Today Current Affairs: 16th November 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Glasgow Agreement:
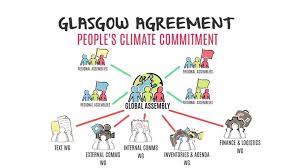
The “Glasgow climate pact” was adopted despite a last-minute intervention by India to water down language on “phasing out” coal to merely “phasing down”.
- The pledges on emissions cuts made at the two-week Cop26 summit in Glasgow fell well short of those required to limit temperatures to 1.5C, according to scientific advice. Instead, all countries have agreed to return to the negotiating table next year, at a conference in Egypt, and re-examine their national plans, with a view to increasing their ambition on cuts.
- One of the fiercest disagreements in the final hours was over the wording of an intention to abandon coal, which was watered down from a “phase-out” to a “phase-down”.
- Yet it marked the first time that such a resolution had been made under the UN climate process.
- Poor countries were also left frustrated at the pact, which they said did not address their concerns about “loss and damage”.
- This refers to the destruction caused by extreme weather, which is now hitting vulnerable countries far harder and more frequently than had been predicted.
RBI’s Retail Direct Scheme:

The Prime Minister has launched the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)- Retail Direct Scheme to open up the Government bond market for the retail investors.
- In February 2021, RBI proposed to allow retail investors to open gilt accounts with the central bank to invest in Government securities (G-secs) directly.
- Under the scheme, retail investors (individuals) will have the facility to open and maintain the ‘Retail Direct Gilt Account’ (RDG Account) with the RBI.
- Retail Investor is a non-professional investor who buys and sells securities or funds that contain a basket of securities such as mutual funds and Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs).
- A Gilt Account can be compared with a bank account, except that the account is debited or credited with treasury bills or government securities instead of money.
- The scheme places India in a list of select few countries offering such a facility.
- Aim:
- The move is aimed at diversifying the government securities market, which is dominated by institutional investors such as banks, insurance companies, mutual funds and others.
- While foreign portfolio investors were allowed to invest in G-secs, their holding is around 2-3% in the overall market.
- Scope:
- It offers a portal avenue to invest in Central government securities, treasury bills, State development loans and sovereign gold bonds.
- They can invest in primary as well as secondary market government securities markets.
Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching Segment (NDS-OM) means RBI’s screen based, anonymous electronic order matching system for trading in Government securities in the secondary market.
Current Account Deficit:

According to a recent report by British brokerage Barclays, India’s trade deficit has been jumping continuously since July 2021. The widening Current Account Deficit (CAD) is driven by the massive spike in commodity prices led by crude oil.
- The CAD is expected to reach $45 billion or 1.4% of GDP by March 2021. This will put pressure on the fragile economic recovery.
- A current account deficit occurs when the total value of goods and services a country imports exceeds the total value of goods and services it exports.
- The balance of exports and imports of goods is referred to as the trade balance. Trade Balance is a part of ‘Current Account Balance’.
Factor involved in India’s Current Account Deficit:
- High Oil Imports: In India, close to 85% of the oil demand is met through imports.
- Due to this it is estimated that every $10 per barrel rise in global crude prices will widen the trade deficit by $12 billion or 35 bps of Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- High Gold Imports: Another force driving down the foreign exchange is gold imports.
- Recovering domestic demand and the ongoing festive season are boosting Gold imports.
- The World Gold Council expects gold demand this year to surpass the 2020 levels and it expects the demand for gold to remain high given the rising wealth effects and incomes.
- Services, the Positive side: The report held that the monthly services surplus has improved from an average of $6.6 billion in 2019 to $7 billion in 2020, and to $8 billion in the first nine months of 2021.
- The report ruled out an alarming situation and said that with record high foreign reserves, there are no major risks to macro stability or balance of payments conditions.
- However, the widening deficit trend may continue for some time as a combination of demand recovery and rising commodity prices will continue to widen the trade deficit sharply.
National Achievement Survey 2021:

The Union Government has conducted the National Achievement Survey (NAS) across India, assessing about 38 lakh students from 1.23 lakh schools in 733 districts in 36 States and Union Territories.
- The survey was last conducted in 2017 and was scheduled to take place in 2020. However, due to the Covid situation, it was postponed until this year (2021).
- It is a nationwide survey to assess the learning outcomes and health of the education system.
- It is the largest, nationwide, sample-based education survey conducted across India.
- It is undertaken by the Ministry of Education.
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducted NAS 2021.
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) designed an assessment framework and tools for NAS-2021.
- It provides a system-level reflection on the effectiveness of school education.
- It collects information on relevant background variables such as school environment, teaching processes, and student home and background factors.
- It covers the whole spectrum of schools including Government schools (both State and Central government), Government-aided schools, and Private schools across India.
- The NAS 2021 was conducted in 22 mediums of instruction that covered English, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Kannada, Hindi, Malayalam, Marathi, Manipuri, Mizo, Punjabi, Odia, Telugu, Tamil, Bodo, Urdu, Garo, Konkani, Khasi, Bhutia, Nepali, and Lepcha.
- It was conducted in different subjects for different grades. The subject and grades wise break up is below:
- Grade 3 and 5: Language, EVS, and Mathematics
- Grade 8: Language, Science, Mathematics, and Social Science
- Grade 10: Language, Science, Mathematics, Social Science, and English
- Objective:
- To provide structured feedback on student learning levels at District, State, and national levels. These inputs are used for policy planning and designing pedagogical interventions to improve quality and ensure equity in learning.
Norovirus:
A highly contagious virus named Norovirus has been detected in Kerala.
- It is a group of viruses that leads to gastrointestinal illness.
- It causes inflammation of the lining of the stomach and intestines, in addition to severe vomiting and diarrhoea.
- Norovirus is resistant to many disinfectants and can heat up to 60°C. Therefore, merely steaming food or chlorinating water does not kill the virus. The virus can also survive many common hand sanitisers.
- A person can be infected with different varieties of norovirus several times in their lives, but developing immunity to one type doesn’t provide protection against other varieties.
- The virus can be transferred from an infected to a healthy individual through contaminated surfaces or food.
- The virus can primarily be transmitted from oral-faecal.
- Disease outbreaks typically occur aboard cruise ships, in nursing homes, dormitories, and other closed spaces.
- The virus can affect people across all age groups but is known to cause serious symptoms in children, the elderly and people with comorbidities.
- Symptoms:
- Diarrhoea, Vomiting, Stomach ache, Gastrointestinal problems etc are the symptoms.
- Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment available to cure the virus, generic medications for diarrhoea and vomiting can help cure the disease.
- Status:
-
- There are 685 million cases annually, of which 200 million are detected among children younger than five years.
Nearly 50,000 children die every year due to diarrhoea caused by the virus.
- There are 685 million cases annually, of which 200 million are detected among children younger than five years.
Tenures Of CBI & ED Directors Extended:

The President promulgated two ordinances that would allow the Centre to extend the tenures of the directors of the Central Bureau of Investigation and the Enforcement Directorate from two years to up to five years.
- The Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act,1946 and the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) Act, 2003 have been amended to give the government the power to keep the two chiefs in their posts for one year after they have completed their two-year terms.
- The chiefs of the Central agencies currently have a fixed two-year tenure, but can now be given three annual extensions.
Amendments in DSPE Act:
- Provided that the period for which the Director holds the office on his initial appointment may, in public interest, on the recommendation of the Committee (the committee led by the Prime Minister and leader of Opposition and CJI as members) and for the reasons to be recorded in writing, be extended up to one year at a time.
- Provided further that no such extension shall be granted after the completion of a period of five years in total including the period mentioned in the initial appointment.
Amendments in CVC Act:
- Provided that the period for which the Director of Enforcement holds the office on his initial appointment may, in public interest, on the recommendation of the Committee (comprising of CVC chief, Revenue and Home Secretaries among others) and for the reasons to be recorded in writing, be extended up to one year at a time.
- Provided further that no such extension shall be granted after the completion of a period of five years in total including the period mentioned in the initial appointment.
Central Bureau of Investigation:
- The CBI was set up in 1963 by a resolution of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Now, the CBI comes under the administrative control of the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- The establishment of the CBI was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption (1962–1964).
- The CBI is not a statutory body. It derives its powers from the DSPE Act, 1946.
- The CBI is the main investigating agency of the Central Government.
- It also provides assistance to the Central Vigilance Commission and Lokpal.
- It is also the nodal police agency in India which coordinates investigations on behalf of Interpol Member countries.
- The CBI is headed by a Director.
- The CBI has jurisdiction to investigate offences pertaining to 69 Central laws, 18 State Acts and 231 offences in the IPC.
Enforcement Directorate:
- Directorate of Enforcement is a specialized financial investigation agency under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- On 1st May 1956, an ‘Enforcement Unit’ was formed, in the Department of Economic Affairs, for handling Exchange Control Laws violations under Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947.
- In the year 1957, this Unit was renamed as ‘Enforcement Directorate’.
H-1B Visa Holders:

The United States has agreed to provide automatic work authorisation permits to the spouses of H-1B visa holders — a move that is likely to benefit thousands of Indian professionals based in the US.
- As per the latest amendments, while L-1 spouses will be given the extension without applying for it, H-4 visa holders will still have to apply for the extension after their employment permit expires.
- This policy amendment is likely to be particularly beneficial for Indian women whose spouses hold H-1B or L-1 visas, as they will now be allowed up to 180 days auto extension on work authorization.
- The American Immigration Lawyers’ Association had filed a class-action lawsuit on behalf of immigrant spouses, many of whom have lost their jobs due to long processing delays for work authorization.
- An H-4 visa is issued to the immediate family members (spouse and children under the age of 21) of H-1B visa holders. Over 94 per cent of H4 visa holders are women, and of these, around 93 per cent are from India.
- L-1 visas are non-immigrant visas that are valid for a relatively short time.
- With this visa, multinationals are able to shift foreign employees to their US offices for specialised positions on a temporary basis.
- The dependent spouse or unmarried children under 21 years of age of an L-1 visa holder are issued L-2 visas to enter the United States.
- L2 visa holders can acquire EAD (Employment Authorisation Documents) to find employment.
NASA’s DART Mission:

On November 24, at around 11.50 am (IST), NASA will launch the agency’s first planetary defense test mission named the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART).
- The spacecraft will be launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
About DART Mission:
- The main aim of the mission is to test the newly developed technology that would allow a spacecraft to crash into an asteroid and change its course.
- DART is a low-cost spacecraft, weighing around 610 kg at launch and 550 kg during impact.
- It also carries about 10 kg of xenon which will be used to demonstrate the agency’s new thrusters called NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster–Commercial (NEXT-C) in space.
- The spacecraft carries a high-resolution imager called Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical Navigation (DRACO).
- Images from DRACO will be sent to Earth in real-time and will help study the impact site and surface of Dimorphos.
- DART will also carry a small satellite or CubeSat named LICIACube (Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids). LICIACube is expected to capture images of the impact and the impact crater formed as a result of the collision.
- It can also capture images of any dust cloud formed during the impact.
- The target of the spacecraft is a small moonlet called Dimorphos (Greek for “two forms”). It is about 160-metre in diameter and the spacecraft is expected to collide when it is 11 million kilometres away from Earth.
- Dimorphos orbits a larger asteroid named Didymos (Greek for “twin”) which has a diameter of 780 metres.
- The spacecraft will navigate to the moonlet and intentionally collide with it at a speed of about 6.6 kilometres per second or 24,000 kilometres per hour. The collision is expected to take place between September 26 and October 1, 2022.
National Interlinking Of Rivers Authority (NIRA):
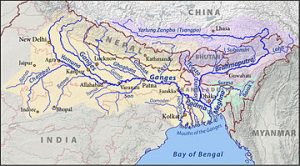
The Centre Government is contemplating creation of the National Interlinking of Rivers Authority (NIRA).
- NIRA is supposed to be an independent autonomous body for planning, investigation, financing and the implementation of the river interlinking projects in the country.
- NIRA will function as an umbrella body for all river linking projects and to be headed by a Government of India Secretary-rank officer.
- It will replace the existing National Water Development Agency (NWDA).
- It will coordinate with neighbouring countries and concerned states and departments and will also have powers on issues related to environment, wildlife and forest clearances under river linking projects and their legal aspects.
- NIRA will have the power to raise funds and act as a repository of borrowed funds or money received on deposit or loan given on interest.
- It will also have the power to set up a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) for individual link projects.
Inter-Linking of Rivers Programme:
- The idea was first mooted during the British Raj when Sir Arthur Cotton, a British general and irrigation engineer suggested linking the Ganga and the Cauvery for navigational purposes.
- Aim: The InterLinking of Rivers programme (ILR) programme is aimed at linking different surplus rivers of the country with deficient rivers so that the excess water from surplus regions could be diverted to deficient regions.
Bhopal’s Habibganj Railway Station : Now Rani Kamlapati Station

The name of Bhopal’s Habibganj railway station has been changed to Rani Kamlapati station.
- The station has been redeveloped at a cost of around Rs 100 crore with private participation — a first such large-scale PPP model in station redevelopment in India, in the works for the past few years.
- Rani Kamlapati was the widow of Nizam Shah, whose Gond dynasty ruled the then Ginnorgarh, 55 km from Bhopal, in the 18th century.
- Kampalati is known to have shown great bravery in facing aggressors during her reign after her husband was killed.
- Kamlapati was the “last Hindu queen of Bhopal”, who did great work in the area of water management and set up parks and temples.
Birth Anniversary Of Birsa Munda:

Birth anniversary of Birsa Munda was observed on November 15th.
- In recognition of his impact on the national movement, the state of Jharkhand was created on his birth anniversary in 2000.
- Bisra Munda was a folk hero and a tribal freedom fighter hailing from the Munda tribe.
- He was a spearhead behind the Millenarian movement that arose in the Bihar and Jharkhand belt in the 19th century under British colonisation. He is also known as ‘Dharti Abba’ or the Earth Father.
- Born on 15th November 1875.
- Bisra wanted to reform the tribal society and so, he urged them to let go of beliefs in witchcraft and instead, stressed on the importance of prayer, staying away from alcohol, having faith in God and observing a code of conduct. Based on these, he started the faith of ‘Birsait’.
- Bisra started a movement called ‘Ulgulan’, or ‘The Great Tumult’.
- His struggle against the exploitation and discrimination against tribals led to a big hit against the British government in the form of the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act being passed in 1908.
- The act restricted the passing on of land from the tribal people to non-tribals.
Munda Rebellion:
- It is one of the most important tribal movements.
- It was led by Birsa Munda in the south of Ranchi in 1899-1900.
- The movement identified following forces as the cause of the misery the Mundas were suffering:
- The land policies of the British were destroying their traditional land system.
- Hindu landlords and moneylenders were taking over their land.
- Missionaries were criticising their traditional culture.
Significance of Munda Rebellion:
- It forced the colonial government to introduce laws so that the land of the tribals could not be easily taken over by dikus (Chotanagpur Tenancy Act, 1908).
- It showed that the tribal people had the capacity to protest against injustice and express their anger against colonial rule.




