Today Current Affairs: 11th November 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Mineral Conservation And Development (Amendment) Rules, 2021:

Ministry of Mines has notified the Mineral Conservation and Development (Amendment) Rules, 2021 on 3rd November, 2021 to amend the Mineral Conservation and Development Rules, 2017 [MCDR].
The highlights of amendments in the Rules are as follows:
- Rules prescribed that that all plans and sections related to mine shall be prepared by combination of Digital Global Positioning System (DGPS) or Total Station or by drone survey in relation to certain or all leases as may be specified by Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM).
- New Rule inserted to provide for submission of digital images of mining area by lessees and Letter of Intent holders.
- Requirement of submitting satellite images obtained from CARTOSAT-2 satellite LISS-IV sensor on the scale of cadastral map deleted in view of the insertion of provision for submission of high resolution Georeferenced Ortho-rectified Multispectral satellite and use of drone survey as per Rule 34A.
- Provision of daily return omitted to reduce compliance burden. Power of taking action against incomplete or wrong or false information in monthly or annual returns given to IBM, in addition to State Govt.
- Allowed engagement of a part-time mining engineer or a part-time geologist for category ‘A’ mines having leased area below 25 hectares.
- This will ease compliance burden for small miners.
Janjatiya Gaurav Divas:

The Union Cabinet has approved declaration of 15th November as Janjatiya Gaurav Divas dedicated to the memory of brave tribal freedom fighters so that coming generations could know about their sacrifices about the country.
- India’s freedom struggle was strengthened by several movements by tribal communities such as Santhals, Tamars, Kols, Bhils, Khasis and Mizos to name a few.
- The date is the birth anniversary of Sri Birsa Munda who is revered as Bhagwan by tribal communities across the country.
- Birsa Munda fought bravely against the country against the exploitative system of the British colonial system and spearheaded movement against British oppression giving a call for ‘Ulgulan’ (Revolution).
- The declaration acknowledges the glorious history and cultural heritage of tribal communities.
- The day will be celebrated every year and would recognize the efforts of the tribals for preservation of cultural heritage and promotion of Indian values of valour, hospitality and national pride.
- Tribal Freedom Fighter Museum at Ranchi where Birsa Munda breathed his last will be inaugurated by Hon’ble Prime Minister.
Reservation Norms For Mandatory Use Of Jute:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved reservation norms for mandatory use of jute in packaging for the Jute Year 2021 -22 (1st July, 2021 to 30th June, 2022) on 10th November, 2021.
- The Mandatory packaging norms approved for Jute Year 2021-22 provide for 100% reservation of the foodgrains and 20% of sugar to be compulsorily packed in jute bags.
- The Jute industry occupies an important place in the national economy of India in general and Eastern Region in particular i.e. West Bengal, Bihar, Odisa, Assam, Tripura, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- The reservations norms under JPM Act provide for direct employment to 0.37 million workers and 4 million farmers in the Jute Sector. JPM Act, 1987 protects interest of Jute farmers, workers and persons engaged in jute goods’ production.
- 75% of the total production of the Jute Industry is Jute Sacking Bags of which 90% is supplied to the Food Corporation of India (FCl) and State Procurement Agencies (SPAs) and remaining is exported/sold directly.
Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme:

The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has given its approval for fixing higher ethanol price derived from different sugarcane based raw materials under the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme for the forthcoming sugar season 2021-22 during ESY 2021-22 from 1st December 2021 to 30th November 2022.
- The Price of ethanol from C heavy molasses route be increased from Rs. 45.69 per litre to Rs. 46.66 per litre,
- The price of ethanol from B heavy molasses route be increased from Rs. 57.61 per litre to Rs. 59.08 per litre,
- The price of ethanol from sugarcane juice, sugar / sugar syrup route be increased from Rs. 62.65 per litre to Rs. 63.45 per litre,
- Additionally, GST and transportation charges will also be payable.
- Government has decided that Oil PSEs should be given the freedom to decide the pricing for 2G ethanol as this would help in setting up advanced biofuel refineries in the country.
- It is important to note that grain-based ethanol prices are currently being decided by Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) only.
- The approval will not only facilitate the continued policy of the Government in providing price stability and remunerative prices for ethanol suppliers, but will also help in reducing the pending arrears of Cane farmers, dependency on crude oil imports and will also help in savings in foreign exchange and bring benefits to the environment.
- The decision to allow Oil PSEs to decide the price of 2G ethanol would facilitate setting up advanced biofuel refineries in the country.
E-Amrit : Web Portal

India launched ‘E-Amrit’, a web portal on electric vehicles (EVs), at the ongoing COP26 Summit in Glasgow, UK.
- E-Amrit is a one-stop destination for all information on electric vehicles—busting myths around the adoption of EVs, their purchase, investment opportunities, policies, subsidies, etc.
- The portal has been developed and hosted by NITI Aayog under a collaborative knowledge exchange programme with the UK government and as part of the UK–India Joint Roadmap 2030, signed by the Prime Ministers of the two countries.
- E-Amrit intends to complement initiatives of the government on raising awareness on EVs and sensitizing consumers on the benefits of switching to electric vehicles.
- In the recent past, India has taken many initiatives to accelerate the decarbonisation of transport and adoption of electric mobility in the country. Schemes such as FAME and PLI are especially important in creating an ecosystem for the early adoption of EVs.
- NITI Aayog intends to add more features and introduce innovative tools to make the portal more interactive and user-friendly.
- The launch was attended by UK High-Level Climate Action Champion Nigel Topping and NITI Aayog Adviser Sudhendu Jyoti Sinha.
17th Edition Of The Climate Change Performance Index:

The 17th edition of the Climate Change Performance Index was released recently.
- CCPI is compiled by Germanwatch, the New Climate Institute, and the Climate Action Network.
- It monitors climate mitigation progress of 60 countries and the European Union.
- It aims to enhance transparency in international climate politics and enables the comparability of climate protection efforts and progress made by individual countries.
- The CCPI assesses countries’ performance in four categories:
- “GHG Emissions” (40% of overall score).
- “Renewable Energy” (20% of overall score).
- “Energy Use” (20% of overall score).
- “Climate Policy” (20% of overall score).
Performance of various countries in the latest index:
- The first three ranks of the overall rankings were kept empty because no country had performed well enough in all index categories to achieve an overall very high rating.
- The first three ranks in the greenhouse gas emissions category, too, were kept empty.
- In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, Sweden, Egypt, Chile and the UK are in the top 7.
Scandinavian countries such as Sweden achieved the best results because of their “outstanding” effort on renewable energy. - Iran and Russia are ranked the lowest in this category.
- Overall, Australia, South Korea and Russia and the United States are among the lowest performing countries along with Kazakhstan and Saudi Arabia.
- China is ranked 37 overall and has an overall rating of “low”.
- In the overall rankings, India is at number 10 with a score of 69.22. It is a high performer except in the renewable energy category, in which it is ranked “medium”.
- The report says that India is benefiting from its relatively low per-capita emissions.
Frothing In Yamuna:

In what has become a repeat occurrence in the city, a layer of froth was seen floating over parts of the Yamuna river near Kalindi Kunj recently, with Chhath devotees standing in toxic foam-laden water to offer prayers.
- The froth is a sign of a polluted river.
- The release of untreated or poorly treated effluents, including sewage from those parts of the city that are not connected to the sewerage network and industrial waste, could lead to frothing.
- Surfactants and phosphates from detergents in households and industrial laundry find their way into the river, as all the sewage is not treated.
- The river is in a lean phase and the water flow is less. Pollutants, therefore, are not diluted. The turbulence at the barrage near Okhla generates foam from the phosphates.
- The sewage treatment plants of Delhi are major contributors of the Pollutants being discharged in the river.
- Pollutants discharge from different types of industry is also a major issue.
- Agriculture activities along the banks of the river in Delhi contributes to river pollution.
- Agricultural waste and pesticide discharge from the Haryana field also contributes to the pollution.
- The low volume of water flow in the river causes the pollutants to accumulate and raise the pollution level.
CharDham Project:
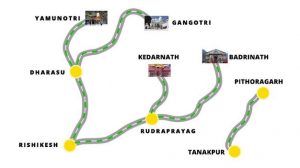
The Supreme Court (SC) has spoken of the need to balance national security concerns with environmental issues in the context of the Army’s request to expand the CharDham Project (CDP) roads leading to the Indo-China border.
- The request came in the context of construction being carried out by China across the border. However, expansion of roads has been opposed by an NGO citing environmental concerns.
- CharDham Pariyojana aims to “improve the connectivity to the Chardham pilgrimage centres (Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, Yamunotri) in the Himalayas, making journeys to these centres safer, faster and more convenient.
- It will widen almost 900 km of highways connecting the pilgrimage sites and the Tanakpur-Pithoragarh stretch of National Highway (NH) 125, a part of the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra route.
- Role in National Security: This project can act as the strategic feeder roads which connect the India-China border with the Army camps in Dehradun and Meerut where missile bases and heavy machinery are located.
- Implementing Agencies: Uttarakhand State Public Works Department (PWD), Border Roads Organisation (BRO) and the National Highway & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
- NHIDCL is a fully owned company of the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways.
Nutrition Smart Village:

As part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, to commemorate the 75th year of Independence of India a programme on “Nutrition Smart Village” will be initiated to strengthen the Poshan Abhiyan.
- This new initiative aims to reach out to 75 villages across India through the network of All India Coordinated Research Project on Women in Agriculture (AICRP-WIA) which is in operation at 13 centres in 12 States of India besides the coordinating institute located at Bhubaneswar.
- The initiative has been undertaken in line with the Prime Minister’s call to all the academicians, agricultural scientists and all the institutions to adopt and transform 75 villages.
- Under the initiative, A total of 75 villages will be adopted by AICRP centres and ICAR-CIWA, for which the AICRP centres will adopt 5 villages each with the remaining to be adopted by ICAR-CIWA with an aim to develop 75 Nutri-Smart villages.
- The objectives of the initiative are promoting nutritional awareness, education and behavioural change in rural areas involving farm women and school children, harnessing traditional knowledge through the local recipe to overcome malnutrition and implementing nutrition-sensitive agriculture through homestead agriculture and Nutri-garden.
MPLAD Scheme:

Citing economic recovery, the Union Cabinet has restored the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) that was suspended in April 2020 subsuming the funds for the scheme in the consolidated fund of India.
- However, the MPs will get ₹2 crore instead of the annual approved ₹5 crore.
- The government had in April, 2020 decided not to operate MPLADS for the Financial Years 2020-21 and 2021-22; and place the MPLADS funds for these two-years at the disposal of the Ministry of Finance to meet the emergent needs of people.
- From ₹5,012 crore spent during 2018-19, an expenditure of just ₹2,491.45 crore was taken up under the scheme in 2019-20.
- The government has said that the funds saved from the MPLAD Scheme have been utilised to enhance the allocation of funds for improving health infrastructure, provide free ration under PM Garib Kalyan Yojana, and free vaccination for the people.
MPLAD scheme:
- Launched in December, 1993.
- Seeks to provide a mechanism for the Members of Parliament to recommend works of developmental nature for creation of durable community assets and for provision of basic facilities including community infrastructure, based on locally felt needs.
- The MPLADS is a Plan Scheme fully funded by Government of India.
- The annual MPLADS fund entitlement per MP constituency is Rs. 5 crore.
- MPs are to recommend every year, works costing at least 15 per cent of the MPLADS entitlement for the year for areas inhabited by Scheduled Caste population and 7.5 per cent for areas inhabited by S.T. population.
- Funds are released in the form of grants in-aid directly to the district authorities.
- The funds released under the scheme are non-lapsable.
- The liability of funds not released in a particular year is carried forward to the subsequent years, subject to eligibility.
- The MPs have a recommendatory role under the scheme.
- The district authority is empowered to examine the eligibility of works, sanction funds and select the implementing agencies, prioritise works, supervise overall execution, and monitor the scheme at the ground level.
- At least 10% of the projects under implementation in the district are to be inspected every year by the district authority.




