Zonal Councils:
The Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation chaired the 25th Central Zonal Council meeting in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, organized by the Inter-State Council Secretariat in collaboration with the Uttar Pradesh Government.
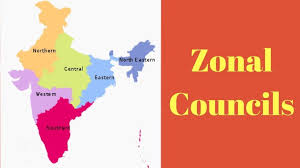
- Zonal Councils are statutory bodies (not constitutional) established under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, as a high-level advisory forum to foster cooperative working among states and to create a healthy inter-State and Centre–State environment.
- The idea of Zonal Councils was first proposed by former Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru in 1956 during debates on the States Reorganisation Commission’s (Fazal Ali Commission, 1953) Report.
- Under Sections 15 to 22 of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, five Zonal Councils were established.
- The North Eastern region has a separate council, the North Eastern Council, created in 1972, set up under the North Eastern Council Act, 1972.
- Union Home Minister (for all 5 Zonal Councils). He is also the ex-officio Chairman of the North Eastern Council (NEC).
Vice-Chairman: Chief Minister of one of the member states (by annual rotation). - The members include the Chief Ministers, Lieutenant Governors, or Administrators of the member States and Union Territories.
- Additionally, from each member state, the Governor nominates two ministers as members of the Council.
- One nominee from NITI Aayog (earlier Planning Commission), Chief Secretaries, and Development Commissioners of the member states.
- Each Zonal Council has a Permanent Committee comprising the Chief Secretaries of member states.
- State-proposed issues are first discussed by this committee, and unresolved matters are then placed before the full Zonal Council for further deliberation.
- Zonal Councils serve as a structured platform for dialogue and coordination on issues involving two or more states or the Centre and states, promoting mutual understanding and cooperation.




