Today Current Affairs: 13th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Tiger Corridor In Rajasthan:

The Rajasthan government will develop a tiger corridor connecting the newly proposed ‘Ramgarh Tiger Reserve’, Ranthambore Tiger Reserve and Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve.
- Sariska Tiger Reserve is another Tiger reserve in Rajasthan.
Animal Corridor:
- Wildlife or animal corridors are meant to ensure safe passage for animals between two isolated habitats.
- In wildlife parlance, corridors are mainly of two types: functional and structural.
- Functional corridors are defined in terms of functionality from the perspective of the animal (basically areas where there has been recorded movement of wildlife).
- Structural corridors are contiguous strips of forested areas and structurally connect the otherwise fragmented blocks of the landscape.
- When structural corridors are affected by human anthropogenic activities, functional corridors automatically widen because of animal use.
- In 2019, the National Tiger Conservation Authority in collaboration with the Wildlife Institute of India published a document, mapping out 32 major corridors across the country, management interventions for which are operationalised through a Tiger Conservation Plan.
- The states are required to submit a Tiger Conservation Plan under section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Arun Hydro Electric Project: Nepal

A MoU has been signed for execution of 679 MW Lower Arun Hydro Electric Project in Nepal between Satluj Jal Vidyut Nigam (SJVN) Central Public Sector Enterprise under Ministry of Power, Government of India & Investment Board of Nepal (IBN) in Kathmandu Nepal.
- The Lower Arun HEP (679 MW) is a downstream development of Arun-3 HEP.
- The Lower Arun Hydro Electric Project is located in Sankhuwasabha and Bhojpur Districts of Nepal.
- The project will not have any reservoir or dam and will be a tail race development of 900 MW Arun3 HEP.
- The project will have four francis type turbines.
- On completion the Project will generate 2970 million units of electricity per annum.
- It is scheduled to be completed in four years after commencement of construction activities and has been allocated to SJVN for 25 years on Build Own Operate Transfer basis.
- Arun 3 Hydro Electric Project is the second project awarded to SJVN in Nepal, the first one being the 900 MW Arun 3 Hydro Electric Project in Sankhuwasabha District.
- Arun-3 Project is being implemented through wholly owned subsidiary company of SJVN i.e. SJVN Arun-3 Power Development Company Limited (SAPDC) incorporated in Nepal.
National Archives Of India:

Culture Minister G. Kishan Reddy said the National Archives’ records related to freedom fighters would be digitised within a year as a part of the commemoration of 75 years of Independence next year.
- The National Archives of India is an Attached Office under the Ministry of Culture.
- It was established in 1891 at Kolkata(Calcutta) as the Imperial Record Department.
- Following the transfer of the capital from Calcutta to Delhi in 1911, the present building of the National Archives of India was constructed in 1926 in Delhi.
- There are over 50 lakhs files/documents presently in the holdings in the National Archives of India.
Right To Repair Laws.:

In recent years, countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws.
- US President Joe Biden signed an executive order calling on the Federal Trade Commission to curb restrictions imposed by manufacturers that limit consumers’ ability to repair their gadgets on their own terms.
- The UK, too, introduced right-to-repair rules that should make it much easier to buy and repair daily-use gadgets such as TVs and washing machines.
Right to repair movement:
- Activists and organisations around the world have been advocating for the right of consumers to be able to repair their own electronics and other products as part of the ‘right to repair’ movement.
- The movement traces its roots back to the very dawn of the computer era in the 1950s.
- The goal of the movement is to get companies to make spare parts, tools and information on how to repair devices available to customers and repair shops to increase the lifespan of products and to keep them from ending up in landfills.
- They argue that these electronic manufacturers are encouraging a culture of ‘planned obsolescence’ — which means that devices are designed specifically to last a limited amount of time and to be replaced.
- This, they claim, leads to immense pressure on the environment and wasted natural resources.
- Large tech companies, including Apple, Microsoft, Amazon and Tesla, have been lobbying against the right to repair.
- Their argument is that opening up their intellectual property to third party repair services or amateur repairers could lead to exploitation and impact the safety and security of their devices.
Kongu Nadu:
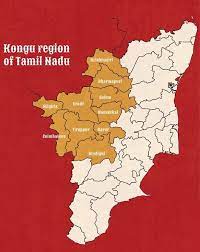
A list of new Union Cabinet ministers issued by the BJP has triggered a debate in political circles in Tamil Nadu, as well as on social media, by referring to ‘Kongu Nadu’, the informal name for a region in the western part of the state.
- The list mentions new minister L Murugan as hailing from ‘Kongu Nadu’.
- This has led to allegations that the BJP of trying to bifurcate the state, with the ruling DMK-Congress alliance saying the “agenda” will not succeed.
- It has also been considered an AIADMK stronghold in the recent past, and is also where the BJP’s limited influence in the state is concentrated.
- Kongu Nadu’ is neither a place with a PIN code nor a name given formally to any region. It is a commonly used name for part of western Tamil Nadu.
- In Tamil literature, it was referred to as one of the five regions of ancient Tamil Nadu. There were mentions of ‘Kongu Nadu’ in Sangam literature as a separate territory.
- In the present state of Tamil Nadu, the term is informally used to refer to a region that includes the districts of Nilgiris, Coimbatore, Tirupur, Erode, Karur, Namakkal and Salem, as well as Oddanchatram and Vedasandur in Dindgul district, and Pappireddipatti in Dharmapuri district.
- The name derives from Kongu Vellala Gounder, an OBC community with a significant presence in these districts.
- The region includes prominent businesses and industrial hubs at Namakkal, Salem, Tirupur and Coimbatore.
IFSCA:

IFSCA has issued a framework for Setting up and operating International Trade Finance Services Platform (‘ITFS’).
- The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has been set up vide IFSCA Act, 2019 to develop and regulate the financial products, financial services and financial institutions in the International Financial Services Centres (IFSCs).
- Towards this end, IFSCA has issued a framework for Setting up and operating International Trade Finance Services Platform (‘ITFS’) for providing Trade Finance Services at International Financial Services Centres (‘IFSCs’).
- The framework will enable Exporters and Importers to avail various types of trade finance facilities at competitive terms, for their international trade transactions through a dedicated electronic platform viz, ITFS.
- This will help in their ability to convert their trade receivables into liquid funds and to obtain short term funding.
India’s Tibet Policy:

Some Chinese nationals protested against the celebration of the birthday of the Dalai Lama in India.
- The Dalai Lama and Tibet is one of the major irritants between India and China relations.
- China considers the Dalai Lama a separatist, who has great influence over Tibetans.
- India seeks to use Tibetan card in order to counter China’s continuing aggression at the Line of Actual Control.
- For centuries, Tibet was India’s actual neighbour, as most of India’s boundaries and the 3500km LAC is with the Tibetan Autonomous Region, and not the rest of China.
- In 1914, it was Tibetan representatives, along with the Chinese that signed the Simla convention with British India that delineated boundaries.
- However, after China’s full accession of Tibet in 1950, that China repudiated the convention and the McMahon line that divided the two countries.
- Further, in 1954, India signed an agreement with China, agreeing to recognize Tibet as “Tibet region of China”.
- In 1959, following the Tibetan uprising, the Dalai Lama (spiritual leader of Tibetan people) and many of his followers fled to India.
- Former Prime Minister Jawahar Lal Nehru gave him and Tibetan refugees shelter, and helped in setting up the Tibetan government in exile.
- The official Indian policy is that the Dalai Lama is a spiritual leader, and the Tibetan community in India, with more than a lakh exiles, is not allowed to undertake any political activity.
Shift in India’s Tibet Policy:
- In the event of increasing tensions between India and China, there has been a shift in India’s Tibet Policy.
- This shift in the policy, earmarks the Indian government actively managing with the Dalai Lama in public forums. For Example,
- In 2014, Prime Minister of India (PM) had invited the head of the Tibetan government in exile in India, Lobsang Sangay, to his swearing in ceremony.
- However, he did not invite him in 2019 after being re-elected for a second five-year term, to ensure a smooth passage for a second informal summit between him and Chinese president Xi Jinping.
- Recently, the Prime Minister of India (PM) wished the Dalai Lama in the first such public acknowledgement since 2013, the first time as PM.
- The shift in India’s Tibet policy is majorly focused on symbolic aspects, but there are many challenges pertaining to India’s Approach to Tibet Policy.
RBI’s Retail Direct Scheme:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced the ‘RBI Retail Direct’ Scheme.
- In February 2021 RBI proposed to allow retail investors to open gilt accounts with the central bank to invest in Government securities (G-secs) directly.
- Under the scheme, retail investors (individuals) will have the facility to open and maintain the ‘Retail Direct Gilt Account’ (RDG Account) with the RBI.
- Retail Investor is a non-professional investor who buys and sells securities or funds that contain a basket of securities such as mutual funds and Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs).
- A Gilt Account can be compared with a bank account, except that the account is debited or credited with treasury bills or government securities instead of money.
- RDG accounts can be opened through an online portal provided for the purpose of the scheme.
- The online portal will give registered users access to primary issuance of G-secs and access to Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching system (NDS-OM).
- The RBI introduced the NDS-OM in August 2005. It is an electronic, screen based, anonymous, order driven trading system for dealing in G-secs.
- It is a one-stop solution to facilitate investment in G-secs by individual investors.
- RBI seeks to democratize the ownership of government debt securities beyond banks and managers of pooled resources such as mutual funds.
India’s First Cryptogamic Garden:

India’s first cryptogamic garden was inaugurated in the Chakrata town of Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- The garden will be housing nearly 50 species of lichens, ferns and fungi (collectively known as Cryptogamae).
Factors Responsible for Location of this Garden:
- This garden is at Deoban in Chakrata at a height of 9,000 ft.
- This site is chosen because of its low pollution levels and moist conditions which are conducive for the growth of these species.
- Further, Deoban has pristine majestic forests of Deodar and Oak which create a natural habitat for cryptogamic species.
Cryptogams:
- A cryptogam is a plant that reproduces with the help of spores.
- The word “Cryptogamae” implies ‘hidden reproduction’, referring to the fact that they do not produce any reproductive structure, seed, or flower.
- Due to this, they are called “flowerless” or “seedless plants” or ‘lower plants’.
- They need a moist environment to survive.
- These are present in aquatic and terrestrial places.
- Algae, bryophytes, lichens, ferns and fungi are the best-known groups of cryptogams.




