Today Current Affairs: 17th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
‘Umang’, ‘Rain Alarm’ And ‘Damini’.:

Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah called for giving maximum publicity to various mobile apps related to weather forecasting like ‘Umang’, ‘Rain Alarm’ and ‘Damini’.
- The Damini app monitors the lightning occurrence all over India and alerts the user of lightning near them by a GPS notification under 20km and 40km.
- Damini app triggers warning about lightning strikes three hours in advance which can help reduce losses to life and property.
- Developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM-Pune) and Earth System Science Organization(ESSO) under the ministry of earth sciences,
- Launched in 2020.
Sankalp Se Siddhi – Mission Van Dhan:

Minister for Tribal Affairs launches the tribal livelihoods initiative “Sankalp Se Siddhi – Mission Van Dhan”
- TRIFED now plans to expand its operations through the convergence of various schemes of different Ministries and Departments and launch the various tribal development programs in Mission Mode under “Sankalp Se Siddhi – Mission Van Dhan” for expediting its implementation in a Mission mode.
- Through this mission, the establishment of 50,000 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras, 3000 Haat Bazaars, 600 Godowns, 200 Mini TRIFOOD Units, 100 Common Facility Centres, 100 TRIFOOD parks, 100 SFURTI clusters, 200 Tribes India retail stores, e-commerce platforms for TRIFOOD and Tribes India brands is being targeted.
WHO Global Tuberculosis Programme:

A virtual high-level event on ‘Global Drive to Scale-up TB Prevention’ was recently organized by WHO Global Tuberculosis Programme.
- The purpose of this special high-level event was to discuss key actions needed at the global and country-level to scale up TB prevention strategies and drive progress towards achieving the 2022 UN High-Level Meeting target on TB preventive treatment.
- TB is an infectious disease caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It typically affects the lungs (pulmonary TB) but can also affect other sites.
- The disease is spread when people who are sick with pulmonary TB expel bacteria into the air, for example by coughing.
- India is aggressively implementing its fully-funded National Strategic Plan to End TB.
- In the last few years, 50 million people have been treated.
- India seeks to achieve a national scale-up of TB preventive treatment (TPT).
- It also seeks to achieve the UN High-Level Meeting (UNHLM) targets of 40 million persons started on TB treatment and 30 million on TPT globally in the remaining 18 months.
- Sub-national Certification of States and Districts instituted in 2020- The initiative marks districts/States-UTs on “Progress towards TB Free Status” under different categories measured with graded milestones of decline in TB incidence.
Inland Vessels Bill, 2021:

The Union Cabinet has given the nod to the Inland Vessels Bill, 2021, which will replace the Inland Vessels Act, 1917.
- The Bill will regulate the safety, security, and registration of inland vessels.
Key features of the Bill:
- It provides for a unified law for the entire country, instead of separate rules framed by the States.
- The certificate of registration granted under the proposed law will be deemed to be valid in all States and Union Territories, and there will be no need to seek separate permissions from the States.
- The Bill provides for a central database for recording the details of the vessel, vessel registration, crew on an electronic portal.
- It requires all mechanically propelled vessels to be mandatorily registered. All non-mechanically propelled vessels will also have to be enrolled at district, taluk or panchayat or village level.
Corporatization Of Ordnance Factory Board:

The Union Cabinet approved a plan to corporatise the Ordnance Factory Board (OFB).
New Structure:
- 41 factories across the country will be dissolved into seven new Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSU). The newly created entities will be 100% owned by the government.
- These entities will be responsible for different verticals of the products such as the Ammunition and Explosives group will be engaged in the production of ammunition while a Vehicles group will engage in the production of defence mobility and combat vehicles.
- All OFB employees in the production units will be transferred to the new corporate entities on a deemed deputation initially for a period of two years without altering their service conditions as central government employees.
Pension liabilities of the retirees and existing employees will continue to be borne by the government.
OFB:
- It is an umbrella body for the ordnance factories and related institutions and is currently a subordinate office of the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- The first Indian ordnance factory was set up in the year 1712 by the Dutch Company as a GunPowder Factory, West Bengal.
- It is a conglomerate of 41 factories, 9 Training Institutes, 3 regional marketing centres and 5 regional controllers of safety.
- Headquarters: Kolkata
- Significance: A major chunk of the weapon, ammunition and supplies for not just armed forces but also paramilitary and police forces comes from the OFB-run factories.
- Production includes Civilian and military-grade arms and ammunition, explosives, propellants and chemicals for missile systems, military vehicles, armoured vehicles, optical devices, parachutes, support equipment, troop clothing and general store items.
Industrial Corridors Scheme:
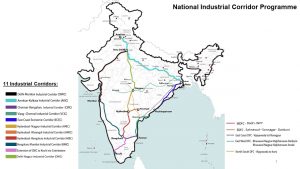
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Government of India signed a USD 484 million loan for the Tamil Nadu Industrial Connectivity Project.
- The loan is to improve transport connectivity and facilitate industrial development in the Chennai – Kanyakumari Industrial Corridor (CKIC) in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- The loan is in line with Strategy 2030, ADB’s long-term corporate strategy, the project emphasises sustainability, climate change resilience, and road safety elements.
- Under Strategy 2030, ADB will expand its vision to achieve a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
- CKIC is part of India’s East Coast Economic Corridor (ECEC).
Industrial Corridors Scheme:
- An industrial corridor is an economic ecosystem built around a transportation corridor connecting two major economic centers, where the transportation corridor serves as the nerve center of the economic activity across the corridor.
- In addition to the transportation corridor, a well-designed industrial corridor contains clusters of industrial production serving regional and global demand, and urban centers proliferating equitable development.
- In 2019, the government approved the development of the five industrial corridor projects, being implemented through National Industrial Corridor Development and Implementation Trust (NICDIT).
- NICDIT is an apex body under the administrative control of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Children And Digital Dumpsites: WHO Report:

The World Health Organization (WHO) in its recent report “Children and Digital Dumpsites” has underlined the risk that children working in informal processing are facing due to discarded electronic devices or e-waste.
- There are as many as 18 million children (as young as five years) and about 12.9 million women work at these e-waste dumpsites every year.
- The e-waste from high-income countries is dumped in the middle- or low-income countries for processing every year.
About the E-waste:
- E-Waste is short for Electronic-Waste.
- It is the term used to describe old, end-of-life or discarded electronic appliances.
- It majorly includes electronic equipment, completely or in part discarded as waste by the consumer or bulk consumer as well as rejects from manufacturing, refurbishment and repair processes.
- It contains over 1,000 precious metals and other substances like gold, copper, lead, mercury, cadmium, chromium, polybrominated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Volume of E-waste:
Global Scenario:
- According to the Global E-waste Statistics Partnership, the volume of e-waste generated is surging rapidly across the globe.
- About 53.6 million tonnes of e-waste were generated in 2019.
- Only 17.4% of this e-waste was processed informal recycling facilities. The rest of it was dumped in low- or middle-income countries for illegal processing by informal workers.
- This is because of the rise in the number of smartphones and computers.
Indian Scenario:
- According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generated more than 10 lakh tonnes of e-waste in 2019-20, an increase from 7 lakh tonnes in 2017-18. Against this, the e-waste dismantling capacity has not been increased from 7.82 lakh tonnes since 2017-18.
- In 2018, the Ministry of Environment had told the tribunal that 95% of e-waste in India is recycled by the informal sector and scrap dealers unscientifically dispose of it by burning or dissolving it in acids.
Deep Ocean Mission:

The Union Cabinet has approved the long-pending Deep Ocean Mission.
- The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean similar to the space exploration started by ISRO about 35 years ago.
- The focus of the mission will be on deep-sea mining, ocean climate change advisory services, underwater vehicles and underwater robotics-related technologies.
- The mission is expected to cost ₹4,077 crore over the next five years.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) will be the nodal Ministry implementing this multi-institutional mission.
Key Components of the mission:
- A manned submersible will be developed to carry three people to a depth of 6,000 metres in the ocean with a suite of scientific sensors and tools.
- An Integrated Mining System will be developed for mining polymetallic nodules at those depths in the central Indian Ocean.
- Development of Ocean Climate Change Advisory Services.
- Development of a component for searching deep-sea flora and fauna, including microbes, and studying ways to sustainably utilise them.
- The next component is to explore and identify potential sources of hydrothermal minerals that are sources of precious metals formed from the earth’s crust along the Indian Ocean mid-oceanic ridges.
- It has a component for studying and preparing detailed engineering design for offshore Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) powered desalination plants.
- The final component is aimed at grooming experts in the field of ocean biology and engineering. This component aims to translate research into industrial applications and product development through on-site business incubator facilities.
8th ASEAN Defence Ministers Meeting (ADMM) Plus Was Held Recently:

It is being hosted by Brunei as it is the chair of the ASEAN grouping this year.
- Consistent with the ADMM guiding principles of open and outward-looking, the 2nd ADMM in Singapore in 2007 adopted the Concept Paper to establish the ADMM-Plus.
- The ADMM-Plus is a platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners to strengthen security and defense cooperation for peace, stability, and development in the region.
- Eight Dialogue Partners are Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the USA (collectively referred to as the “Plus Countries”).
- It aims to promote mutual trust and confidence between defense establishments through greater dialogue and transparency.
- Agreed five areas of practical cooperation under this mechanism are:
- Maritime security, counter-terrorism, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, peacekeeping operations and military medicine.
- In 2013, a new priority area of humanitarian mine action was agreed.
World Sea Turtle Day:

World Sea Turtle Day is celebrated on 16 June, every year to educate people on the need to conserve the world’s Sea turtles and their habitats.
- Turtles are the world’s oldest reptile groups in existence, across the world found even before lizards and snakes.
- The first few years of a marine turtle’s life are often referred to as the ‘lost years.
- That’s because the time between when the hatchlings emerge until they return to coastal shallow waters to forage is incredibly difficult to study. The lost years they spend at sea – which can be up to 20 years – largely remain a mystery to humans.
- The seven species of sea turtle are Loggerhead, Green, Leatherback, Hawksbill, Olive Ridley, Kemp’s Ridley, and Flatback. Out of these seven, two species, Hawksbill and Kemps Ridley are considered critically endangered.
- Turtles are found in India, in the coastal states of Odisha, Chennai, and Maharashtra.
- The country is home to five exquisite varieties of turtles, namely:
- Olive Ridley Turtle (Lepidochelys olivacea)
- Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia mydas)
- Hawksbill Turtle (Eretmochelys imbricate)
- Leathery Turtle (Dermochelys coriacea)
- Eastern Mud turtle (Kinosternun subrubum subrubum)
- India’s famous Green Sea turtles are the largest hard-shelled sea turtles and are about 120 cms in length and 136-159 kgs in weight.
Jalgaon Banana:

A consignment of fiber and mineral-rich GI CERTIFIED Jalgaon banana has been exported to Dubai from Tandalwadi village, Jalgaon district of Maharashtra. In 2016, Jalgaon Banana got GI certification which was registered with Nisargraja Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) in Jalgaon.
- India is the world’s leading producer of bananas with a share of around 25 percent in total output.
- Banana is widely grown in the tropical, subtropical, and coastal regions of India.
- Andhra Pradesh is the largest producer in India followed by Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
- All these states contribute more than 70 percent of the country’s banana production.
- The country’s banana export has been rising sharply because of the adoption of farm practices as per the global standards.
- The majority of banana exports from India are to West Asian and North African countries like UAE, Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and Iran.
Dedicated Freight Corridor:
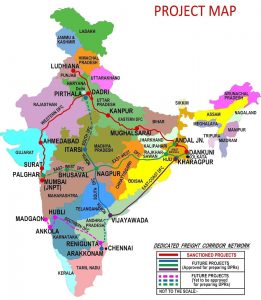
The Indian Army has successfully conducted trial runs of military trains loaded with vehicles and equipment on the dedicated freight corridor.
- It ferried heavy equipment from New Rewari station in Haryana to New Phulera in Rajasthan.
Dedicated Freight Corridor
- Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India is constructing the Western DFC (1506 Route km) and Eastern DFC (1875 route km including Sonnagar-Dankuni PPP Section).
- The EDFC starting from Sahnewal near Ludhiana (Punjab) will pass through the states of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Jharkhand to terminate at Dankuni in West Bengal.
- The Western Corridor connecting Dadri in Uttar Pradesh to Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT) in Mumbai will traverse through the states of UP, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra of WDFC.
- The following two (2) sections of DFC have been commissioned and dedicated to the nation by Hon’ble Prime Minister of India:-
- Bhaupur to Khurja (351 km) of Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) on January 29, 2020.
- Rewari to Madar (306 km) of Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC) on January 7, 2021.
Who Was Fakir Mohan Senapati ?:

Remembering Fakir Mohan Senapati on his 103rd death anniversary. He passed away on June 14, 1918.
- Fakir Mohan Senapati (13 January 1843 – 14 June 1918) was an Indian writer, poet, philosopher and social reformer.
- He is often referred to as Utkala Byasa Kabi (Odisha’s Vyasa). He is regarded as the father of Odia nationalism and modern Odia literature.
- He played a leading role in establishing the distinct identity of Odia language. He is known to have introduced novel writing, short story, and autobiography genres in Odia literature.
- Chha Maana Atha Guntha is the first Indian novel to deal with the exploitations of landless peasants by the feudal Lord. It was written much before the October revolution of Russia or much before the emerging of Marxist ideas in India.
- His “Rebati” (1898) is widely recognized as the first Odia short story.
- He wrote a long poem, Utkala Bhramanam, that first appeared in 1892.




