Today’s Current Affairs: 7th aug 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana:

The Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas provided valuable insights into the Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana in a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
- Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN Yojana was launched in March 2019.
- It focuses on integrated bio-ethanol projects for Second Generation (2G) ethanol using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable feedstocks.
- Total financial allocation: Rs. 1969.50 crore (2018-19 to 2023-24).
- Under this scheme the maximum financial assistance of Rs.150 crore per project for commercial projects and Rs.15 crore per project for demonstration projects has been prescribed for enhancing commercial viability, promoting R&D, and adoption of technologies in the field of production of 2G ethanol.
- Key states benefiting: Punjab, Haryana, Odisha, Assam, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh.
- PM JI-VAN Yojana to Enhance Bio-ethanol: Imposition of additional excise duty on non-blended fuels, Ethanol Purchase Agreements (EPA), diversification of feedstock, separate price for 2G ethanol, reduced GST on ethanol for EBP Programme.
Jharkhand Competitive Examination (Measure For Control And Prevention Of Unfair Means In Recruitment) Bill, 2023:

The Jharkhand Assembly passed the Jharkhand Competitive Examination (Measure for Control and Prevention of Unfair Means in Recruitment) Bill, 2023, introducing strict provisions to curb cheating in competitive exams.
- The Bill aims to uphold the integrity of examinations and ensure a fair and transparent selection process for various recruitment processes.
- The Jharkhand Competitive Examination Bill, 2023, is a significant step towards promoting ethical practices in competitive exams.
- The Bill mandates two severe penalties for wrongdoers – life imprisonment and a fine of up to ₹10 crore.
- These measures are aimed at deterring individuals from resorting to unfair means in competitive exams.
- According to the legislators’ recommendation, an examinee caught copying for the first time will face a reduced punishment of one year, instead of the previously proposed three years.
- Similarly, for a second offense, the punishment will be three years, down from the earlier proposal of seven years.
- Under the Bill’s provisions, if an examinee is caught cheating for the first time, they will be fined ₹5 lakh.
- Failing to pay this fine will lead to an additional punishment of nine months imprisonment.
- For a second offense, the examinee will be fined ₹10 lakh, and if the fine remains unpaid, they will face an additional sentence of thirty months.
- In addition to the monetary fine and imprisonment, any examinee found guilty will be barred from sitting in any competitive examination for a period of 10 years.
City Investments To Innovate, Integrate And Sustain 2.0:

The Government has approved the ‘City Investments to Innovate, Integrate and Sustain 2.0 (CITIIS 2.0)’.
- CITIIS 2.0 is a part of the Smart Cities Mission and aims to promote integrated waste management and climate-oriented reform actions.
- CITIIS will consider Smart City Projects in the following four themes:
- Sustainable Mobility.
- Public Open Spaces.
- Urban E-governance and ICT.
- Social and Organisational Innovation for Low-Income Settlements.
- The program will run for a period of four years, i.e., from 2023 till 2027.
- The program envisages to support competitively selected projects promoting circular economy with focus on integrated waste management at the city level, climate-oriented reform actions at the State level, and institutional strengthening and knowledge dissemination at the National level.
- CITIIS 2.0 aims to leverage and scale up the learnings and successes of CITIIS 1.0.
- CITIIS 1.0 was launched jointly in 2018 and consisted of three components:
- 12 city-level projects selected through a competitive process.
- Capacity-development activities in the State of Odisha.
- Promoting integrated urban management at the national level through activities undertaken by , National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA), which was the Program Management Unit (PMU) for CITIIS 1.0.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon : Genetic Cause
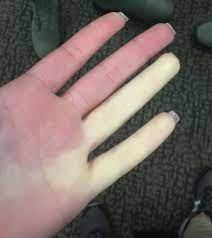
The genetic causes of Raynaud’s phenomenon was recently probed by researchers at Queen Mary University of London’s Precision Healthcare Research Institute (PHURI) and Berlin’s Berlin Institute of Health (BIH).
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon is a condition that causes the blood vessels in the extremities to narrow, restricting blood flow.
- The episodes or “attacks” usually affect the fingers and toes.
- In rare cases, attacks occur in other areas such as the ears or nose.
- An attack usually happens from exposure to cold or emotional stress.
- During a Raynaud’s attack, the arterioles and capillaries in your fingers and toes tighten more than they should.
- This condition is named for the French doctor who first identified it in 1862. You may hear it called by many names. There are two types:
- Primary Raynaud’s(or Raynaud’s disease):
- It happens without any other illness behind it.
- The symptoms are often mild.
- Secondary Raynaud’s (Raynaud’s syndrome, Raynaud’s phenomenon):
- It results from another illness.
- It’s often a condition that attacks your body’s connective tissues, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- It’s less common, but it’s more likely to cause serious health problems.
- This can include things like skin sores and gangrene. These happen when cells and tissue in your toes and fingers die from lack of blood.
- Primary Raynaud’s(or Raynaud’s disease):
Samudrayaan Project : First Mission To Explore Ocean

Union Minister of Earth Sciences recently said that India’s ambitious Samudrayaan project is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
- Samudrayaan Project is India’s first manned mission to explore the deep ocean.
- It is designed to study the deep ocean resources and conduct biodiversity assessments as well.
- The mission will not disturb the ecosystem as the submersible is used solely for exploration purposes.
- The project is part of the larger Deep Ocean Mission, which supports the Central Government’s Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) is the nodal ministry to implement this multi-institutional ambitious mission.
- MATSYA 6000 is a manned submersible vehicledeveloped by the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai.
- It was developed under the Samudrayaan mission to facilitate humans in the deep ocean in exploring mineral resources.
- It is designed with the capability of operating in the deep sea for 12 hours while in case of emergency, it can also operate up to 96 hours with all the necessary measures for human safety.
- Expected to be launched in 2024-25, it would make India only one among six countries (US, Russia, Japan, France, and China) to have piloted a crewed under-sea expedition beyond 5,000 metres.
Neerakshi : Underwater Vehicle For Mine Detection

India recently launched ‘Neerakshi’- Autonomous Underwater Vehicle for mine detection.
- Neerakshi is an autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) designed to detect mines.
- Named “Neerakshi” meaning “Eyes in the Water” is first of its kind in the country and is expected to undergo user trials by the Indian Navy, Coast Guard, and Army before a commercial launch.
- It is a collaboration of Kolkata-based warship maker Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) Ltd and MSME entity Aerospace Engineering Private Ltd (AEPL).
- The AUV, currently capable of mine detection, is part of GRSE’s broader ambitions to create autonomous sea surface vehicles, sea-based drones, and explore green propulsion technologies.
- It can be used for a variety of functions ranging from mine detection to mine disposal to underwater survey,
- It is a 2.1-metre long cylindrical unmanned vehicle about a foot in diameter and weighing around 45 kg.
- It has an endurance of nearly 4 hours, and is capable of operating up to a depth of 300m.
Messier 57 : New Image
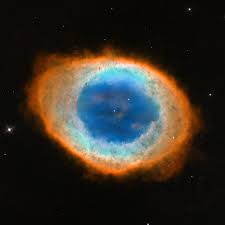
Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to capture new image of Messier 57, more popularly known as the Ring Nebula.
- Messier 57 is about 2,000 light-years away in the constellation Lyra and was discovered in 1779.
- The object is exceptionally bright and can be spotted with moderately-sized telescopes.
- It was born from a dying star that expelled its outer layers into space, making it a planetary nebula.
- Planetary nebulae come in a variety of shapes and patterns, some that include delicate glowing rings, wispy clouds and expanding bubbles.
- James Webb Space Telescope was built in collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency and was launched in December 2021.
- It is presently at a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point, approximately 1.5 million km beyond Earth’s orbit.
- It’s the largest, most powerful infrared space telescope ever built.
- Objectives: It will examine every phase of cosmic history; from the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets to the evolution of our Solar System.
Sahakar 22 : National Cooperative Development Corporation

National Cooperative Development Corporation had earlier launched its own initiative named Sahakar– 22, during FY 2017-18.
- Sahakar 22 is initiative of NCDC included the following:
- FOCUS 222 – NCDC’s focused assistance for Cooperatives in 222 Districts (including 117 Aspirational Districts identified by NITI Aayog);
- PACS HUB – Transformation of PACS and other Coops as Apna Kisan Resource Centres;
- AENEC – Act East and North East Cooperatives;
- CEMtC – Centres of Excellence to Market through Cooperatives;
- SAHAKAR PRAGYA – Capacity Development through Laxmanrao Inamdar National Academy for Cooperative Research Development (LINAC).
NCDC:
- The National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) was established by an Act of Parliament in 1963 as a statutory Corporation.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Cooperation.
- Functions:
- Planning, promoting and financing programmes for production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, food stuffs, certain other notified commodities e.g., fertilisers, insecticides, agricultural machinery, lac, soap, kerosene oil, textile, rubber etc.,
- Supply of consumer goods and collection, processing, marketing, storage and export of minor forest produce through cooperatives, besides income generating stream of activities such as poultry, dairy, fishery, sericulture, handloom etc.
Unmesha And Utkarsh Festivals:

The President of India inaugurated ‘Unmesha’ – International Literature Festival and ‘Utkarsh’ – Festival of Folk and Tribal Performing Arts at Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- These festivals were organised by Sahitya Akademi and Sangeet Natak Akademi, respectively, with the purpose of celebrating inclusivity and cultural diversity.
- UNMESHA is India’s most inclusive and Asia’s largest literature festival in terms of the number of languages represented.
- More than 575 authors in 102 languages are expected to participate in over 75 events in ‘Unmesha 2023’, and writers from 13 countries will participate in the festival.
- This will be the second edition of ‘Unmesha’. The first event was held in Shimla in June 2022.
- UTKARSH festival showcases the folk and tribal Performing Arts
- It casts a spotlight on the treasure trove of India’s folk and tribal heritage, endowing these expressive art forms with a resplendent stage to captivate and enthral.
- ‘Utkarsh’ serves as a vital launchpad for traditional artists and performers to unfurl their artistry, safeguarding the priceless heritage of myriad communities.
- ‘Utkarsh’ brings forth a vivid tableau of cultural diversity, nurturing an appreciation for indigenous arts and underscoring their intrinsic value in an increasingly interconnected world.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) has undergone a significant shift in prevalence in India, as per a recent study published in the Lancet journal.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of chronic inflammatory conditions that affect the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- These conditions cause inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive tract, leading to various symptoms and complications.
- The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the GI tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly involves the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
- The inflammation in Crohn’s disease can extend deep into the layers of the bowel tissue and may involve skip lesions (affected areas separated by healthy ones).
- Ulcerative colitis is type of IBD affects the large intestine (colon) and the rectum.
- The inflammation in ulcerative colitis usually begins in the rectum and spreads continuously up the colon in a continuous pattern.
- The inner lining of the colon becomes inflamed, leading to the formation of ulcers.
- It can vary in severity and may include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea (which can be bloody in ulcerative colitis)
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Rectal bleeding (common in ulcerative colitis)
- Joint pain and inflammation
- The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but IBD is the result of a weakened immune system. Possible causes are:
- The immune system responds incorrectly to environmental triggers, such as a virus or bacteria, which causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients:
Union Health Minister recently said that India has started manufacturing 38 active pharmaceutical ingredients, or APIs, in the last one and a half years.
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are the active components in a pharmaceutical drug that produces the required effect on the body to treat a condition.
- APIs are produced by processing chemical compounds.
- In a biologic drug, the active ingredient is known as a bulk process intermediate (BPI).
- APIs are the key active components that interact with specific receptors or target molecules in the body to bring about the desired physiological or therapeutic response
- All drugs are made up of two core components: (1) Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API), which is the central ingredient, and (2) excipients.
- Excipients are substances other than the drug that helps deliver the medication to your system.
- Excipients are chemically inactive substances, such as lactose or mineral oil.
- Some of these materials are used to help the medication remain stable and to control absorption when you take the drug.
Clouded Leopard:

Ecologist observed that the Clouded leopard on its hide does not follow any specific pattern of operating in a certain space, unlike other carnivores.
- Clouded leopard is a wild cat inhabiting dense forests of the Himalayas through mainland Southeast Asia into South China.
- The clouded leopard is categorised into two species: the mainland clouded leopard distributed from central Nepal to peninsular Malaysia, and the Sunda clouded leopard (Neofelis diardi) native to Borneo and Sumatra.
- The mainland clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) is often likened to the Ice Age sabretooth because it has the largest canines in proportion to its skull size among all cat species.
- It also has rotating rear ankles that enable it to climb down head first from trees, unlike the other felines.
- They seemed to go wherever they pleased without worrying about other predators, primarily because of their ability to climb trees, even hang upside down from large branches.
- It most often inhabits primary evergreen tropical forests and also lives in secondary forests, logged forests, dry tropical forests, grassland, mangrove swamp, scrubland, and coastal hardwood forest.
- In India, it is found in Sikkim, northern West Bengal, Meghalaya subtropical forests, Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, Assam, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is the State animal of Meghalaya.
- Conservation status
- IUCN: Vulnerable
Indian Mini Satellite-1 : ISRO
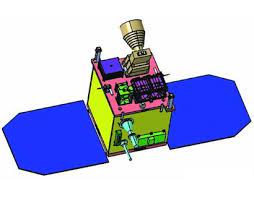
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that it began transferring IMS-1 Satellite Bus technology to Alpha Design Technologies.
- Indian Mini Satellite-1 was developed by the UR Rao Satellite Centre of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is a small satellite platform designed to enable low-cost access to space.
- The IMS-1 bus weighs about 100 kilograms and can carry a 30-kilogram payload.
- The solar arrays onboard generate 330 watts of power.
- It comes with four reaction wheels with a 1 Newton thruster that is good for pointing accuracy with an accuracy threshold of 0.1 Degrees.
- It was used in previous ISRO missions like IMS-1, Youthsat and Microsat-2D.
- It would enable low cost access to space by providing dedicated platform for payloads for earth imaging, ocean and atmospheric studies, microwave remote sensing and space science missions with a quick turnaround time.
Bhu-Vision : IoT-Based Automated Soil Testing

A revolutionary IoT-based automated soil testing and agronomy advisory platform, Bhu-Vision was officially launched at AICRP (ICAR-IIRR), Hyderabad.
- Bhu-Vision is also known as KRISHI-RASTAA Soil Testing System.
- It has been jointly developed by ICAR-IIRR(Indian Council of Agricultural Research -Indian Institute of Rice Research) and KrishiTantra.
- This system seamlessly conducts 12 key soil parameter tests in just 30 minutes.
- It provides quick and accurate results directly to farmers and stakeholders through a soil health card on their mobile devices.
Indian Institute of Rice Research:
- It was established as All India Coordinated Rice Improvement Project (AICRIP) by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) in 1965.
- Headquarter: Hyderabad.
- Mandate :
- Basic and strategic research for enhancing rice productivity under irrigated ecosystem
- Coordination of multi-location testing to develop location specific varieties and technologies for various ecosystems.
- Dissemination of technologies, capacity building and establishing linkages




