Today’s Current Affairs:4th October 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
PRIP (Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector) Scheme:

The government recently invited applications for research and innovation projects under its Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector scheme to make it a globally competitive and innovation-driven sector.
- The PRIP scheme was launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers, to transform India into a global powerhouse for R&D in the Pharma MedTech sector.
- The scheme was notified in 2023 with a total financial outlay of ₹5000 crores.
- The aim of the scheme is to promote industry-academia linkage for R&D in priority areas and to inculcate the culture of quality research and nurture our pool of scientists.
- It focuses on two components:
- Component A: Strengthening research infrastructure through establishment of Centres of Excellence (CoE) in the seven existing National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs).
These CoEs would be set up in pre identified areas with a financial outlay of Rs 700 Crores. - Component B: Promoting research in the pharmaceutical sector by encouraging research in six priority areas wherein financial assistance will be provided for the industries, MSMEs, SMEs, startups working with government institutes, and for both in- house and academic research.
- Component A: Strengthening research infrastructure through establishment of Centres of Excellence (CoE) in the seven existing National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs).
- The component has a financial outlay of 4250 Crores.
- Bigger companies can seek funding of up to ₹125 crore, while startups can secure up to ₹1 crore over a period of five years, based on their milestones.
Exercise Drone Kavach:

The Spear Corps under Eastern Command of the Indian Army recently conducted Exercise ‘Drone Kavach’ in the forward areas of Eastern Arunachal Pradesh.
- It was conducted by the Indian Army’s Spear Corps, operating under the Eastern Command.
- The four-day exercise was conducted in the forward areas of Eastern Arunachal Pradesh.
- The exercise showcased the Army’s combat readiness for the next generation of drone warfare, besides validating state-of-the-art drone technologies.
- It was also attended by personnel of the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) deployed in forward areas.
- As part of it, a series of tactical manoeuvers and combat situations were exercised to validate the Army’s preparedness for operating in a multi-domain, technology-infused battlefield scenario.
- Tactics, techniques, and procedures pertaining to target acquisition, active/passive counter-drone measures, and target neutralisation with assured success were rehearsed under simulated conditions.
- Newly raised structures at the unit level were also exercised for developing tactics, techniques, and procedures in consonance with the overall employment philosophy and mandated operational tasks.
Ichamati River:

As the Durga Puja immersions commenced on the Ichamati river, a heightened security presence was initiated on the India-Bangladesh border.
- Ichamati River is a trans-boundary river which flows through India and Bangladesh.
- It also forms part of the boundary between the two countries.
- It is one of the bifurcations of the Mathabhanga River (a distributary of the Padma) and originates at Mahjdia village in the Nadia district of West Bengal.
- It flows through the Nadia and North 24 Parganas districts of West Bengal.
- Then it forms part of the India–Bangladesh international border. Later, it enters Bangladesh’s Satkhira and Khulna districts.
- It covers a distance of around 216 km before discharging into the Kalindi River at Hasnabad in North 24 Parganas District and finally outfalls into the Bay of Bengal near Moore Island.
- Ichhamati River and its tributaries form a large oxbow lake complex in North 24-Paraganas district near Bangaon.
- The river is facing siltation leading to thin flow of water in the dry season and floods in the rainy season.
Waste to Art Wall:

The Nagpur Municipal Corporation (NMC) launched a unique initiative titled “Waste to Art Wall” at Prem Nagar, Satranjipura Zone.
- The project aims to beautify public spaces while promoting awareness on cleanliness and waste management.
- It is an urban sanitation and recycling initiative where discarded waste materials are reused to create artistic walls in public spaces.
- Organisation Involved: Nagpur Municipal Corporation (NMC).
- Features:
- Transforms waste into art, improving city aesthetics and encouraging recycling.
- Serves as a community space – residents now use the clean back lane for gatherings and children’s events.
- Acts as a tool for awareness on sanitation and citizen participation in waste management.
Trichloroethylene:
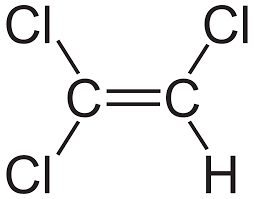
Long-term exposure to the industrial solvent Trichloroethylene (TCE) outdoors may be linked to an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, according to a recent study.
- Trichloroethylene (TCE) is a volatile, colorless liquid organic chemical.
- TCE does not occur naturally and is created by chemical synthesis.
- It is used primarily to make refrigerants and other hydrofluorocarbons and as a degreasing solvent for metal equipment.
- TCE is also used in some household products, such as cleaning wipes, aerosol cleaning products, tool cleaners, paint removers, spray adhesives, and carpet cleaners and spot removers.
- Commercial dry cleaners also use trichloroethylene as a spot remover.
- TCE may be found in the air, water, and soil at places where it is produced or used.
- It breaks down slowly and remains in the environment for a long time.
- It readily passes through soil and can accumulate in groundwater.
- People in the general population can be exposed to TCE by inhaling it in indoor and outdoor air, drinking contaminated water, or eating foods that have been washed or processed with contaminated water.
- People with prolonged or repeated exposure to TCE could experience liver problems and may have an increased risk of developing liver or kidney cancer.
- TCE also has genotoxic and immunotoxic potential, and some studies indicate that it may be a teratogen.
- There is also increasing evidence supporting the association between TCE exposure and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and several reproductive and developmental toxicity endpoints, including infertility in males and females, impaired fetal growth, and cardiac teratogenesis.
Neurons : New Study
A new study (2025) has identified Dendritic Nanotubes (DNTs) in the brains of mice and humans, a new form of neuron-to-neuron connection.
- New Discovery: Neurons may also connect via nanotubes (DNTs), enabling:
- Direct electrical signal transfer.
- Protein transport (including amyloid-beta, linked to Alzheimer’s).
- Neurons (nerve cells) are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system.
- They are responsible for:
- Receiving sensory input from the environment.
- Sending motor commands to muscles.
- Processing and transmitting electrical and chemical signals.
- Structure of Neuron:
- Dendrites → receive incoming signals.
- Cell Body (Soma) → integrates signals.
- Axon → carries impulses away from the cell body.
- Axon Terminals → release neurotransmitters at synapses.
- Traditionally, neurons communicate via synapses where neurotransmitters cross gaps.
Snow Leopard : New Data
Himachal Pradesh has recorded 83 snow leopards (up from 51 in 2021) as per the latest survey by the Wildlife Wing of the State Forest Department in collaboration with the Nature Conservation Foundation (NCF).
Key details of the Survey:
- The exercise, covering 26,000 sq km across Spiti Valley, Kinnaur, Pangi, Lahaul, and Great Himalayan National Park, involved 271 camera traps.
- First official sighting of Pallas’s Cat in Kinnaur and rediscovery of Woolly Flying Squirrel in Lahaul also reported.
- For the first time globally, indigenous women from Kibber contributed to data analysis, highlighting inclusive community participation in conservation.
- Himachal Pradesh is the first state in India to complete a population estimation of snow leopards, setting a cost-effective, scalable model for monitoring.
Snow Leopard (Panthera uncia):
- Declared State Animal of Ladakh and Himachal Pradesh.
- Found across 12 range countries – Afghanistan, Bhutan, China, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan.
- India is home to an estimated 500–700 snow leopards spread across the Himalayas and Trans-Himalayan region.
- Mascot of Khelo India Winter Games 2024: named Sheen-e She (Shan) in Ladakh.
Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF):

The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched a tool called SARAL (Simplified and Automated Research Amplification and Learning) to make scientific research more accessible and understandable.
- Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) established under: ANRF Act, 2023, functioning under the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- The Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) has been merged into ANRF.
- Core objective: To seed, grow, and promote R&D, and foster a research and innovation culture across universities, colleges, research institutions, and R&D labs in India.
- Acts as an apex body providing high-level strategic direction to research, in line with the National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
- Funding target: ₹50,000 crore for the period 2023–2028, with ~70% expected from private sector contributions.
- Develop an AI Science & Engineering Open India Stack to revolutionize sectors like drug and chemical discovery, aerospace design, advanced materials, climate and weather studies.
- Envisaged as a single-window clearance mechanism for R&D funding in academic and research institutions.
- SARAL uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to generate simplified summaries of complex research papers in the form of videos, podcasts, posters, and presentations for wider outreach.
Sir Creek Region:
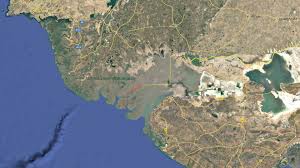
The Defence Minister of India warned Pakistan against any aggression in the Sir Creek region, stating that India would give a “resounding and decisive response” that could alter “history and geography”.
- Sir Creek is a 96 km long tidal estuary located in the marshy Rann of Kutch region, separating Gujarat (India) from Sindh (Pakistan).
- It flows into the Arabian Sea and is a strategically sensitive zone due to its proximity to the international boundary.
- The area is significant for security, fishing rights, oil and gas exploration, and Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) determination.
- The dispute arises from differing interpretations of the 1914 Bombay Government Resolution signed between Sindh (then under British India) and the Ruler of Kutch.
- Pakistan’s claim: The boundary lies on the eastern bank of the creek (giving the creek to Sindh).
- India’s claim: The boundary should follow the thalweg principle (mid-channel line of navigable waters).
- Pakistan’s counter-argument: Sir Creek is not navigable, hence the thalweg principle doesn’t apply.
- India’s stand: The creek is navigable during high tide, so international maritime norms apply.
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for 2023-24:

The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for 2023-24.
Key Highlights of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for 2023-24:
- Gross Value Added (GVA): Grew by 11.89%, higher than both output (5.80%) and input (4.71%), showing better efficiency and higher value generation.
- Top Industries in Terms of GVA: Growth was led by basic metals, motor vehicles, chemicals, food products, and pharmaceuticals, industries that are both export-oriented and labor-intensive.
- Together, these sectors contributed nearly 48% of total industrial output.
- Top 5 states by GVA: Maharashtra (16%), Gujarat (14%), Tamil Nadu (10%), Karnataka (7%), and Uttar Pradesh (7%).
- Employment grew 5.92% year-on-year, showing that industrial growth translated into jobs. This sector added more than half a crore (57 lakh) jobs during the last decade 2014-15 to 2023-24.
- Average emoluments rose by 5.6%, keeping pace with output growth, though wage gains still lagged behind overall GVA growth.
- Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka are the top 5 States in respect of employment.
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI):
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) under MoSPI conducts the ASI, with MoSPI ensuring its coverage and data quality.
- The ASI covers factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948, bidi and cigar units under the Bidi & Cigar Workers Act, 1966, electricity undertakings not registered with the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), and large establishments with 100 or more employees listed in the Business Register of Establishments (BRE) maintained by state governments.
Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT):

The Government of India has invoked the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) with Singapore to ensure cooperation in the investigation into the death of singer Zubeen Garg, who died in Singapore.
- Mutual Legal Assistance Treaties (MLATs) are bilateral or multilateral agreements that enable countries to cooperate in criminal matters such as terrorism, trafficking, cybercrime, smuggling, and financial frauds.
- MLATs provide a structured and legally binding framework for investigation, evidence sharing, and prosecution, ensuring that criminals do not escape justice due to jurisdictional gaps.
- MLATs strengthen international cooperation, reciprocity, and speed in handling transnational crimes.
- India provides Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA) through bilateral/multilateral treaties, international conventions, or reciprocity.
- India has signed MLATs with 42 countries (as of 2019). In India the MLA requests are routed through the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), which acts as the Central Authority, with support from the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) when required through diplomatic channels.
Food Grain Storage In India:
India has achieved a record foodgrain production of 353.96 million tonnes for 2024-25, as per the Third Advance Estimates. To preserve this surplus, modern storage infrastructure is crucial to minimize post-harvest losses, ensure safe storage, and stabilize prices. The foodgrain storage system in India is a network of facilities and mechanisms designed to preserve harvested foodgrains, prevent post-harvest losses, and ensure year-round availability for consumers and the Public Distribution System (PDS). It integrates centralized, decentralized, and cold storage infrastructures, linking farmers, state agencies, and markets. Around 60-70% of the foodgrain produced is stored at the household level by small farmers, utilizing traditional indigenous storage methods like Morai and Mud Kothi.
Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme:
India’s Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS) has drawn USD 13 billion investment proposals, nearly double its target. With 60% participation from MSMEs, the scheme is set to boost domestic production, reduce import dependence, and create 1.41 lakh direct jobs, strengthening India’s push to become a global electronics hub.The ECMS, launched in April 2025 as a complement to the India Semiconductor Mission, seeks to strengthen India’s electronics value chain beyond finished goods and chip fabrication by boosting Domestic Value Addition (DVA) and linking Indian firms with Global Value Chains (GVCs). ECMS supports horizontal linkages with automobile, power, and industrial sectors. Scheme Tenure: 6 years (1 year of gestation period) i.e. from FY2025-26 to FY2031-32. The ECMS provides turnover-linked, capex-linked, or hybrid fiscal incentives, with a portion of both turnover and capex incentives linked to employment generation. Incentives will be given on a first-come, first-served basis to firms ready for early production.
Typhoon Bualoi:
The death toll in Vietnam from Typhoon Bualoi and subsequent floods has risen to 36, with over 210,000 houses damaged and agricultural losses worth $435 million.It is a tropical cyclone (Category 2-equivalent at peak) in the Northwest Pacific Ocean, locally called Typhoon Opong in the Philippines. It was the 20th named storm and the 9th typhoon of the 2025 Pacific typhoon season.It is Formed from a disturbance north of Yap. Named Opong by PAGASA (Philippines) and Bualoi by JMA (Japan Meteorological Agency). Made multiple landfalls in the Philippines before intensifying into a typhoon and hitting Hà Tĩnh, Vietnam.
Swiss glaciers lost 3% of their total ice mass in 2024–25:
Swiss glaciers lost 3% of their total ice mass in 2024–25, marking the fourth-largest reduction on record, according to GLAMOS.About 1,400 glaciers in the Alps, but one-quarter of volume lost since 201. The largest glacier in Switzerland is the Aletsch Glacier (also known as the Great Aletsch Glacier or Grosser Aletschgletscher). Rivers – Source of Rhône (to Mediterranean) and Rhine (to North Sea), also Ticino (to Po) and Reuss (to Aare). Mountains – Alps dominate; major peaks include Dufourspitze (4,634 m), Matterhorn (4,478 m), Weisshorn, and Dom. Jura Mountains lie in northwest; Mittelland plateau in between.
SARAL Tool:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) launched the SARAL tool to simplify scientific research papers. It uses AI to generate layperson summaries and make research more accessible to society. SARAL (Simplified and Automated Research Amplification and Learning) is an AI-based tool that converts complex research papers into easy-to-understand summaries. Launched by: Developed by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF).Aim is to make scientific knowledge more inclusive and accessible, enabling citizens, policymakers, and industry to understand and apply research outputs. It Uses AI to extract key insights from research publications. It Generates videos, podcasts, posters, and presentations for wider outreach. It is Linked to the creation of an AI Science and Engineering Open India Stack for applications in drug discovery, aerospace, climate science, and advanced materials.
India’s First Dugong Conservation Reserve:
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) officially recognized India’s first Dugong Conservation Reserve, located in Palk Bay, Tamil Nadu, during the 2025 IUCN World Conservation Congress. This recognition marks a crucial step in safeguarding one of India’s most endangered marine mammals the dugong. Established in September 2022 by the Tamil Nadu government under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, the Dugong Conservation Reserve spans an area of 448.34 sq. km. in the northern Palk Bay. The region hosts over 12,250 hectares of seagrass meadows, which are essential feeding grounds for dugongs, also known as “sea cows.” These meadows also act as carbon sinks and breeding zones for many marine species, enhancing coastal biodiversity and fish production.
India has been re-elected to Part II of the ICAO Council:
India has been re-elected to Part II of the Council of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a specialized agency of the United Nations. The re-election, announced during the 42nd ICAO Assembly in Montreal, Canada, reaffirms India’s status as one of the largest contributors to international civil air navigation infrastructure. ICAO is a UN agency that manages the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport.
The ICAO Council is divided into three parts,
- Part I includes states of chief importance in air transport.
- Part II includes states making the largest contributions to international air navigation services.
- Part III represents states with special interests in air navigation or aviation.
Mann Ki Baat Completes 11 Years:
On 3 October 2025, Mann Ki Baat, the monthly radio address by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, completed 11 years since its first broadcast. The inaugural episode aired on 3 October 2014, coinciding with Vijayadashami. Over these years, the programme has evolved into more than a broadcast it has become a symbol of people’s aspirations, stories, and citizen‑government dialogue.It was Launched in October 2014, Mann Ki Baat began with the goal of giving the Prime Minister a direct voice to the Indian people via radio.
Centre raises MSP for all mandated Rabi crops in 2026‑27 season:
The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved a significant Minimum Support Price (MSP) hike for all mandated Rabi crops for the 2026‑27 marketing season. This decision aims to ensure better returns for farmers and promote crop diversification. Alongside this, a major initiative the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses—was also launched to reduce import dependency and increase domestic production. Minimum Support Price (MSP) is the assured price at which the government procures crops from farmers, offering a safeguard against market volatility. It plays a crucial role in price stabilization, influences cropping patterns, and encourages the cultivation of key food crops, especially during volatile market conditions.




