Today Current Affairs: 8th December 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Assam Rifles:

Killing of over a dozen civilians in Mon district of Nagaland saw angry crowds vandalise camps of Assam Rifles in the district.
- While the botched operation was launched by the Indian Army, Assam Rifles, which has the responsibility of the area where the incident occurred, issued a statement expressing regret over the loss of innocent lives.
- Assam Rifles is one of the six central armed police forces (CAPFs) under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- The other forces being the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), the Border Security Force (BSF), the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) and the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB).
- It is tasked with the maintenance of law and order in the North East along with the Indian Army and also guards the Indo-Myanmar border in the region.
- Assam Rifles is the oldest paramilitary force raised way back in 1835 in British India with just 750 men.
Kasturirangan Committee Report:

Karnataka Chief Minister Basavaraj Bommai informed the Centre that the state is opposed to the Kasturirangan Committee report on Western Ghats.
- He said that declaring Western Ghats as ecologically sensitive zone would adversely affect the livelihood of people in the region.
- However, the experts called the state’s opposition disastrous for the ecologically fragile Western Ghats.
Gadgil Committee:
- It defined the boundaries of the Western Ghats for the purposes of ecological management.
- It proposed that this entire area be designated as ecologically sensitive area (ESA).
- Within this area, smaller regions were to be identified as ecologically sensitive zones (ESZ) I, II or III based on their existing condition and nature of threat.
- It proposed to divide the area into about 2,200 grids, of which 75 per cent would fall under ESZ I or II or under already existing protected areas such as wildlife sanctuaries or natural parks.
- The committee proposed a Western Ghats Ecology Authority to regulate these activities in the area.
Recommendations of Kasturirangan Committee:
- A ban on mining, quarrying and sand mining.
- No new thermal power projects, but hydro power projects allowed with restrictions.
- A ban on new polluting industries.
- Building and construction projects up to 20,000 sq m was to be allowed but townships were to be banned.
- Forest diversion could be allowed with extra safeguards.
Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD): NASA

NASA has launched its new Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD).
- It is the agency’s first-ever laser communications system.
- The LCRD will help the agency test optical communication in space.
About LCRD:
- LCRD is a technology demonstration that will pave the way for future optical communications missions.
- The LCRD payload is hosted onboard the US Department of Defense’s Space Test Program Satellite 6 (STPSat-6).
- It will be in a geosynchronous orbit, over 35,000km above Earth.
- Optical communications systems are smaller in size, weight, and require less power compared with radio instruments.
- A smaller size means more room for science instruments.
- Less weight means a less expensive launch.
- Less power means less drain on the spacecraft’s batteries.
- With optical communications supplementing radio, missions will have unparalleled communications capabilities.
Laser VS radio:
- Laser communications and radio waves use different wavelengths of light.
- Laser uses infrared light and has a shorter wavelength than radio waves. T
- his will help the transmission of more data in a short time.
Raigad Fort:

President Ram Nath Kovind recently visited Raigad Fort and paid tribute to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- The fort, which was earlier called Rairi, was the seat of the Maratha clan Shirke in the 12th century.
- The fort changed hands a number of times from the dynasty of Bahaminis to the Nizamshahis and then the Adilshahis.
- In 1656, Chhatrapati Shivaji captured it from the More’s of Javli who were under the suzerainty of the Adilshahi Sultanate.
- In 1662, Shivaji formally changed the fort’s name to Raigad and added a number of structures to it. By 1664, the fort had emerged as the seat of Shivaji’s government.
- The fort not only helped Shivaji challenge the supremacy of the Adilshahi dynasty but also opened up the routes towards Konkan for the extension of his power.
- The fort was known to early Europeans as the Gibraltar of the East. Its decisive feature is a mile and a half flat top which has adequate room for buildings. In its prime, the fort had 300 stone houses and a garrison of 2,000 men.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji is the tallest and the most revered icon in Maharashtra and there is a constant attempt by political parties of all hues to appropriate his legacy.
- Due to the significance of Raigad in his life, many political leaders make it a point to visit the fort.
India- Russia Annual Summit:

21st annual India-Russia summit was held recently. It was attended by Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Russian President Vladimir Putin.
- Alongside, the inaugural 2+2 ministerial meeting was also held.
- The meeting saw the signing of 28 agreements across sectors from defence to energy to space exploration, science and technology, heavy engineering, to trade and investment.
- Russia’s President Vladimir Putin extended an invitation to PM Modi to visit Russia for the 22nd India-Russia Annual Summit in 2022.
- The two leaders expressed satisfaction at the sustained progress in the ‘Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership’ between both countries despite the challenges posed by the Covid.
- The role of connectivity through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and the proposed Chennai-Vladivostok Eastern Maritime Corridor figured in the discussions.
- The two leaders looked forward to greater inter-regional cooperation between various regions of Russia, in particular with the Russian Far East, with India’s states.
- They agreed that both countries share common perspectives and concerns on Afghanistan and appreciated the bilateral roadmap charted out at the NSA level for consultation and cooperation on Afghanistan.
- The completion of 5 decades of the 1971 Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation and 2 decades of Declaration on Strategic Partnership is symbolic of the long standing and time-tested India-Russia relations characterized by mutual trust, respect for each other’s core national interests and similarity of positions on various international and regional issues.
Narcotic Drugs And Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Bill, 2021 was recently introduced in Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to replace an ordinance promulgated on September 30 this year.
- The bill was introduced by the government to rectify an error that made provisions in Section 27 of the Act — providing for punishment of those financing illicit trafficking — inoperable.
- This happened in 2014, when the Act was amended in 2014 to ease access of narcotic drugs for medical necessities, but the penal provision was not amended accordingly.
- In June 2021, the Tripura High Court found the oversight in the law and directed the Union Home Ministry to amend the provisions of Section 27.
- The drafting error was highlighted when an accused moved a special court in Tripura contending that he could not be charged for the offence as Section 27 A is referred to a blank list.
- The Tripura High Court subsequently asked the Centre to amend the law.
- The anomaly crept in when the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act was amended in 2014 to allow better medical access to narcotic drugs, removing state barriers in transporting and licensing of “essential narcotic drugs”.
- Prior to the 2014 amendment, clause (viiia) of Section 2 of the Act, contained sub-clauses (i) to (v), wherein the term ‘illicit traffic’ had been defined.
- This clause was re-lettered as clause (viiib) by the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Act, 2014, as a new clause (viiia) in section 2 defining ‘essential narcotic drugs’ was inserted. However, inadvertently consequential change was not carried out in section 27A of the NDPS Act.
- Few experts have observed that the Bill violated the fundamental rights of a citizen as it provides retrospective effect to offences starting 2014.
- It also violates the fundamental rights in Article 21 because you can be punished for an offence for which there is a law in existence at the time of commission of the offence.
Aatmanirbhar Skilled Employees Employer Mapping (ASEEM) Portal:

Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship has launched Aatmanirbhar Skilled Employees Employer Mapping (ASEEM) portal, which acts as a directory of skilled workforce.
- The objective is to provide a platform that matches supply of skilled workforce with the market demand, thereby facilitating better livelihood opportunities for youth and availability of ready skilled manpower to employers.
- ASEEM portal is being managed by National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) under the aegis of Ministry.
- As on 16.07.2021, 1.3 crore candidates have been registered on ASEEM portal which includes directly registered candidates and the candidates registered on Skill India Portal (SIP).
- ASEEM as such consists of three IT based AI (artificial intelligence) driven interfaces for stakeholder interactions:
- A job application for individuals with access to hyper local jobs using machine learning and automated match based on persona.
- A demand and campaign management system for employers to forecast the current and future demand.
- A management dashboard for analytics and insights. This could also be used for future decision making.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
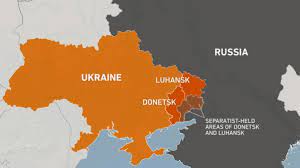
The US intelligence reports said the tension on the Russia-Ukraine border represents a major security crisis for the region, with the potential to snowball into a broader conflict.
- Ukraine says that Russia has amassed around 90,000 troops at the border.
- Ukraine and Russia share hundreds of years of cultural, linguistic and familial links.
- For many in Russia and in the ethnically Russian parts of Ukraine, the shared heritage of the countries is an emotional issue that has been exploited for electoral and military purposes.
- As part of the Soviet Union, Ukraine was the second-most powerful Soviet republic after Russia, and was crucial strategically, economically and culturally.
Cause of Conflict:
- Balance of Power: Ever since Ukraine split from the Soviet Union, both Russia and the West have vied for greater influence in the country in order to keep the balance of power in the region in their favour.
- Buffer Zone for Western Countries: For the US and the European Union, Ukraine is a crucial buffer between Russia and the West.
- As tensions with Russia rise, the US and the EU are increasingly determined to keep Ukraine away from Russian control.
- Russian Interest in Black Sea: The unique geography of the Black Sea region confers several geopolitical advantages to Russia.
Firstly, it is an important crossroads and strategic intersection for the entire region. - Access to the Black Sea is vital for all littoral and neighboring states, and greatly enhances the projection of power into several adjacent regions.
- Secondly, the region is an important transit corridor for goods and energy
65th Mahaparinirvan Diwas:

Prime Minister has paid tributes to Babasaheb Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar on Mahaparinirvan Diwas.
- Parinirvana, regarded as one of the major principles as well as goals of Buddhism, is a Sanskrit term which means release or freedom after death.
- As per the Buddhist text Mahaparinibbana Sutta, the death of Lord Buddha at the age of 80 is considered as the original Mahaparinirvana.
- 6th December is observed to commemorate the unfathomable contribution to society given by Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar and his achievements.
- Owing to Ambedkar’s status as a Buddhist leader, his death anniversary is referred to as Mahaparinirvana Diwas.
Babasaheb Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar:
- Birth: 14th April 1891 in Mhow, Central Province (now Madhya Pradesh).
- Dr. Ambedkar was a social reformer, jurist, economist, author, polyglot orator and a scholar of comparative religions.
- In 1916, he received a doctorate degree from Columbia University, becoming the first Indian to do so.
- He is known as the Father of the Indian Constitution and was India’s first law minister.
- He established a fortnightly newspaper “Mooknayak” in 1920 which laid the foundations of an assertive and organised Dalit politics.
- He founded Bahishkrit Hitkarini Sabha (1923), devoted to spreading education and culture amongst the downtrodden.
- He was appointed by the Bombay Presidency Committee to work in the Simon Commission in 1925.
- He led the Mahad Satyagraha in March 1927 to challenge the regressive customs of the Hindus.
- The Kalaram Temple Movement of 1930 formed a pivotal role in the Dalit movement in India in which Ambedkar led a protest outside the Kalaram temple which did not allow Dalits to enter the temple premises.
- He participated in all three round-table conferences.
- In 1932, he signed the Poona pact with Mahatma Gandhi, which abandoned the idea of separate electorates for the depressed classes (Communal Award).
- However, the seats reserved for the depressed classes were increased from 71 to 147 in provincial legislatures and to 18% of the total in the Central Legislature.
- In 1936, he was elected to the Bombay Legislative Assembly as a legislator (MLA).
- In 1947, he was appointed Chairman of the Drafting Committee for the new Constitution.
- He accepted Prime Minister Nehru’s invitation to become Minister of Law in the first Cabinet of independent India.
- He resigned from the Cabinet in 1951, over differences on the Hindu Code Bill (aimed at reforming Hindu society).
- In 1956, he converted to Buddhism.
- He passed away on 6th December 1956.
- He was conferred Bharat Ratna in 1990.
- Chaitya Bhoomi is a memorial to B.R. Ambedkar which is located in Dadar, Mumbai.
- Important Works: Newspaper Mooknayak (1920); The Annihilation of Caste (1936); The Untouchables (1948); Buddha Or Karl Marx (1956), The Buddha and His Dhamma (1956), etc.
Hornbill Festival:

The state government has decided to call off the ongoing Hornbill Festival in protest against the killing of 14 civilians by security forces.
- Nagas celebrate this festival to revive, protect, sustain and promote the richness of the Naga heritage and traditions.
- It occurs during 1 – 10 December on an annual basis.
- It is also called the “Festival of Festivals”.
- The festival pays tribute to Hornbill, the most admired and revered bird for the Nagas for its qualities of alertness and grandeur.
- It is organized by State Tourism and Art & Culture Departments and also supported by Union Government.
- Hornbill Festival was established on 1st December 1963 and was inaugurated by the then President Dr. S Radhakrishnan




