Today’s Current Affairs: 1st sep 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
CE-20 Cryogenic Rocket Engine : Successfully Tested For Mission Gaganyaan

Indian Space Research Organisation’s Liquid Propulsion Research Centre (IPRC) in Mahendragiri has successfully tested the cryogenic rocket engine to be used in its ‘Mission Gaganyaan’.
- CE-20 cryogenic engine has been designed and developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), a subsidiary of ISRO.
- It will power the Cryogenic Upper Stage of the LVM3launch vehicle.
- ISRO will use it for its ‘Mission Gaganyaan’ for sending man to space in 2024.
- It is the first Indian cryogenic engine to feature a gas-generator cycle.
- It is one of the most powerful upper-stage cryogenic engines in the world.
- This engine develops a nominal thrust of 186.36 kN in vacuum.
- The cryogenic stage is technically a very complex system due to its use of propellants at extremely low temperatures and the associated thermal and structural problems.
- It uses liquid fuels (Oxygen liquifies at -183 deg C and Hydrogen at -253 deg C) that are cooled to very low temperatures.
- A Cryogenic rocket stage is more efficient and provides more thrust for every kilogram of propellant it burns compared to solid and earth-storable liquid propellant rocket stages.
Mahendragiri Frigate:

India’s latest warship, Mahendragiri, at the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Mumbai launched
- It is the seventh and last stealth frigate of Project 17A Frigates.
- It is named after a mountain peak in Eastern Ghats located in Odisha.
- The ship is being built by the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai.
- Project 17A was launched by the defence forces of India to construct a series of stealth guided-missile frigates.
- Under the Project 17A programme, four ships by Mumbai-based Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and three by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE) are being built.
- These warships follow the Project 17 Class Frigates (Shivalik Class) and boast enhanced stealth features, advanced weapons, sensors, and platform management systems.
- Project 17A ships have been designed in-house by the Indian Navy’s Warship Design Bureau WDB.
- As much as 75% of the orders for equipment and systems of Project 17A ships are from indigenous firms, including MSMEs.
- The first six ships of the project have been launched so far by MDL & GRSE between 2019-2023.
India’s 6th Minor Irrigation Census:

The Ministry of Jal Shakti has released the 6th census of minor irrigation schemes (with reference year 2017-18), shedding light on the state of irrigation practices across India.
- So far, five censuses were conducted in 1986-87, 1993-94, 2000-01, 2006-07, and 2013-14.
Highlights of the Report:
- A total of 23.14 million minor irrigation (MI) schemes have been reported in the country.
- Among these, 21.93 million (94.8%) are groundwater (GW) schemes, and 1.21 million (5.2%) are Surface Water (SW) schemes.
- Dug-wells have the highest share in MI schemes followed by shallow tube-wells, medium tube-wells and deep tube-wells.
- The 6th MI census recorded an increase of about 1.42 million MI schemes compared to the previous census.
- Nationally, GW schemes saw a 6.9% increase, while SW schemes increased by 1.2%.
- Uttar Pradesh leads in MI schemes in India, followed by Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
- Maharashtra is the leading State in dug-wells, surface flow and surface lift schemes.
- Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka and Punjab are the leading States in shallow tube-wells, medium tube-wells and deep tube-wells, respectively.
- In SW schemes, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Odisha and Jharkhand have the highest share.
- Approximately 96.6% of MI schemes are under private ownership.
- Among GW schemes, 98.3% are owned by private entities, and in SW schemes, this share is 64.2%.
- For the first time, data on the gender of MI scheme owners was collected.
- 18.1% of individually owned schemes are owned by women.
- Around 60.2% of schemes are financed through a single source.
- Own savings of individual farmers contribute significantly to single-source financing (79.5%).
- 39.8% of schemes have more than one source of finance.
World Sanskrit Day 2023:

In 2023, the celebration of World Sanskrit Day takes place on 31st August.
- The first World Sanskrit Day was celebrated in 1969.
- World Sanskrit Day or Vishwa Sanskrit Diwas is celebrated on Purnima Tithi (Full moon) of Shravana month every year.
- It serves as a tribute to the birth anniversary of Paṇini, a distinguished Sanskrit scholar and grammarian.
- This day is celebrated to show gratitude and respect towards the Sanskrit language.
- Sanskrit is among the 22 official languages included in the Eight Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- It is also included among 6 Classical languages besides Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, and Odia.
- In 2010, Sanskrit was declared the second official language of Uttarakhand.
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) Report:

The Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report by the University of Chicago reveals that fine particulate air pollution (Particulate Matter 2.5) reduces the average Indian’s life expectancy by 5.3 years.
- This figure is based on the World Health Organization’s (WHO) guideline of 5 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3)
Key Findings:
- Particulate pollution is the primary threat to Indian health, reducing life expectancy by 5.3 years on average.
- Cardiovascular diseases diminish life expectancy by about 4.5 years, while malnutrition reduces it by 1.8 years.
- All 1.3 billion Indians live in areas exceeding the WHO guideline for annual average particulate pollution.
- Approximately 67% of the population lives in regions surpassing India’s own air quality standard of 40 µg/m3
- India contributed over 59% of the world’s increase in pollution from 2013 to 2021.
- The Northern Plains are the most polluted region in India and about 39% of residents may lose eight years of life expectancy compared to WHO guidelines.
Pacific Decadal Oscillation:
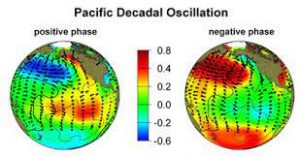
A recent study revealed that a cyclical event called the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, which repeats every 20-30 years, could make cyclones that originate near the Equator more frequent in the coming years.
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a long-term ocean fluctuation in the Pacific Ocean.
- The term PDO was coined in about 1996 by Steven Hare at the University of Washington.
- It can be known only after several years of measuring ocean temperatures and their interaction with the atmosphere.
- The PDO waxes and wanes approximately every 20 to 30 years.
- From ocean surface topography data, together with other ocean and atmospheric data, scientists can determine whether we are in a ‘cool’ phase or a ‘warm’ phase.
- Cool phase is characterised by a cool wedge of lower-than-normal sea-surface heights/ocean temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific and a warm horseshoe pattern of higher-than-normal sea-surface heights connecting the north, west and southern Pacific.
- Warm’ or ‘positive’ phase occurs when the west Pacific Ocean becomes cool, and the wedge in the east warms.
- The change in location of the cold and warm water masses alters the path of the jet stream.
- The jet stream in the northern hemisphere delivers storms across the United States.
Successful Sequencing Of Y Chromosome:
For the first time, scientists have successfully sequenced the Y chromosome, providing insights that could impact the understanding of male infertility and various health issues.
- Y chromosome sequence will aid the study of conditions and disorders linked to this chromosome, including male infertility.
- Significance for health and longevity, as it contains genes related to cancer and cardiovascular disease prevention.
- Y chromosome’s role in age-associated diseases, men’s shorter lifespans, and cellular ageing could be further explored with this complete sequence.
- The Y chromosome presented challenges due to its repetitive nature.
- Unlike other chromosomes, a significant portion of the Y chromosome consists of repetitive sequences and palindromes.
PRIP Scheme : Approved

The Union Cabinet approved the Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma-MedTech sector (PRIP) scheme.
- The scheme has an outlay of ₹5,000 crore for five years, from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
- Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma-MedTech sector (PRIP) scheme launched in 2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- Objectives is to transform the Indian Pharma MedTech sector from cost-based to innovation-based growth by strengthening the research infrastructure in the country.
- The scheme promotes industry-academia linkage for R&D in priority areas to inculcate the culture of quality research and nurture our pool of scientists. (Integrated Pharmaceutical Database Management System 2.0)
- The scheme is proposed to have two components as follows:-
- Component A: Strengthening the Research Infrastructure, It will encompass the setting up of Centres of Excellence at the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research (NIPERs).
- Component B: Promotion of Research in Pharma MedTech sector.




