Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 1st July 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- State of the World Population 2020 report:
- TOP (Tomato-Onion-Potato) :
- National level committee for reform in criminal law.:
- G4 Flu Virus:
- CogX 2020:
- Other important current affairs
1. State of the World Population 2020 report:
Recently, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) has released the State of the World Population 2020 report, titled ‘Against my will: defying the practices that harm women and girls and undermine equality’.
- It highlights at least 19 human rights violations against women and focuses on the three most prevalent ones, Female Genital Mutilation (FGM), extreme bias against daughters, in favor of sons and child marriage.
Global Data:
- The number of missing women has more than doubled over the past 50 years, who were at 61 million in 1970.
Missing females/women:
- These are women missing from the population at given dates due to the cumulative effect of postnatal and prenatal sex selection in the past. The phrase was coined by Amartya Sen.
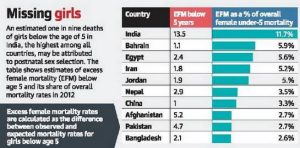
- In Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan excess female mortality of girls below 5 years of age was under 3%.
Excess female mortality:
- It is the difference between observed and expected mortality of the girl child or avoidable death of girls during childhood.
- According to estimates averaged over a five year period (2013-17), annually, there were 1.2 million missing female births, at a global level.
- One in three girls missing globally due to sex selection, both pre- and post-natal, is from India, i.e. 46 million out of the total 142 million.
- India has the highest rate of excess female deaths at 13.5 per 1,000 female births or one in nine deaths of females below the age of 5 due to postnatal sex selection.
- In India, around 460,000 girls went missing at birth, which means they were not born due to sex-selection biases, each year between 2013 and 2017.
- India (40%) along with China (50%) account for around 90% of the estimated 1.2 million girls lost annually to female foeticide.
Female Genital Mutilation:
- It involves the partial or total removal of external female genitalia or other injuries to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons.
- The practice has no health benefits for girls and women and can cause severe bleeding, problems in urinating, cysts, infections, as well as complications in childbirth and increased risk of newborn deaths.
- An estimated 4.1 million girls will be subjected to female genital mutilation in 2020.
- Extreme Bias against Daughters, in favor of sons: An extreme and continuing preference for sons over daughters in some countries has fuelled gender-biased sex selection or extreme neglect which leads to girls’ death as children, resulting in missing females.
- The report examines the issue of missing women by studying sex ratio imbalances at birth as a result of gender-biased sex selection as well as excess female mortality.
The advent of technology and increased access to ultrasound imaging allow parents to terminate a foetus after knowing its gender.
Marriage squeeze:
- It happens when prospective grooms far outnumber prospective brides, which further results in human trafficking for marriage as well as child marriages.
These violations result in fewer choices for females and putting them under the sexual, economic and legal control of men, curbing their human rights.
Child Marriage:
- Every day, around 33,000 girls under age 18 are forced into marriage, usually to much older men.
In India, child marriage is directly linked to poverty, poor education and geographic location and the rural and urban divide.
2.TOP (Tomato-Onion-Potato) :

Union Minister for Food Processing announced the Extension of Operation Greens from TOP (Tomato-Onion-Potato) crops to all Perishable Fruits & Vegetables (TOP to Total).
- Operation Greens Scheme, being implemented by MoFPI has been extended from tomato, onion, and potato (TOP) crops to other notified horticulture crops for providing subsidy for their transportation and storage from the surplus production area to major consumption centers.
- The objective of the intervention is to protect the growers of fruits and vegetables from making distress sale due to lockdown and reduce the post-harvest losses.
- Duration of Scheme: For the period of six months from the date of notification i.e., 11/06/2020.
- Eligible entities: Food Processors, FPO/FPC, Co-operative Societies, Individual farmers, Licensed Commission Agent, Exporters, State Marketing/Co-operative Federation, Retailers, etc. engaged in processing/ marketing of fruits and vegetables.
- The pattern of Assistance: Ministry will provide subsidy @ 50 % of the cost of the following two components, subject to the cost norms – Transportation of eligible crops from surplus production cluster to consumption center; and/or Hiring of appropriate storage facilities for eligible crops (for maximum period of 3 months).
3.National level committee for reform in criminal law.:

Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has constituted a national level committee for reform in criminal law.
Committee For Reform In Criminal Law:
- The committee has been constituted under Ranbir Singh and several other members.
- The committee would be gathering opinions online by consulting with experts and collating material for their report to the government.
- The consultation exercise would start on 4th July 2020 and go on for the next three months.
- The codification of criminal laws in India was done during the British rule, which more or less remains the same even in the 21st century.
- Lord Thomas Babington Macaulay is said to be the chief architect of codifications of criminal laws in India.
- Criminal law in India is governed by the Indian Penal Code, 1860, Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, and Indian Evidence Act, 1872, etc.
Need for Reforms:
- Colonial Era Laws: The criminal justice system is a replica of the British colonial jurisprudence, which was designed with the purpose of ruling the nation and not serving the citizens.
- The purpose of the criminal justice system was to protect the rights of the innocents and punish the guilty, but nowadays the system has become a tool of harassment of common people.
- According to Economic Survey 2018-19, there are about 3.5 crore cases pending in the judicial system, especially in the district and subordinate courts, which leads to the actualisation of the maxim “Justice delayed is justice denied.”
- India has one of the world’s largest number of undertrial prisoners.
- According to NCRB -Prison Statistics India (2015), 67.2% of our total prison population comprises undertrial prisoners.
- Investigation: Corruption, huge workload, and accountability of police is a major hurdle in speedy and transparent delivery of justice.
- Madhav Menon Committee: It submitted its report in 2007, suggesting various recommendations on reforms in the CJSI.
- Malimath Committee Report: It submitted its report in 2003 on the Criminal Justice System of India (CJSI).
- The Committee had opined that the existing system “weighed in favor of the accused and did not adequately focus on justice to the victims of crime.” It has provided various recommendations to be made in the CJSI, which were not implemented.
4.G4 Flu Virus:

Recently, scientists have identified a “newly emerged” strain of influenza virus that is infecting Chinese pigs and that has the potential of triggering a pandemic.
- Named G4, scientists believe that it has descended from the H1N1 strain that was responsible for the 2009 swine flu pandemic.
- A Pandemic happens if a new strain emerges that can easily spread from person to person.
- G4 Strain:
- It was identified through surveillance of influenza viruses in pigs through a study carried out from 2011 to 2018 in ten provinces of China.
- It can grow and multiply in the cells that line the human airways.
- It has the capability of binding to human-type receptors (like the SARS-CoV-2 virus).
- Scientists found evidence of recent infection in people who worked in abattoirs and the swine industry in China.
- However, it is not clear whether the new strain can transmit from one human to another.
- Current flu vaccines do not appear to protect against it, although they could be adapted to do so if needed.
5.CogX 2020:

Recently MyGov Corona Helpdesk Chatbot has bagged two awards under categories (1) “Best Innovation for Covid-19 – Society” and (2) “People’s Choice Covid-19 Overall Winner” at the recently held CogX 2020.
- CogX is a prestigious Global Leadership Summit and Festival of Artificial Intelligence & Emerging Technology held annually in London with over 15,000 participants in attendance from the highest levels of business, government, industry, and research.
- The CogX Awards are given out to the best-of-the-best in AI and emerging technologies across the world.
- MyGov Corona Helpdesk demonstrated the true Public, Private Partnership (PPP), wherein, citizen-centric services were provided by MyGov, while the state-of-the-art technological solution including infrastructure was designed, developed, and deployed by a private partner- JioHaptik Technologies Limited.
- This Chatbox has been developed by MyGov, JioHaptik Technologies Limited, and WhatsApp.
- MyGov (launched in 2014) is the world’s largest citizen engagement platform, which facilitates two-way communication between the Government and Citizen and facilitates participatory governance in India.
Other important current affairs:
1. Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the extension of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana till Deepawali & Chhath Puja, i.e. till the end of November.
- During this five-month period from July till the end of November, more than 80 crore people will be provided 5 kg free wheat/rice per month. Along with providing 5kg free rice/wheat to each member of a family, 1 kg free whole chana will also be provided to each family per month.
- The government will spend more than Rs 90,000 crore on the extension of the scheme. If the amount spent towards it in the previous three months is added together, a total of almost Rs 1.5 lakh crore would be spent towards the scheme.
- The Modi government had announced an additional allocation in the world’s largest food security scheme – PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana – earlier this year, which aimed to ensure sufficient foods with the poor and needy amid the coronavirus crisis.
- The food grains were to be distributed to all the beneficiaries under the targeted public distribution system (TPDS) for Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and priority household (PHH) ration cardholders.
2.Recently, the World Bank has approved a five-year loan (for the second phase) to the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) or Namami Gange Project worth Rs.3,000 crore to help stem pollution in the Ganga river basin.
- So far, 313 projects worth Rs. 25,000 crore have been sanctioned under the mission.
- The First Phase: The Namami Gange has already received Rs. 4,535 crore from the World Bank as part of the first phase (valid until December 2021) of the National Ganga River Basin.
- The Second Phase: Hybrid Annuity Projects: The loan would fund three new ‘Hybrid Annuity Projects’ in Agra, Meerut, and Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh for the tributaries of the Ganga.
- Cleaning Projects: Some of the projects include spillover projects from the first phase of the mission as well as cleaning projects in tributaries such as the Yamuna and Kali rivers.
- DBOT Projects: Rs.1,209 crore is provided for the ongoing DBOT (Design, Build, Operate and Transfer) projects in Buxar, Munger, Begusarai in Bihar.
- Other Initiatives: It would include institutional development, improving investment resilience to Covid-19 like emergency situations, the performance-based incentive for Urban Local Bodies, and communication, and management programs.
3. According to the data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the eight-core sector industries contracted by 23.4% in May 2020.
- In April 2020 the eight core sectors had contracted by 37%.
- In May 2019 the eight core sectors had grown by 3.8%.
- Core Sector Data: Except for fertilizer, all seven sectors — coal, crude oil, natural gas, refinery products, steel, cement, and electricity — had recorded negative growth in May.
- The fertilizer production showed growth at 7.5% after two consecutive months of contraction.
- The steel and cement showed shrinkage of 48.4% and 22.2% respectively.
- The main reason for contraction was factories remained affected by a lack of labor and cash shortages owing to the nationwide lockdown.
- Experts are of the opinion that aftershocks of the lockdown will continue to affect the domestic industry in the coming months.
4. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released data relating to India’s International Investment Position (IIP) as at end-March 2020.
- Annual Variations during April 2019 – March 2020
- International financial assets of Indian residents increased by 73.9 billion dollars due to the rise in reserve assets and overseas direct investment by 64.9 billion dollars and 13.0 billion dollars, respectively, though other investments declined marginally during the year.
- Despite a fall of 13.7 billion dollars in portfolio investment during the year, international financial liabilities increased by 16.3 billion dollars as direct investment and other investments rose by 19.0 billion dollars and 11.0 billion dollars, respectively.
- Overall, net claims of non-residents on India declined by 57.6 billion dollars during the year.
5. Union Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister laid the foundation stone of Indian Oil Corporation’s (IOC) Technology Development & Deployment Centre as its second R&D Campus at Faridabad.
- The new campus would focus on the demonstration and deployment of various technologies developed by Indian Oil R&D and will work in tandem with the existing campus at Sector-13, Faridabad.
- It is going to focus on non-conventional energy domains besides the conventional ones and will aim at the indigenization of several frontline and sunrise technologies.
6. The central government has extended the term of K.K. Venugopal as Attorney General (AG) for one year.
- Venugopal was appointed the 15th AG of India in 2017. He succeeded Mukul Rohatgi who was AG from 2014-2017.
- The Attorney General (AG) of India is a part of the Union Executive. AG is the highest law officer in the country.
- Article 76 of the Constitution provides for the office of AG of India.
- AG is appointed by the President on the advice of the government.
- S/he must be a person who is qualified to be appointed a judge of the Supreme Court, i.e. s/he must be a citizen of India and must have been a judge of some high court for five years or an advocate of some high court for ten years or an eminent jurist, in the opinion of the President.
- Term of the Office: Not fixed by the Constitution.
- Removal: Procedures and grounds for the removal of AG are not stated in the Constitution. S/he holds office during the pleasure of the President (may be removed by the President at any time).
- Duties and Functions: To give advice to the Government of India (GoI) upon such legal matters, which are referred to her/him by the President. To perform such other duties of a legal character that are assigned to her/him by the President.
7.A clash took place between Van Gujjars and the Uttarakhand forest officials in the Rajaji National Park.
- Location: Haridwar (Uttarakhand), along the foothills of the Shivalik range, spans 820 square kilometers.
- Background: Three sanctuaries in the Uttarakhand i.e. Rajaji, Motichur, and Chila were amalgamated into a large protected area and named Rajaji National Park in the year 1983 after the famous freedom fighter C. Rajgopalachari; popularly known as “Rajaji”.
- This area is the North-Western Limit of the habitat of Asian elephants.
- Forest types include sal forests, riverine forests, broad-leaved mixed forests, scrubland, and grassy.
It possesses as many as 23 species of mammals and 315 bird species such as elephants, tigers, leopards, deers and ghorals, etc. - It was declared a Tiger Reserve in 2015.
- It is home to the Van Gujjars in the winters.




