Today Current Affairs: 10th November 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Swarna Jayanti Fellowship: DST

Seventeen scientists from scientific institutions across India have been awarded the Swarnajayanti Fellowships for their innovative research ideas and the potential of creating impact on R&D in different disciplines.
- Scientists selected for the award will be allowed to pursue unfettered research with a freedom and flexibility in terms of expenditure as approved in the research plan.
- The Swanajayanti Fellowship scheme was instituted by Govt. of India to commemorate India’s fiftieth year of Independence.
- Under the scheme the awardees are facilitated by the Department of Science & Technology, GOI with support for all the requirements for performing the research including a fellowship of Rs. 25,000/- per month for five years.
- In addition, DST supports the awardees by giving them a research grant of 5 lakh Rupees for 5 years. The fellowship is provided in addition to the salary they draw from their parent Institution.
- In addition to fellowship, grants for equipment, computational facilities, consumables, contingencies, national and international travel and other special requirements, are covered based on merit.
Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Report (Index) 2021:

The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has released the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Report (Index) 2021.
- The LEADS report is aimed at gauging the logistics performance of states and Union Territories (UT) and identifying areas where they can improve logistics performance.
- It was launched in 2018.
- States are ranked based on quality and capacity of key infrastructure such as road, rail and warehousing as well as on operational ease of logistics including security of cargo, speed of terminal services and regulatory approvals.
- The report is structured along the three dimensions which collectively influence logistics ease- Infrastructure, Services, and Operating and Regulatory Environment which are further categorised into 17 parameters.
- India’s logistics costs account for 13-14% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), compared to 7-8% in developed countries.
- The government was aiming to bring down logistics costs by 5% over the next 5 years.
- Estimated logistics costs in India are currently about 14%, which is quite high compared to 8-10% globally.
- Efficient logistics was pivotal to bring ease and empowerment to businesses as well as citizens.
- Logistics contributed immensely in our fight against Covid-19 by taking essential supplies including liquid Medical Oxygen throughout the country during the 2nd wave.
Ranking of States:
Top Performers:
- Gujarat, Haryana and Punjab have emerged as the top performers in the LEADS 2021 index respectively.
- This is the third year in a row that Gujarat remained on top of the rankings.
- Delhi stands at the top rank among Other UTs.
- North Eastern States and Himalayan Region: Jammu and Kashmir is the top ranker followed by Sikkim and Meghalaya.
Freedom Of Air:
India has launched a direct flight between Srinagar and Sharjah (UAE) operated by budget airline GoFirst (formerly known as GoAir). The flight was to operate through Pakistani airspace.
- However, the flight was denied permission to enter Pakistan and the flight had to take a longer route to reach the destination.
- This has raised the concern of Pakistan violating the first freedom of the air.
Freedom of Air:
- The freedom of air means a country grants airlines of a particular country the privilege to use and/or land in another country’s airspace.
- Freedom of air rule emanates from the Chicago Convention in 1944.
- The signatories to the convention decided to set rules that would act as fundamental building blocks to international commercial aviation.
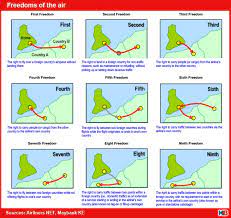
- The convention provides Nine freedoms of air, but only the first five freedoms have been officially recognized by the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO).
- First Freedom Right: It is granted by one State to another State or States to fly across its territory without landing.
In the case of the GoFirst flight (Indian carrier) was using the airspace of Pakistan (the second country) and was landing in the UAE (the third country). - Second Freedom Right: The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services, granted by one State to another State or States to land in its territory for non-traffic purposes.
- This means an Air India flight from New Delhi to New York can land at a British airport to get refuelled without embarking or disembarking passengers.
- Third Freedom Right: To put down, in the territory of the first State, traffic coming from the home State of the carrier.
- Fourth Freedom Right: To take on, in the territory of the first State, traffic destined for the home State of the carrier.
- Fifth Freedom Right: To put down and to take on, in the territory of the first State, traffic coming from or destined to a third State.
Delhi Regional Security Dialogue On Afghanistan:

In the coming days, India will be hosting the ‘Delhi Regional Security Dialogue on Afghanistan’.
- The meeting will be held at the level of National Security Advisors (NSAs) and will be chaired by India’s NSA Ajit Doval.
About the Meeting:
- Invited Participants: India’s top security establishment, the National Security Council Secretariat, has taken the lead in organising the in-person meeting.
- Invitations were sent to Afghanistan’s neighbours such as Pakistan, Iran, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, and other key players including Russia, and China.
- After the withdrawal of US forces and the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan, India is concerned about security in the region.
- Objective: In this context, India has taken this initiative to organise a conference of regional stakeholders and important powers on the country’s current situation and future outlook.
- This meeting could be India’s attempt to secure for itself a seat at the table to decide the future course of action on Afghanistan.
- The meeting also reflects the need to actively engage with the world to protect India’s security interests.
- The Central Asian countries, as well as Russia and Iran, have confirmed participation.
- The enthusiastic response is a manifestation of the importance attached to India’s role in regional efforts to promote peace and security in Afghanistan.
- Pakistan’s National Security Advisor has held that he would not attend the meeting.
- China has also decided to skip a regional security meeting due to scheduling difficulties, but is open to maintaining discussions with India through bilateral channels.
- India is of the view that the denial by Pakistan to attend this meeting reflects its mindset of viewing Afghanistan as its protectorate.
- India is not ready to directly deal with the new Taliban dispensation in Afghanistan.
- India reiterates that Afghanistan should:
- Not allow safe havens for terror on its soil.
- The administration should be inclusive.
- The rights of minorities, women, and children must be protected.
- The Afghanistan peace process should be led, owned and controlled by the Afghan people.
Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities), Rules 2011:

To safeguard interest of consumers, the Department of Consumer Affairs under Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution has omitted the Rule 5 of the Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities), Rules 2011 defining the Schedule II prescribing the pack sizes of various types of commodities.
- A new provision has been introduced to indicate the unit sale price on pre packed commodities, which will allow easier comparison of the prices of the commodities at the time of purchase.
- Earlier, the month and year in which the commodity is manufactured or pre-packed or imported was required to be mentioned in the package. Representation from Industry and associations in this respect has been received to remove this ambiguity.
- For reducing compliance burden and removing the ambiguity of declaration of date on pre packed commodities for consumers, the declaration has now been required to the month and year in which the commodity is manufactured for the pre packed commodities.
- The provisions of declarations of MRP has been simplified by removing illustration and providing for making the mandatory declaration of MRP in Indian currency inclusive of all taxes.
- This has allowed the manufacturer/packer/importer to declare the MRP on the pre packed commodities in a simplified manner.
Global Drug Policy Index:

The inaugural Global Drug Policy Index, released on Sunday by the Harm Reduction Consortium, ranks Norway, New Zealand, Portugal, the UK and Australia as the five leading countries on humane and health-driven drug policies.
- The five lowest-ranking countries are Brazil, Uganda, Indonesia, Kenya, and Mexico.
- India’s rank is 18 out of 30 countries.
- It is a data-driven global analysis of drug policies and their implementation.
- It is composed of 75 indicators running across five broad dimensions of drug policy: criminal justice, extreme responses, health and harm reduction, access to internationally controlled medicines, and development.
Zika virus:
With a rise in the number of Zika virus cases in Uttar Pradesh, doctors have advised that people should avoid all non-essential travel to areas reporting cases. Currently close to 90 persons, including 17 children, have tested positive for the virus from the State.
- According to information released by the World Health Organisation (WHO), a majority of those infected with Zika virus disease either remain asymptomatic (up to 80%) or show mild symptoms of fever, rash, conjunctivitis, body ache, joint pains.
- The Zika virus is predominantly transmitted by infected mosquitoes from the Aedes genus, mainly Aedes aegypti. The Aedes mosquitoes also spread dengue, chikungunya and yellow fever.
- The virus was first identified in Uganda in 1947 in monkeys.
- Apart from the mosquitoes, an infected person can also spread the virus.
- Generally, the symptoms include fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise, or headache. It lasts for about two to seven days. Most infected people do not develop any symptoms.
- Zika virus infection during pregnancy can cause infants to be born with microcephaly (smaller than normal head size) and other congenital malformations, known as congenital Zika syndrome.
- It has no treatment or vaccine. Instead, the focus is on relieving symptoms and includes rest, rehydration and acetaminophen for fever and pain.
Dengue fever:
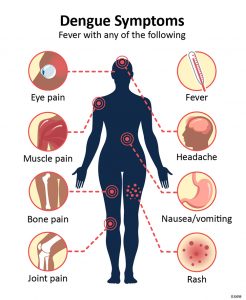
The rate of spread of dengue in Delhi is rampant, with the total number of cases reported in just the first week of November being 1,171. The number of dengue cases reported in the national capital in the month of October was 1,196.
- The spike in dengue, malaria and chikungunya cases across Delhi is leading the local bodies and authorities to increase their fogging and spraying drives.
- The citizens are also being directed to make sure that there is no stagnant water collected near or inside their houses, as it provides a breeding space for the disease.
- Dengue virus is transmitted through the bite of a female Aedes (Ae.) mosquito.
- Aedes is a day time feeder and can fly up to a limited distance of 400 meters.
- Although it usually results in mild illness, severe dengue infections can sometimes prove fatal.
- World Health Organization (WHO) estimates suggest an annual incidence of 100-400 million dengue infections every year, with its global incidence growing dramatically “in recent decades”.
- Incidence of dengue has grown dramatically around the world in recent decades, with a vast majority of cases under-reported, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- WHO estimates 39 crore dengue virus infections per year, of which 9.6 crore show symptoms.
- India registered over 1 lakh dengue cases in 2018 and over 1.5 lakh cases in 2019, according to the National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP).
Mullaperiyar Dam Issue:

The Kerala government has withdrawn its decision granting permission to Tamil Nadu for felling 15 trees downstream the Baby Dam at Mullaperiyar reservoir as part of efforts to strengthen the structure.
- The state government said that action will be taken against the officials who had sanctioned the move.
- Both the states are at loggerheads over the stability of the structure, with Kerala demanding that a new dam must be constructed and Tamil Nadu saying that a new structure is not needed. Also, Kerala has been against increasing water levels at the dam, citing structural stability.
- Last month, the Supreme Court directed the Supervisory Committee to take an immediate and firm decision on the maximum water level that can be maintained at Mullaperiyar dam, amid torrential rain in Kerala.
- The SC constituted a permanent Supervisory Committee in 2014 to oversee all the issues concerning Mullaperiyar dam. The dam is a source of friction between Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- Kerala said the water level should not go above 139 feet, the same as what the court had ordered on August 24, 2018, when the State was hit by floods. It is because the lives of 50 lakh people would be in danger if the water level in the dam is raised.
- However, Tamil Nadu objected to this decision citing the Supreme Court judgments of 2006 and 2014, which fixed the maximum water level at 142 feet.
- Although the dam is located in Kerala, it is operated by Tamil Nadu following an 1886 lease indenture for 999 years (the Periyar Lake Lease Agreement) that was signed between the Maharaja of Travancore and the Secretary of State for India for the Periyar Irrigation works.
- Constructed between 1887 and 1895, the dam redirected the river to flow towards the Bay of Bengal, instead of the Arabian Sea and provide water to the arid rain region of Madurai in Madras Presidency.
- The dam is located on the confluence of the Mullayar and Periyar rivers inKerala’s Idukki district.
- Tamil Nadu claims that although it has undertaken measures to strengthen the dam, the Kerala government has blocked any attempt to raise the reservoir water level – resulting in losses for Madurai farmers.
Winter Session Of Parliament : November 29 To December 23

The Cabinet Committee on Parliament Affairs (CCPA) has recommended that the Winter session of Parliament be held from November 29 to December 23.
- Last year, the winter session could not be held due to the onslaught of the pandemic, which had witnessed the curtailment of the Budget and the Monsoon sessions.
- Article 85 requires that there should not be a gap of more than six months between two sessions of Parliament.
- The Constitution does not specify when or for how many days Parliament should meet.
- The maximum gap between two sessions of Parliament cannot be more than six months. That means the Parliament should meet at least twice a year.
- A ‘session’ of Parliament is the period between the first sitting of a House and its prorogation.
- In practice, the Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs, comprising senior ministers, decides on the dates for parliament’s sitting and it is then conveyed to the president.
- So, the executive, headed by the prime minister, which steers the business to be taken up by parliament will have the power to advise the president to summon the legislature.
City Of Srinagar Has Joined The UNESCO Network Of Creative Cities (UCCN):

UNESCO announced that the city of Srinagar has joined the UNESCO Network of Creative Cities (UCCN). It has been designated aa a Creative City of Craft and Folk Arts.
- Srinagar joins Chennai and Varanasi – UNESCO Cities of music, Jaipur – UNESCO City of crafts and folk arts; Mumbai – UNESCO city of film and Hyderabad – UNESCO City of gastronomy.
- Worldwide, 49 new cities have joined the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) following their designation by UNESCO Director-General Audrey Azoulay, in recognition of their commitment to placing culture and creativity at the heart of their development and to sharing knowledge and good practices.
- The Network now numbers 295 cities reaching 90 countries that invest in culture and creativity – crafts and folk art, design, film, gastronomy, literature, media arts, and music – to advance sustainable urban development.
Financial Inclusion:

India is now ahead of China in financial inclusion metrics, with mobile and Internet banking transactions rising to 13,615 per 1,000 adults in 2020 from 183 in 2015 and the number of bank branches inching up to 14.7 per 1 lakh adults in 2020 from 13.6 in 2015, which is higher than in Germany, China and South Africa, as per a report.
- States with higher financial inclusion / more bank accounts have also seen a perceptible decline in crime along with a meaningful drop in consumption of alcohol and tobaccos.
- Under the no-frills accounts scheme, the number of persons with deposit accounts at banks has significantly increased, becoming comparable with emerging economy peers and even some of the advanced economies
- In the use of digital payments also, there has been noteworthy progress.
- The number of no-frills bank accounts opened has reached 43.7 crore with ₹1.46 lakh crore in deposits as of October 20, 2021.
- Of these, almost two-thirds are operational in rural and semi-urban areas and more than 78% of these accounts are with state-owned banks, 18.2% with regional rural banks, and 3% are opened by private sector banks.
- The number of banking outlets in villages / banking correspondent (BCs) had risen from 34,174 in March 2010 to 12.4 lakh in December 2020, the report showed.




