Today Current Affairs: 11th August 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
9th Instalment Of Financial Benefit Under Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):

The Prime Minister released the 9th instalment of financial benefit under Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN).
- Further, the Prime Minister also interacted with farmer beneficiaries during the event.
PM-KISAN:
- Under the scheme, the Centre transfers an amount of Rs 6,000 per year, in three equal instalments, directly into the bank accounts of all landholding farmers irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- It was launched in February 2019.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Identification of Beneficiaries: - The entire responsibility of identification of beneficiary farmer families rests with the State/UT Governments.
- Objectives:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.
World Tribal Day, 2021:

World Tribal Day or International Day of the World’s Indigenous Peoples is observed on 9th August every year.
- It is aimed at promoting and protecting the rights of the world’s indigenous population and to acknowledge the contributions that indigenous people make towards world issues such as environmental protection.
- The day recognizes the first meeting of the United Nations Working Group on Indigenous Populations in Geneva in 1982.
- It has been celebrated every year since 1994, in accordance with the declaration by the United Nations.
- To date, numerous indigenous peoples experience extreme poverty, marginalization, and other human rights violations.
- Theme 2021: “Leaving no one behind: Indigenous peoples and the call for a new social contract.”
- Indigenous peoples are inheritors and practitioners of unique cultures and ways of relating to people and the environment.
- They have retained social, cultural, economic and political characteristics that are distinct from those of the dominant societies in which they live.
- There are over 476 million indigenous peoples living in 90 countries across the world, accounting for 6.2% of the global population.
India Plastics Pact

The India Plastics Pact, the first in Asia, will be launched in September in collaboration with Confederation of Indian Industries (CII) and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
- Recently, a report published on closing the plastic circular Gap, suggested that there is a dire need to make large scale global interventions to manage plastic waste.
- The Plastics Pacts are business-led initiatives and transform the plastics packaging value chain for all formats and products.
- The Pacts bring together everyone from across the plastics value chain to implement practical solutions.
- The India Plastics Pact is an ambitious, collaborative initiative that aims to bring together businesses, governments and NGOs across the whole value chain to set time-bound commitments to reduce plastics from their value chains.
- While the India Plastics Pact will be active in India, it will link globally with other Plastics Pacts.
- The Pact will develop a road map for guidance, form action groups composed of members, and initiate innovation projects.
- Members’ accountability is ensured through ambitious targets and annual data reporting.
- The vision, targets and ambition of the India Plastics Pact are aligned with the circular economy principles of the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy.
- The Pact aims to transform the current linear plastics system into a circular plastics economy that will:
- Reduce the use of problematic plastics,
- Retain valuable materials in the economy for use in other products,
- Generate jobs, investment and opportunities in the plastics system in India.
- It aims to promote public-private collaborations that enable solutions to eliminate the plastics we do not need, bring innovation to packaging design, and to capture the value of the plastics we use.
EUBOEA:

Wildfires are continuing to rip through the Greek island of Evia with strong winds driving flames towards villages. Greece is experiencing its most severe heatwave in 30 years in which temperatures have spiked to 45C.
- Euboea or Evia is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete.
- It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait.
- Euboea was believed to have originally formed part of the mainland, and to have been separated from it by an earthquake.
- This is fairly probable, because it lies in the neighbourhood of a fault line.
Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021:

Parliament has passed the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021 with the Lok Sabha clearing it. The Rajya Sabha has already approved it.
- The Bill amends the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
- The Constitution empowers the President to specify the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in various states and union territories.
- Further, it permits Parliament to modify this list of notified STs.
- The Bill removes the Abor tribe from the list of identified STs in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Further, it replaces certain STs with other tribes in the list
- Khampti is replaced with Tai Khamti,
- Mishmi, Idu, and Taroan are replaced with Mishmi-Kaman (Miju Mishmi), Idu (Mishmi), and Taraon (Digaru Mishmi),
- Momba is replaced with Monpa, Memba, Sartang, and Sajolang (Miji)
- Any Naga Tribes is replaced with Nocte, Tangsa, Tutsa, and Wancho.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
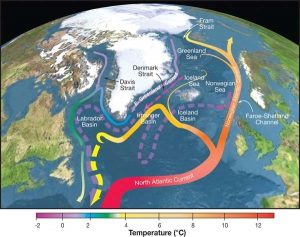
A study published in Nature Climate Change notes that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), is losing its stability. According to the IPCC’s Report (AR6) released on August 9, it is very likely that AMOC will decline over the 21st century.
- The AMOC is a large system of ocean currents. It is the Atlantic branch of the ocean conveyor belt or Thermohaline circulation (THC), and distributes heat and nutrients throughout the world’s ocean basins.
- AMOC carries warm surface waters from the tropics towards the Northern Hemisphere, where it cools and sinks. It then returns to the tropics and then to the South Atlantic as a bottom current. From there it is distributed to all ocean basins via the Antarctic circumpolar current.
- The findings support the assessment that the AMOC decline is not just a fluctuation or a linear response to increasing temperatures but likely means the approaching of a critical threshold beyond which the circulation system could collapse.
- Gulf Stream, a part of the AMOC, is a warm current responsible for mild climate at the Eastern coast of North America as well as Europe. Without a proper AMOC and Gulf Stream, Europe will be very cold.
- Modelling studies have shown that an AMOC shutdown would cool the northern hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe. It can also have an effect on the El Nino.
Seekho Aur Kamao Scheme

Minister of Minority affairs informed Rajya Sabha about the Seekho Aur Kamao scheme.
- Seekho Aur Kamao is a skill development scheme for youth of 14 – 35 years age group and aiming at providing employment and employment opportunities, improving the employability of existing workers, school dropouts etc.
- The scheme ensures 75% placement, out of which 50% should be in organized sector.
- As per scheme guidelines, the implementing organizations will be required to establish linkages with placement services.
- For the candidates interested in self employment after availing the training, the organization shall arrange easy micro finance/ loans for them through financial institutions, National Minority Development Finance Corporation (NMDFC), banks etc.
- Post placement support of Rs. 2000/- per month is provided to placed trainees for two months as placement assistance.
- In the last 7 years appx. 3.92 lakh persons have been benefitted under this employment oriented scheme.
India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) -2021:

Anil Kumar Jain, the CEO, National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI), Ministry of Electronics & IT and the Chairman of Coordination Committee, India Internet Governance Forum 2021 (IGF), announced the launch of India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) -2021.
- The Forum will act as the platform for various stakeholders to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet
- IIGF- 2021 will be planned for three days, starting from 20th October, 2021. The theme of this year’s meeting is Inclusive Internet for Digital India.
- With this announcement, the Indian chapter of the United Nations based forum namely Internet Governance Forum has begun.
- It’s an Internet Governance policy discussion platform to bring representatives together from various groups, considering all at par to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
- Multi Stakeholder concept
- This mode of engagement is referred to as the multi-stakeholder model of Internet Governance, which has been the key feature for the Internet’s success.
- Multi Stakeholder concept is well adopted by IGF (Internet Governance Forum) under United Nations and by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
Bio-Bank Of The World In Ayurveda

Union Ayush Minister assured all help for establishing the first Bio-Bank of the world in Ayurveda at All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA).
- AIIA is a public Ayurveda medicine and research institution located in New Delhi.
- It was established in 2015.
- It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of AYUSH.
- The institute would offer postgraduate and doctoral courses in various disciplines of Ayurveda and will focus on fundamental research of Ayurveda, drug development, standardization, quality control, safety evaluation and scientific validation of Ayurvedic medicine.
Mid-Day Meal Scheme:

A national level meet was recently organised by the National Human Rights Commission to discuss the status of various policies to ensure Right to Food and nutrition.
Following are the suggestions made by the experts at the end of the meet:
- Extend the midday meal scheme up to Class XII.
- Start an urban employment guarantee scheme.
- Come up with a public distribution system (PDS) not exclusively linked to Aadhaar.
About the Mid-Day meal scheme:
- The scheme guarantees one meal to all children in government and aided schools and madarsas supported under Samagra Shiksha.
- Students up to Class VIII are guaranteed one nutritional cooked meal at least 200 days in a year.
- The Scheme comes under the Ministry of HRD.
- It was launched in the year 1995 as the National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education (NP – NSPE), a centrally sponsored scheme. In 2004, the scheme was relaunched as the Mid Day Meal Scheme.
- The Scheme is also covered by the National Food Security Act, 2013.
Objective:
- Address hunger and malnutrition, increase enrolment and attendance in school, improve socialisation among castes, provide employment at grassroot level especially to women.
Nutritional norms:
- In terms of calorie intake, as per the MDM guidelines, the children in primary schools must be provided with at least 450 calories with 12 grams of protein through MDM while the children in upper primary schools should get 700 calories with 20 grams of protein, as per MHRD.
- The food intake per meal by the children of primary classes, as provided by MHRD is 100 grams of food grains, 20 grams of pulses, 50 grams of vegetables and 5 grams of oils and fats.
- For the children of upper-primary schools, the mandated breakup is 150 grams of food grains, 30 grams of pulses, 75 grams of vegetables and 7.5 grams of oils and fats.
South Africa Grants Patent To An Artificial Intelligence System:

South Africa, first time in the world, has granted a patent to an ‘artificial intelligence system’ relating to a “food container based on fractal geometry” innovation.
- The innovation involves interlocking food containers that are easy for robots to grasp and stack.
- The patent has been given to an artificial intelligence (AI) system (called DABUS); not a human being.
- DABUS stands for “device for the autonomous bootstrapping of unified sentience”.
- It is an AI system created by Stephen Thaler, a pioneer in the field of AI and programming.
- The system simulates human brainstorming and creates new inventions.
- DABUS is a particular type of AI, often referred to as “creativity machines” because they are capable of independent and complex functioning.
- Creativity machines can process and critically analyse data, learning from it.
- This process is known as machine learning.
- Once the machine learning phase has occurred, the machine is able to “autonomously” create without human intervention.
- The patent application listing DABUS as the inventor was filed in patent offices around the world, including the U.S., Europe, Australia, and South Africa.
- The United States Patent and Trademark Office and the European Patent Office rejected these applications in the formal examination phase.
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change (IPCC):

The Indian Ocean is warming at a higher rate than other oceans, said the latest report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released.
- The authors of the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report, “Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis”, said the warming of the ocean would lead to a rise in sea levels, leading to frequent and severe coastal flooding in low-level areas.
- The planet was irrevocably headed towards warming by 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial times in the next two decades.
- The report recommended that countries strive to achieve net zero emissions — no additional greenhouse gases are emitted — by 2050.
- The Fifth Assessment Report was released in 2014.
- India will witness increased heatwaves and flooding, which will be the irreversible effects of climate change.
- The current overall global warming trends are likely to lead to an increase in annual mean precipitation over India, with more severe rain expected over southern India in the coming decades.
- With a 7,517-km coastline, India would face significant threats from the rising seas.
- The 3,000-plus-page report said warming is already accelerating sea level rise and worsening extremes such as heatwaves, droughts, floods and storms.




