Today Current Affairs: 16th March 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
What Is Medical And Wellness Tourism?

The Ministry of Tourism has formulated a National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism.
- The policy envisages promoting India as a Medical Value Travel (MVT) and Wellness destination.
- Medical & Wellness tourism may be defined as ‘activities related to travel and hosting a foreign tourist who stays at least one night at the destination region for the purpose of maintaining, improving or restoring health through medical intervention’ .
- Mission is to create a robust framework and synergy amongst the Ministries of Central Government and State Governments and Private Sector for promoting India as a Medical Value Travel (MVT) and Wellness destination.
- For this, a new National Medical and Wellness Tourism Board will be created as Minister of Tourism as its Chairman.
- It will provide a dedicated institutional framework to take forward the cause of promotion of Wellness & Medical Tourism.
- The Ministry of Tourism, releases global print, electronic and online media campaigns in important and potential markets overseas, under the ‘Incredible India’ brand line.
- ‘Medical Visa’ has been introduced, which can be given for specific purposes to foreign travellers coming to India for medical treatment.
- ‘E- Medical Visa’ and ‘E-Medical Attendant Visa’ have also been introduced for 156 countries.
- The Ministry of Tourism provides financial Assistance under Market Development Assistance Scheme to Medical Tourism Service Providers accredited by National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) for participation in Medical/ Tourism activities.
Regulatory Framework For Microfinance Loans: Highlights

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allowed Microfinance Institutions(MFI) the freedom to set interest rates they charge borrowers, with a caveat that the rates should not be usurious.
- The guidelines will take effect 1st April 02022.
- Earlier in 2021, the RBI proposed to lift the interest rate cap on MFI.
Highlights of the Guidelines:
- The RBI revised the definition of a microfinance loan to indicate a collateral-free loan given to a household having annual income of up to Rs. 3 lakh.
- Earlier, the upper limits were Rs.1.2 lakh for rural borrowers and Rs.2 lakh for urban borrowers.
- As per the revised norms, Regulated Entities (REs) should put in place a board-approved policy regarding pricing of microfinance loans, a ceiling on interest rate and all other charges applicable to microfinance loans.
- Each RE shall disclose pricing-related information to a prospective borrower in a standardised, simplified factsheet.
- There shall be no prepayment penalty on microfinance loans.
- Penalty, if any, for delayed payment shall be applied on the overdue amount and not on the entire loan amount.
- Any change in interest rate or any other charge shall be informed to the borrower well in advance and these changes shall be effective only prospectively.
- Recovery of Loans: RE would have to put in place a mechanism for identification of the borrowers facing repayment-related difficulties, engagement with such borrowers and providing them necessary guidance about the recourse available.
- To ensure due notice and appropriate authorisation, the RE will provide the details of recovery agents to the borrower while initiating the process of recovery.
What Is Flood Plain Zoning?
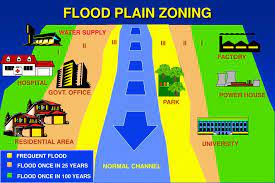
The Ministry of Jal Shakti has informed the Rajya Sabha that the states of Manipur, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand and erstwhile State of Jammu & Kashmir had enacted the National Floodplains Zoning Policy.
- However, delineation and demarcation of flood plains is yet to be undertaken.
- Earlier, the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) presented a report on preparedness and response to floods in the Kerala assembly.
- The report pointed out that the state is yet to enact flood plain zoning legislation, 45 years after the Union Government circulated to all states a model draft bill for flood plain zoning legislation.
- Flood Plain Zoning has been recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
- The basic concept of flood plain zoning is to regulate land use in the flood plains to restrict the damage caused by floods.
- It aims at determining the locations and the extent of areas for developmental activities in such a fashion that the damage is reduced to a minimum.
- It envisages laying down limitations on development of both the unprotected as well as protected areas.
- In the unprotected areas, boundaries of areas in which developmental activities will be banned, are to be established to prevent indiscriminate growth.
- In the protected areas, only such developmental activities can be allowed, which will not involve heavy damage in case the protective measures fail.
- Zoning cannot remedy existing situations, although, it will definitely help in minimising flood damage in new developments.
- Flood plain zoning is not only necessary in the case of floods by rivers but it is also useful in reducing the damage caused by drainage congestion particularly in urban areas.
- Model Bill for Flood Plain Zoning clauses about flood zoning authorities, surveys and delineation of flood plain area, notification of limits of flood plains, prohibition of the use of the flood plains, compensation and most importantly removing obstructions to ensure free flow of water.
- It seeks to replace dwellings in low-lying areas by parks and playgrounds as absence of human settlement in those areas would cut down loss of lives and property.
What Is Phosphorus Bomb?

Ukrainian police has accused Russian forces of launching phosphorus bomb attacks (chemical weapon) in the Lugansk and Donetsk regions of eastern Ukraine, collectively known as the Donbas.
- International law prohibits the use of white phosphorus shells in heavily populated civilian areas, but allows them in open spaces to be used as cover for troops.
What is Phosphorus Bomb?
- White phosphorus munitions are weapons that use one of the common allotropes of the chemical element phosphorus.
- White phosphorus is pyrophoric (it is ignited by contact with air), burns fiercely, and can ignite cloth, fuel, ammunition, and other combustibles.
- Apart from this, it is also used in smoke, illumination, and burning elements of tracer ammunition.
- In addition to its offensive capabilities, white phosphorus is a highly efficient smoke-producing agent, reacting with air to produce an immediate blanket of phosphorus pentoxide vapour.
- In addition to direct injuries caused by fragments of their casings, white phosphorus munitions can cause injuries in two main ways: burn injuries and vapour inhalation.
First Gati Shakti Cargo Terminal:

Indian Railways’ first Gati Shakti Cargo Terminal commissioned in Asansol Division in pursuance of the Prime Minister’s vision “Gati Shakti”.
- This is the first such GCT commissioned in Indian Railways since the publication of GCT policy in December 2021
- It is expected to enhance Indian Railways’ earnings. The commissioning of this terminal and more such terminals will have a very positive impact on the economy of the nation.
PM Gati Shakti Scheme:
- In 2021 the government launched the ambitious Gati Shakti scheme or National Master Plan for multi-modal connectivity plan, with the aim of coordinated planning and execution of infrastructure projects to bring down logistics costs.
- Aim: To ensure integrated planning and implementation of infrastructure projects in the next four years, with focus on expediting works on the ground, saving costs and creating jobs.
- The Gati Shakti scheme will subsume the Rs 110 lakh crore National Infrastructure Pipeline that was launched in 2019.
- Besides cutting logistics costs, the scheme is also aimed at increasing cargo handling capacity and reducing the turnaround time at ports to boost trade.
- It also aims to have 11 industrial corridors and two new defence corridors – one in Tamil Nadu and other in Uttar Pradesh.
- Extending 4G connectivity to all villages is another aim. Adding 17,000 kms to the gas pipeline network is being planned.
- It will help in fulfilling the ambitious targets set by the government for 2024-25, including expanding the length of the national highway network to 2 lakh kms, creation of more than 200 new airports, heliports and water aerodromes.
What Is a Non-Performing Asset?

Despite a host of loan restructuring schemes and packages announced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the government, the Covid pandemic has hit the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) very hard.
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) of MSMEs, or loans defaulted by these enterprises, rose by Rs 20,000 crore to Rs 1,65,732 crore as of September 2021 from Rs 1,45,673 crore in September 2020.
- Bad loans of MSMEs now account for 9.6 % of gross advances of Rs 17.33 lakh crore as against 8.2 % in September 2020.
- Earlier, the Ministry of MSME launched the MSME Innovative Scheme (Incubation, Design and IPR) along with the MSME IDEA HACKATHON 2022.
- NPA refers to a classification for loans or advances that are in default or are in arrears on scheduled payments of principal or interest.
- In most cases, debt is classified as non-performing, when the loan payments have not been made for a minimum period of 90 days.
- Gross non-performing assets are the sum of all the loans that have been defaulted by the individuals who have acquired loans from the financial institution.
- Net non-performing assets are the amount that is realised after provision amount has been deducted from the gross non-performing assets.
The Global Entrepreneurship Monitor Project:

The Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) is an international project which seeks to provide information on the entrepreneurial landscape of countries.
- GEM carries out survey-based research on entrepreneurship and entrepreneurship ecosystems around the world and is being led by Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India, Ahmedabad.
- As per Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) India Report (21-22), India’s entrepreneurial activity expanded in 2021, with its Total Entrepreneurial Activity rate(percentage of adults (aged 18–64) who are starting or running a new business) increased to 14.4% in 2021, up from 5.3% in 2020.
- Further, Established Business Ownership rate (percentage of adults (aged 18–64) who are currently the owner-manager of an established business, i.e. owning and managing a business that has paid salaries, wages or any other payments to the owners, for more than 42 months)increased to 8.5%, from 5.9% in 2020.
Man-Portable Air-Defence Systems:

On March 13, 2022 United States President Joe Biden approved a $200-million arms package for Ukraine, which would include U.S. made Stinger Missiles, which are a type of shoulder-fired Man-Portable Air-Defence Systems (MANPADS).
- Man-Portable Air-Defence Systems are short-range, lightweight and portable surface-to-air missiles that can be fired by individuals or small groups to destroy aircraft or helicopters.
- They help shield troops from aerial attacks and are most effective in targeting low-flying aircrafts.
- MANPATs or Man-Portable Anti-Tank Systems work in a similar manner but are used to destroy or incapacitate military tanks.
- MANPADS can be shoulder-fired, launched from atop a ground-vehicle, fired from a tripod or stand, and from a helicopter or boat.
- Weighing anywhere between 10 to 20 kilograms and not being longer than 1.8 metres, they are fairly lightweight as compared to other elaborate weapon systems, making them easy to operate by individual soldiers.
- Operating MANPADS requires substantially less training.
- The most common make of MANPADs is the U.S.-made Stinger missiles.
- Stinger’s Russian or Soviet-made counterparts are the Igla MANPADS, which also employ infrared technology.
- Sweden makes the RBS-70 MANPADS serieswhile China’s version, FN-6, is akin to the Stinger.
What Are Supplementary Demands For Grants?

The government has sought approval from Parliament to spend an extra ₹1.07 lakh crore in the current fiscal year.
- The additional spending of Rs1.58 trillion is required for expenditure commitments towards settling loans taken from National Small Savings Funds for PM Awas Yojana and higher fertiliser subsidy outgo.
- The supplementary demand for grants is needed for government expenditure over and above the amount for which Parliamentary approval was already obtained during the Budget session.
- Supplementary, additional or excess grants and Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants are mentioned in the Constitution of India 1949.
- Article 115: Supplementary, additional or excess grants.
- Article 116: Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants.
- When grants, authorised by the Parliament, fall short of the required expenditure, an estimate is presented before the Parliament for Supplementary or Additional grants.
- These grants are presented and passed by the Parliament before the end of the financial year.
- When actual expenditure incurred exceeds the approved grants of the Parliament, the Ministry of Finance presents a Demand for Excess Grant.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India bring such excesses to the notice of the Parliament.
- The Public Accounts Committee examines these excesses and gives recommendations to the Parliament.
- The Demand for Excess Grants is made after the actual expenditure is incurred and is presented to the Parliament after the end of the financial year in which the expenses were made.
International Maths Day 2022:
14th March, every year is observed as the International Day of Mathematics.
- The International Day of Mathematics is a project led by the International Mathematical Union with the support of numerous international and regional organizations.
- The first International Day of Mathematics was marked in March 2020.
- March 14 is already celebrated in many countries as Pi Day because that date is written as 3/14 in some countries and the mathematical constant Pi is approximately 3.14.
- The theme for the 2022 International Day of Mathematics is Mathematics Unites.
- National Mathematics Day Celebrated every year on December 22.
- It is observed to honor the birth anniversary of the famous mathematician Srinivasa Ramanujan who greatly contributed towards mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series and continued fractions.
- 2021 marks 134th birth anniversary of Dr Ramanujan.
What Are Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)?

Indian researchers have developed a simple technique of separating the constant background of the Solar Corona and revealing the dynamic corona.
- The technique has been developed jointly by the Aryabhatta Research Institute and the Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
- The simple approach of subtracting the constant background can improve efficiency of identification of Coronal Mass Ejections (CME).
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona.
- They can eject billions of tonnes of coronal material and carry an embedded magnetic field (frozen in flux) that is stronger than the background solar wind interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) strength.
- CMEs travel outward from the Sun at speeds ranging from slower than 250 km per second (km/s) to as fast as near 3,000 km/s.
- The fastest Earth-directed CMEs can reach our planet in as little as 15-18 hours. Slower CMEs can take several days to arrive.
- They expand in size as they propagate away from the Sun, and larger CMEs can reach a size comprising nearly a quarter of the space between Earth and the Sun by the time it reaches our planet.
- They cause radio and magnetic disturbances on the Earth.
- They can drive the Space Weather in near-Earth space.
Gallium Nitride Ecosystem Enabling Centre And Incubator : Bengaluru

Gallium Nitride Ecosystem Enabling Centre and Incubator (GEECI) has been set up in Bengaluru.
- The facility has been jointly set up by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and IISc Bengaluru.
- It is aimed at establishing GaN based Development Line Foundry facility, especially for RF and power applications, including strategic applications.
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) is believed to be the second most important material after silicon for electronics chips.
- Properties of Gallium Nitride: High heat capacity, Sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low, faster-switching speed, higher thermal conductivity and lower on-resistance.
- GaN is a semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
- Gallium Nitride Technology is of strategic importance with its application in the field of 5G, space and defense.
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) plays a key role in enabling e-vehicles and wireless communication.
Maternal Mortality In India (2017-19):

The Registrar General of India’s Sample Registration System (SRS) released the latest special bulletin on Maternal Mortality in India (2017-19).
- As per the World Health Organisation, maternal death is the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management.
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) is defined as the number of maternal deaths during a given time per 1,00,000 live births during the same time.
- The MMR of India has declined by 10 points. It has declined from 113 in 2016-18 to 103 in 2017-19 (8.8 % decline).
- The country had been witnessing a progressive reduction in the MMR from 130 in 2014-2016, 122 in 2015-17, 113 in 2016-18, and to 103 in 2017-19.
- India was on the verge of achieving the National Health Policy (NHP) target of 100/lakh live births by 2020 and certainly on track to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals target of 70/ lakh live births by 2030.
- Many developed countries have successfully brought down MMR to single digits. Italy, Norway, Poland and Belarus have the lowest MMR of two, while it is seven in both Germany and the UK, 10 in Canada and 19 in the US.
- Most of India’s neighbours — Nepal (186), Bangladesh (173) and Pakistan (140) — have a higher MMR. However, China and Sri Lanka are way ahead with MMRs of 18.3 and 36 respectively.
- The number of States that have achieved the SDG target has now risen from five to seven — Kerala (30), Maharashtra (38), Telangana (56), Tamil Nadu (58), Andhra Pradesh (58), Jharkhand (61), and Gujarat (70).
- Kerala has recorded the lowest MMR which puts Kerala way ahead of the national MMR of 103.
- Kerala’s Maternal MMR has dropped by 12 points.
- The last SRS bulletin (2015-17) had put the State’s MMR at 42 (later adjusting it to 43).
- There are now nine States that have achieved the MMR target set by the NHP, which include the above seven and Karnataka (83) and Haryana (96).
- Uttarakhand (101), West Bengal (109), Punjab (114), Bihar (130), Odisha (136) and Rajasthan (141) — have the MMR in between 100-150, while Chhattisgarh (160), Madhya Pradesh (163), Uttar Pradesh (167) and Assam (205) have the MMR above 150.




