Mitochondrial DNA Mutations : Study
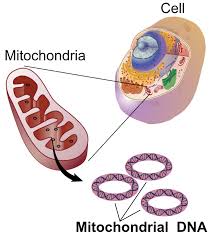
A recent study published in Genome Research highlights that deletion mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) play a significant role in age-related muscle loss.
Findings on the mtDNA Mutations:
- Deletion mutations in mtDNA reduce its size and functionality, gradually eroding mitochondrial efficiency.
- These mutated mtDNA molecules outcompete healthy ones, leading to a decline in ATP production.
- Deletion mutations create chimeric genes by fusing different mitochondrial genes, forming abnormal sequences.
- Chimeric genes disrupt mtDNA expression, accelerating mitochondrial dysfunction and muscle degradation.
- Older individuals exhibit a two-fold increase in chimeric mitochondrial mRNA, correlating with biological aging.
- Mutations also affect brain and muscle tissues, emphasizing their systemic impact on aging.
- mtDNA deletion mutations and chimeric mRNA are key indicators of biological aging.
- Understanding these markers could pave the way for therapies to prevent or repair mutations, delaying age-related muscle loss.




