Mycetoma : Study
The world’s only research centre on mycetoma, a neglected tropical disease common among farmers, has been destroyed in Sudan’s two-year war, its director and another expert say.
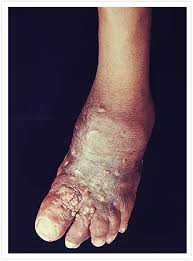
- Mycetoma is a chronic, progressively destructive infectious disease of the subcutaneous tissues, that spreads to affect the skin, deep tissues and bone.
- It was first reported in the mid-19th century in Madurai, India, and hence was initially called Madura foot.
- It is a unique neglected tropical disease caused by a substantial number of microorganisms of fungal or bacterial origins.
- The disease commonly affects young adults, mostly males aged between 15 and 30 years in developing countries.
- Mycetoma occurs in tropical and subtropical environments characterized by short rainy seasons and prolonged dry seasons that favour the growth of thorny bushes.
- The causative organisms of mycetoma are distributed worldwide but are endemic in tropical and subtropical areas in the so called ‘Mycetoma belt’, which includes, among others, Venezuela, Chad, Ethiopia, India, Mauritania, Mexico, Senegal, Somalia, Sudan, Thailand, and Yemen.
- Transmission occurs when the causative organism enters the body through minor trauma or a penetrating injury, commonly thorn pricks.
- There is a clear association between mycetoma and individuals who walk barefooted and are manual workers.
- Symptoms are similar for bacterial and fungal mycetoma.
- Both appear as firm, painless masses under the skin. These masses usually appear on a person’s foot but can form anywhere on the body.
- Mycetoma masses start small, but over time they can grow larger and develop oozing sores.
- The affected limb can become deformed or unusable.
- The discharge from the oozing sores can contain sand-like particles called “grains,” that can be white, yellow, red, brown, or black.
- If left untreated or treatment fails, it can spread to other areas of the body and even result in blood infections.
- Long-term mycetoma can eventually destroy the underlying muscle and bone.
- For bacterial mycetoma, treatment consists of a combination of antibiotics, whereas for fungal mycetoma, treatment consists of a combination of antifungal drugs and surgery.




