Today’s Current Affairs: 5th January 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Spina Bifida:

Many countries across the world have initiated programmes to create awareness to prevent Spina Bifida through folic acid supplementation but India is yet to do so.
- It is a birth defect of the spinal cord that causes serious childhood paralysis.
- It occurs when the spine and spinal cord of a foetus do not fully develop during the embryonic period.
- The condition occurs during early pregnancy, and can range from mild to severe.
- The cause is not known. It’s thought that a combination of genetic, nutritional and environmental risk factors causes the condition.
- Types of Spina Bifida
- Myelomeningocele: It is the most serious form of the condition. In this type, part of the spinal cord and nerves are exposed through a sac at the opening of the gap in the spine.
- Meningocele: It is a less common type of spina bifida that occurs when the meninges, or the protective membranes around the spinal cord, push out through the opening in a fluid-filled sac.
- Spina bifida occulta: It is the mildest form of the condition in which one or more of the vertebrae not forming properly, resulting in a small gap.
- Symptoms: Bowel and bladder issues, back pain, weakness or lack of movement in the legs and loss of sensation in the legs.
- Prevention: It can be prevented largely by having folic acid the early weeks of pregnancy.
- Treatment: There is no cure for the condition; however, treatment options are available to manage symptoms.
Design Linked Incentive Scheme:

The Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme is critical to anchoring India in the most strategic and value-intensive segment of the global semiconductor value chain—chip design.
- It is a key instrument in advancing India’s ambition to develop a strong fabless capability.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) under the Semicon India Programme.
- The scheme aims to reduce import dependence, strengthen supply chain resilience, and enhance domestic value addition.
- Eligibility: Start-ups and MSMEs are eligible for financial incentives and design infrastructure support for semiconductor product design & deployment.
- Other domestic companies are eligible for financial incentives for deploying semiconductor designs.
- The DLI Scheme supports: Semiconductor design across the full lifecycle—from design and development to deployment—covering Integrated Circuits (ICs), chipsets, Systems-on-Chip (SoCs), systems and IP cores.
- Nodal Agency: C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing).
Notifiable Disease:

The Delhi government is set to declare rabies a notifiable disease to strengthen disease surveillance.
- A notifiable disease is any disease that is required by law to be reported to government authorities.
- Effective notification allows the authorities to monitor the disease and provides early warning of possible outbreaks.
- The Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897provides the legal framework for notifying diseases in India.
- Criteria for Declaring a Disease as Notifiable may be:
- It is of interest to national or international regulations or control programs.
- Its national/ State/District incidence.
- Its severity (potential for rapid mortality).
- Its communicability/Its potential to cause outbreaks.
- Significant risk of international spread.
- Medical practitioners and diagnostic labs are required to notify the local health department of cases of notified diseases.
- In India, the state government is responsible for determining which diseases must be reported to the medical officer in their area and to notify the diseases.
- The government and regional authorities maintain a list of notifiable diseases in India, which is subject to change as new diseases are added or existing ones are removed.
- Examples: Cholera, tuberculosis, AIDS, dengue, hepatitis, leprosy, meningitis, plague, and measles.
WHO’s International Health Regulations (1969): Mandates countries to report diseases for global surveillance and advisory purposes.
Double-Humped Bactrian camel:

Ladakh’s double-humped Bactrian camels are set to debut at the 77th Republic Day parade.
- It is scientifically known as Camelus bactrianus.
- It is large even-toed ungulates are renowned as Ladakh’s “silent warriors”.
- They are native to the harsh and arid regions of Central Asia.
- They occupy habitats in Central Asia from Afghanistan to China, primarily up into the Mongolian steppes and the Gobi desert.
- Small populations of these camels are found in high altitude cold deserts of Ladakh’s Nubra Valley.
- Characteristics of Double-Humped Bactrian camel:
- The two humps, serves as a reservoir of fat that can be converted into water and energy during long treks where food is scarce.
- They possess thick, shaggy coats that fluctuate with the seasons, growing dense to withstand temperatures as low as minus 40 degrees Celsius.
- Their nostrils are sealable to block out frozen dust, while their broad feet act like natural snowshoes.
- They are among the few land animals that can survive by eating snowto meet their hydration needs.
- Diet: Bactrian camels are omnivores but primarily herbivores and eat various types of plants.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered.
Archaea : New Study:
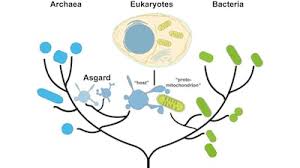
According to a study published, a DNA sequence that signals cells in almost all other organisms to stop synthesising proteins instead encodes a rare amino acid in some archaea.
- Archaea, which means “ancient things” in Greek, are one of the oldest forms of life on Earth and belong to a group called the third domain of life.
- They thrive in extreme habitats such as hot springs, cold deserts and hypersaline lakes.
- Characteristics of Archaea:
- Archaea (singular archaeon) are a primitive group of microorganisms.
- They are single-celled organisms without nucleus or organelles, and have a similar size and shape as bacteria, but differ from them biochemically.
- Their membrane is made of a unique type of lipids and most archaea have a cell wall.
- These slow-growing organisms are also present in the human gut, and have a potential relationship with human health.
- They are known for producing antimicrobial molecules, and for anti-oxidant activity with applications in eco-friendly waste-water treatment.
- Archaea are extremely difficult to culture due to challenges in providing natural conditions in a laboratory setting.
- Many archaea live in some of the harshest environments on Earth, which makes them ideal for studying how life can survive in tough conditions.
Taimoor Missile:

The Pakistan Air Force has successfully conducted a flight test of the indigenously developed Taimoor Weapon System recently.
- It is an air-launched cruise missile developed by Pakistan.
- It is capable of striking enemy land and sea targets with high precision.
- It uses subsonic turbojet propulsion for long-range efficiency.
- It has a range of upto 600 kilometers, carrying a conventional warhead.
- Stealth design: Box-shaped fuselage, X-type tail, foldable wings.
- The missile is designed to fly at very low altitudes, allowing it to effectively evade hostile air and missile defence systems.
- It relies on a mix of inertial, satellite, and terrain-based guidance for accurate navigation.
- Cruise missiles are unmanned vehicles that are propelled by jet engines, much like an airplane.
- They can be launched from ground, air, or sea platforms.
- Cruise missiles remain within the atmosphere for the duration of their flight and can fly as low as a few meters off the ground.
Rah-Veer:
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways reiterated protections and incentives under the Rah-Veer (Good Samaritan) Scheme to encourage bystanders to help road accident victims without fear of legal or procedural harassment.Rah-Veer is a Good Samaritan initiative notified under Section 134A of the Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019, protecting citizens who help road accident victims during the Golden Hour from legal, police, or hospital-related harassment.
State-led capital spending:
State governments’ ability to sustain capital expenditure has come under focus as several States breached the 3% fiscal deficit norm using enhanced borrowing space during FY2021–FY2025.State-led capital spending refers to expenditure by State governments on asset creation such as roads, irrigation, power, health, education infrastructure, and urban development.It is distinct from revenue spending as it raises long-term productive capacity and crowds in private investment.Combined capital expenditure and loans & advances of 28 States grew at a CAGR of 18.5%, doubling to ₹8.4 trillion.Expansion driven by GST compensation loans (₹2.6 trillion in FY21–22) and 50-year interest-free capex loans (₹3.7 trillion over FY21–FY25).Additional borrowing of 0.5–1.1% of GSDP allowed under Union government relaxations and 15th Finance Commission provisions.Power sector reforms enabled several States to access ~₹1.3 trillion in extra borrowing between FY22–FY25.
Sunrise Festival 2025–26:
Arunachal Pradesh celebrated the inaugural Sunrise Festival 2025-26 at Dong village in Anjaw district, the easternmost point where sunrise first touches Indian territory.Sunrise Festival is an adventure-led cultural tourism festival to establish Arunachal Pradesh as a global hub for nature, culture, adventure, and heritage celebrations centered around the sunrise.Dong is home to the indigenous Meyor (Zakhring) tribe, known as the Sunrise People, whose culture, traditions, and belief systems are deeply rooted in sun worship.It featured cultural presentations from multiple tribes of Arunachal Pradesh namely Mishmi, Singhpho, Galo, Wancho, Nocte, Adi, Apatani, Nyishi, and Monpa, offering a living showcase of state’s rich and diverse indigenous heritage.Dong Village is located in Anjaw district’s Dong Valley at the tri-junction of India, China, and Myanmar. It lies just 7 km from Walong, a major theatre of the 1962 Chinese aggression.
Suryastra Rocket Launcher:
The Indian Army has signed an emergency procurement contract with NIBE Limited for the indigenous Suryastra long-range rocket launcher, enabling fast-track acquisition within the Emergency Procurement framework. The system is being domestically produced under a technology collaboration with Elbit Systems, while the Defence Acquisition Council has extended Emergency Procurement powers to allow contract signing until 15 January 2026.Suryastra is India’s first Made-in-India, multi-calibre, long-range rocket launcher system developed by Pune-based NIBE Limited in collaboration with Israel’s Elbit Systems.It leverages Elbit’s PULS (Precise & Universal Launching System) architecture to deliver precision surface-to-surface strikes at ranges of up to 150 km and 300 km, marking the first domestic production of a high-precision rocket launcher with 300 km strike capability. It has demonstrated a high accuracy of less than five metres circular error probable (CEP) in trials and can also fire loitering munitions up to 100 km.




