000 km zone around the Pacific Ocean marked by intense seismic and volcanic activity. It hosts 75% of Earth’s volcanoes (over 450) and 90% of earthquakes.
- This eruption ranks among Indonesia’s largest since 2010, when Mount Merapi erupted, killing over 350 people and displacing hundreds of thousands.
- Merapi, located in Yogyakarta, is Indonesia’s highly active and known for frequent eruptions and deadly pyroclastic flows (fast-moving avalanches of hot gas and volcanic debris) posing major hazards over the past two decades.
Right to Repair in India:
India accepted a proposal to introduce a Repairability Index for electronics. This marks a key step towards making the Right to Repair a consumer right. However, experts warn that India’s informal repair economy—rich in tacit, generational knowledge—is being neglected in digital and AI policy frameworks. Right to Repair’ refers to the legal right of consumers to repair and modify their own products or access affordable third-party services.
Global Trend: EU mandates access to spare parts and manuals; U.S. states and the UN SDG 12 also push for repair-based sustainability. Department of Consumer Affairs launched a Right to Repair portal (2023), covering electronics, autos, and farm tools.
Rising bird deaths near turbines:
India added 3.5 GW of wind power in early 2025, marking 82% annual growth, but a Wildlife Institute of India study raised concerns over rising bird deaths near turbines in Rajasthan’s Thar Desert, sparking debate on the ecological impact of renewables.
Findings from the WII Study (Thar Desert):
- Conducted over a 3,000 sq. km area in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan.
- Studied 90 wind turbines and found 124 bird carcasses.
- Estimated 4,464 bird deaths per 1,000 sq. km per year.
- In control sites with no turbines, no bird deaths were recorded.
- Critically endangered species like the Great Indian Bustard are at risk.
- The study found raptors to be the most affected bird group.
- Collisions with both wind turbine blades and associated power lines were major causes.
RBI Approves Merger of New India Co-operative Bank with Saraswat Bank:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved the merger of New India Co-operative Bank with Saraswat Co-operative Bank, the largest urban co-operative bank in the country. The merger will officially take effect from August 4, 2025.
Under the approved Scheme of Amalgamation,
- Saraswat Bank will take over all assets and liabilities of New India Co-operative Bank.
- All branches of New India Co-operative Bank will now function as Saraswat Bank branches.
- Customers and depositors of New India Co-operative Bank will be treated as customers of Saraswat Bank, with their interests fully protected.
- This step is expected to provide greater stability, enhanced services, and stronger financial backing for customers of the merged entity.
Operation Akhal:
Operation Akhal, a joint anti-terror operation in Kulgam district of Jammu and Kashmir, entered its third day, with at least one terrorist killed amid continued firefight by Indian security forces. A high-intensity counter-terrorism operation launched in the Akhal Khulsan forest area of Kulgam, Jammu & Kashmir. Launched by: Jointly conducted by the Indian Army’s Chinar Corps, Jammu & Kashmir Police, and the Special Operations Group (SOG). Aim is to neutralize 3–5 terrorists based on intelligence inputs, tighten internal security, and dismantle local terror modules.
Matri Van Initiative:
The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, along with the Union Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs launched the ‘Matri Van’ initiative.It is an initiative under the ‘Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam’ Programme of Government of India.It is a theme based urban forest dedicated to nurturing generations through mother-nature-inspired green efforts – would be developed in an area of 750 acres in the Aravalli Hill area. It is envisioned as a unique ecological and cultural space that will contribute to biodiversity, public well-being, and urban sustainability. This vision would be achieved through a multi-stakeholder collaboration involving CSR partners, Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs), NGOs, multinational corporations (MNCs), school children and government organizations. The main components of the ‘Matri Van’ would include removal of existing bushes like Kabuli Kikar (Prosopis juliflora) and plantation of Dhak/Amaltash Trees along Gurugram-Faridabad Road, while creating theme-based Plantation Groves to restore local ecology in the Aravallis. It would further include nature trails, cycle track, yoga places, sitting places/gazebos, public facilities, parking at four corners, treated water irrigation system/misting/sprinkling, waterbodies at selected locations for conservation of water and to check urban flooding.
Polar Anticyclone:
Chile and Argentina ranked among the coldest places on Earth, outside the polar regions as polar anticyclone grips region.
- Polar Anticyclone is a wind system associated with a region in which high atmospheric pressure develops over or in the vicinity of the poles.
- The polar anticyclone is strongest in the cold season of the year.
- The Siberian anticyclone is an example of a polar anticyclone, as is the high-pressure area that forms over Canada and Alaska during the winter.
- Polar anticyclones are created by the cooling of surface layers of air.
- This cooling causes the air near the surface to become denser and, at the same time, causes an inflow of air at high levels to replace the denser, sinking air.
- These processes increase the mass of air above the surface, thus creating the anticyclone.
- The weather within the central regions of these anticyclones is typically clear and quite cold.
- The strength of polar anticyclones is greatest near the Earth’s surface.
- It frequently migrate eastward and equator ward in the winter season, bringing cold waves to warmer latitudes. In the summer they provide cool, dry weather as they move toward the Equator.
- The boundary separating the cold polar air from the warmer air is called the polar front, and along this frontal surface the extratropical cyclones, or wave cyclones, form. See also front.
Ham Radio:

Indian astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla interacted with the country’s students using a ham radio from the International Space Station (ISS).
- Amateur radio, popularly known as ham radio, is a licensed radio service that relies on radio waves for establishing communication.
- Ham radio service is largely deployed for educational and knowledge purposes, for emergency or SOS communication.
- Using a dedicated frequency, a transceiver and an antenna, communication can be set up between two licensed hams by trained ham operators.
- The communication can be hyper-local, global, and in space. In India, any individual above the age of 12 is permitted to operate a ham radio.
- In India, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology issues these licences.
- Even though the technology to establish communications has advanced, the radio remains one of the most reliable and stable modes of communication.
- It is effective and an alternate medium of establishing communication.
- Previously, there have been instances when ham radio came to the rescue when traditional communication lines broke down, either due to man-made scenarios (like wars) or natural disasters such as earthquakes, cyclones, and floods.
- In India, ham radio was used for making emergency contacts during the Bhuj earthquake (2001), the Indian Ocean tsunami (2004), the floods of Uttarakhand (2013) and more such calamities.
Apache AH-64E Attack Helicopter:

The Indian Army is set to receive the first batch of long-awaited Apache AH-64E attack helicopters from the US soon.
- Apache AH-64E Attack Helicopter is the world’s most advanced multi-role combat helicopter.
- It is widely used for advanced reconnaissance, precision strikes, and close air support missions globally.
- Country of Origin: United States
- Manufacturer: Boeing
- It is also known as the Apache Guardian.
- The AH-64E attack helicopter is the latest version of the Apache used by the US Army.
- It is designed and equipped with open systems architecture to incorporate the latest communications, navigation, sensor, and weapon systems.
- It has greater thrust and lift, joint digital operability, improved survivability, and cognitive decision aiding.
- The AH-64E includes a new integrated infrared laser that allows for easier target designation and enhanced infrared imagery that blends infrared and night vision capabilities.
- Its primary armament includes the 30 mm M230 Chain Gun, which delivers high rates of fire with remarkable accuracy.
- The helicopter can carry up to 16 AGM-114 Hellfire missiles, renowned for their effectiveness against armored and fortified targets.
- For additional versatility, the aircraft supports Hydra 70 unguided rockets and air-to-air missiles such as the Stinger, extending its combat engagement options across various mission profiles.
- Apache for Indian defence forces:
- The Indian Air Force has a fleet of 22 AH-64E Apache attack helicopters, and in 2020, Boeing signed an agreement with the Government of India for the acquisition of six more Apache helicopters for the Indian Army.
Television Rating Point : Amendment

The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting recently proposed amendments to the Policy Guidelines for Television Rating Agencies-2014 to ensure that the TRP system reflects the diverse and evolving media consumption habits of viewers across the country.
- Television Rating Point (TRP) is a metric used to measure the popularity and viewership of television programs.
- The more viewers a program has, the higher its TRP rating.
- It is calculated by measuring the viewership of a particular program over a period of time, usually a week.
- TRP ratings are used by broadcasters and advertisers to determine the popularity of different TV programs.
- According to the TRP of a TV channel or programme, advertisers decide where to display their advertisements, and investors will decide about the investment of the money.
- TRP is calculated by the Indian agency the Broadcast Audience Research Council (BARC) using “BAR-O-meters”, that are installed in televisions in selected households.
- BARC India is a joint industry company founded by stakeholder bodies that represent broadcasters, advertisers, and advertising, and Media Agencies.
- BARC has installed “BAR-O-meters” in over 58,000 impanelled households.
- These gadgets record data about the channel or programme watched by the family members or selected people. This method is called the People meters.
- The data is then extrapolated to estimate the viewership of the entire population.
- Another method is known as picture matching, where the people meter records a small portion of the picture that is being watched on the TV.
- This data is collected from a set of homes in the form of pictures and later on is analysed to calculate the TRPs.
- The BARC releases weekly TRP results every Thursday ranking all TV channels and TV programmes.
Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals:
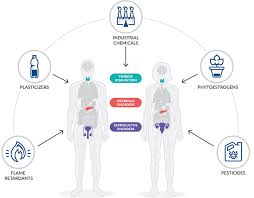
Beyond choking oceans and clogging landfills, plastics are now infiltrating our bodies through microplastic particles and a cocktail of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs).
- The endocrine system is made up of glands that make hormones.
- Hormones are the body’s chemical messengers.
- They carry information and instructions from one set of cells to another.
- The endocrine system influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies.
- Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) are natural or man-made chemicals that interfere with the normal function of your body’s endocrine system.
- Since EDCs come from many different sources, people are exposed in several ways, including the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the water we drink.
- EDCs also can enter the body through the skin.
- EDCs interfere with the way the body’s hormones work.
- Some EDCs act like “hormone mimics” and trick our body into thinking that they are hormones, while other EDCs block natural hormones from doing their job.
- There are approximately 85,000 man-made chemicals in the world, with at least 1,000 classifiable as EDCs.
- Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates are common examples of EDCs found in plastic.
Roll Cloud:

A rare roll cloud appeared over Portugal’s coast recently, surprising beachgoers as strong winds hit during an ongoing extreme heatwave.
- A roll cloud is a low, horizontal, tube-shaped, and relatively rare type of arcus cloud.
- Roll clouds usually appear to be “rolling” about a horizontal axis.
- They usually appear at an altitude of 2,000 to 7,000 meters, and continue to curl visibly.
- They are more often seen in areas with complex terrain and changeable weather—both in the mountains and on the coasts of the oceans. For example, in the Alps, around Japan, Scotland, and northern Australia.
- During severe weather, roll clouds can be confused with funnel clouds, as the roll cloud will show clear signs of rotation along the horizontal and vertical axes, like a tornado.
- Roll clouds are helpful to meteorologists because their appearance sometimes heralds bad weather—strong winds, thunderstorms, storms, or even tornadoes.
- A sharp, rapid roll of clouds can indicate a storm is about to intensify, while a smooth movement can mean calmer weather.
- Along the edge of a thunderstorm, they can serve as a precursor to more active and serious weather in the immediate future.
- An arcus cloud is a low, horizontal cloud formation that typically forms along the leading edge of a thunderstorm outflow or cold front.
Garciniakusumae:

Botanist’s discovered a new garcinia species in Assam and named it as Garciniakusumae.
- Garciniakusumae is a new tree species belonging to the genus Garcinia, commonly referred to as thoikora in
- It is a dioecious evergreen tree that can grow up to 18 metres tall, Garcinia kusumae was observed to flower from February to April, with fruit maturing between May and June.
- Morphological analysis revealed distinguishing characteristics, including up to 15 staminate flowers per fascicle, fewer stamens per flower (except in Garcinia assamica), and berries with blackish resinous exudations.
- The fruit holds local cultural and medicinal value.
- According to the study, the sun-dried pulp is used to prepare a sherbet(soft drink) with salt and sugar, consumed during hot days to prevent heat stroke and alleviate thirst.
- It is also used in curries with fish and employed as a traditional remedy for diabetes and dysentery.
- The seed aril, slightly sour and sweet, is eaten raw, often with salt, chillies, and a dash of mustard oil.
PARAKH Rashtriya Sarvekshan Dissemination Portal:

The PARAKH Rashtriya Sarvekshan Dissemination Portal was launched.
- PARAKH Rashtriya Sarvekshan Dissemination Portal provides open access to National and State-level data on student performance.
- This tool is expected to serve as a key resource for States/UTs to design targeted improvement plans to enhance learning outcomes and bridge skill gaps.
- PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) is a unit established within NCERT in 2023 to standardise school board assessments nationwide.
- PARAKH team will consist of leading assessment experts with a deep understanding of the education system in India and internationally.
- Objective is to fulfil the basic objectives of setting norms, standards, guidelines and implement activities related to student assessment along with other tasks as mandated by the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- The mandate of PARAKH is to work on bringing the school boards across the States and the Union Territories to a common platform.
- Major areas of focus
- Capacity Development in Competency Based Assessment
- Large-Scale Achievement Survey
- Equivalence of School Boards
- Holistic Progress Cards for the Foundational, Preparational, Middle and Secondary Stages.
Gaden Phodrang Trust : In News
The 14th Dalai Lama announced that the institution of the Dalai Lama will continue and that the Gaden Phodrang Trust shall be the “sole authority to recognize the future reincarnation”.The Gaden Phodrang Trust of the Dalai Lama is a non-profit charitable organisation established by the 14th Dalai Lama to support his various religious, cultural and humanitarian initiatives. It was named after the historical Gaden Phodrang, the traditional government of Tibet led by the Dalai Lamas until 1959, The Trust continues the legacy of promoting Tibetan Buddhism, preserving Tibetan culture, and supporting education and healthcare for Tibetan communities in exile.It refers to the residential quarters of the Dalai Lama lineage from the second Dalai Lama onward at Drepung Monastery in Lhasa.
SAKSHAM-3000
Minister of State for Communications and Rural Development launched high capacity SAKSHAM-3000.It is a high-capacity, compact 25.6 Tbps switch-router tailored for modern data centres. It is a state-of-the-art data centre switch-cum-router designed for next-generation digital infrastructure developed by Development of Telematics (C-DOT). It was built to power large-scale computing clusters, cloud infrastructure, 5G/6G networks and AI workloads, the device supports 32 ports of 400G and a flexible range of Ethernet speeds ranging from 1G to 400G. Its ultra-low latency, wire-speed processing, and modular CROS (C-DOT Router Operating System) operating system position it as a versatile solution for roles ranging from leaf to super-spine nodes in a CLOS network.The platform aims to address the evolving needs of large enterprises, telecom operators, and hyperscale data centres.
Custodial death in Tamil Nadu:
The custodial death in Tamil Nadu has once again brought the issue of custodial torture into the spotlight. torture refers to the infliction of physical or mental suffering on individuals held in police or other authorities. It represents a serious violation of human rights and dignity and frequently results in custodial deaths—fatalities that occur while a person is under custody.Between 2016 and 2022, Tamil Nadu (highest among southern states) reported 490 custodial deaths, while the national total stood at 11,656. Uttar Pradesh recorded the highest number with 2,630 deaths.In 2022, Tamil Nadu detained 2,129 people under preventive laws, accounting for half of India’s total. Scheduled Castes (SCs) faced disproportionate custodial violence, making up 38.5% of detainees despite being only 20% of the population in Tamil Nadu.
What is an AI Web Crawler?
US and UK publishers have started blocking Artificial Intelligence (AI) web crawlers to prevent unauthorised use of their content.This has renewed calls in India for consent-based copyright safeguards and fair revenue sharing, raising key concerns in digital governance, copyright enforcement, and ethical AI use.An AI web crawler is a type of automated software or bot that scans and collects content from the internet specifically to help train AI models like Large Language Models (LLMs), or to provide live information retrieval for AI assistants.
Types:
- Model Training Crawler: Extract website data to train generative AI models
- Examples: GPTBot (OpenAI), Amazonbot (Amazon), GoogleOther (Google)
- Live Retrieval Crawlers: These bots pull real-time data from websites to supplement pre-trained models during user queries, ensuring up-to-date and cited responses in AI search tools
- It is used by AI platforms like Bing, ChatGPT, etc., to stay updated.
50 Years of CITES:
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) completed 50 years on 1st July 2025. CITES, also known as the Washington Convention, was signed on 3rd March 1973 during the World Wildlife Conference and came into force on 1st July 1975. It was drafted following a 1963 resolution adopted by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) to regulate wildlife trade. The Convention now has 185 Parties, including India (a member since 1976) and the European Union. Administered by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) in Geneva, CITES regulates international trade in over 40,000 species of wild animals and plants, including live specimens and wildlife-derived products. The treaty aims to ensure that such trade is sustainable, legal, and traceable, supporting biodiversity, local livelihoods, and national economies in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. CITES regulates international trade through permits for export, import, re-export, and sea introduction. Each member country appoints management and scientific authorities to oversee licensing and conservation advice.
Appendices System:
Appendix I: Species threatened with extinction. Trade is highly restricted.
Appendix II: Species not endangered but need controlled trade to avoid risk.
Appendix III: Species protected by at least one country that seeks cooperation to regulate trade.
BHARAT Study: Mapping Healthy Ageing Biomarkers
The Indian Institute of Science, under the Longevity India Programme, has launched the BHARAT (Biomarkers of Healthy Aging, Resilience, Adversity, and Transitions) study to map ageing biomarkers and build a baseline for healthy ageing specific to the Indian population.Ageing varies across individuals and populations, driven by molecular, cellular, environmental, lifestyle, and socioeconomic factors, meaning chronological age may not reflect true biological age.Current biomarkers and diagnostic standards are often based on Western biomarkers and cut-offs (like cholesterol, vitamin D, CRP levels), which may not be accurate or applicable to Indians, risking misdiagnosis and ineffective treatment.
PM-POSHAN scheme: In news
A century after its inception in Madras, the PM-POSHAN scheme continues to combat hunger and promote education, but a new report highlights persistent ground-level challenges like fund delays, caste discrimination, and rising costs. Pradhan Mantri Poshan Shakti Nirman Yojana
Launched In: 2021–22 replacing the 1995 Midday Meal Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (60:40 Centre-State cost-sharing) Objective is to Provide one hot cooked meal per day to students of Classes 1–8 in government and government-aided schools.




