Today’s Current Affairs: 17th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Global Report on Food Crises, 2025:

The Global Report on Food Crises 2025, reveals that acute hunger has reached a new record high globally.
- The Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) is an annual, consensus-based technical report coordinated by the Food Security Information Network (FSIN) in support of the Global Network Against Food Crises (GNAFC).
- It is produced through a partnership of key UN agencies (including FAO, WFP, UNICEF), the European Union, and other international organisations and NGOs.
- The GRFC provides in-depth analysis of acute food insecurity and malnutrition at global, regional, and country levels, identifying immediate and underlying drivers, and guiding humanitarian and development interventions.
Key Findings of the 2025 GRFC:
- In 2024, 295.3 million people in 53 countries faced acute food insecurity, up from 281.6 million in 2023. This marks the sixth consecutive annual increase and the highest level since reporting began.
- Nearly a quarter of the population in the assessed countries suffered from acute hunger, with 1.9 million people facing famine conditions (IPC/CH Phase 5)-more than double the previous year.
- Humanitarian allocations to food sectors could fall by up to 45% in 2025, threatening life-saving nutrition services for at least 14 million children and disrupting aid in major crisis zones.
- Over 37 million children under five in 26 countries suffered from acute malnutrition in 2024, with more than 10.2 million experiencing severe acute malnutrition.
Stagflation: Intensified In The United States

In May 2025, concerns over stagflation have intensified in the United States. Banks are now sitting on $482.4 billion in unrealized losses from securities investments, a 32.5% increase from the previous quarter, according to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
- Stagflation is an economic phenomenon where an economy experiences three adverse conditions simultaneously:
- High inflation (rising prices)
- Stagnant or slow economic growth
- High unemployment
- The term was first used in the 1960s and became prominent during the 1970s oil crisis.
- Stagflation is particularly challenging because the usual economic tools to fight inflation or unemployment often worsen the other problem.
- Causes of Stagflation:
- Supply Shocks: Sudden spikes in the cost of essential resources (like oil) increase production costs, leading to both inflation and reduced output.
- Policy Errors: Poorly coordinated fiscal and monetary policies, such as excessive government spending or delayed interest rate hikes, can fuel inflation while failing to stimulate growth.
- Tariff Increases: Recent U.S. tariffs have raised input costs, potentially triggering stagflation by increasing prices and reducing demand.
Shingles Disease:
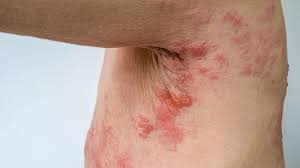
A recent large-scale study from South Korea, published in the European Heart Journal, reveals that individuals vaccinated against shingles have a 23% lower risk of cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
- After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nerve cells and can reactivate years later, especially when the immune system is weakened due to age, illness, or immunosuppressive medications.
- Shingles typically presents as a painful rash, often forming a stripe of blisters on one side of the torso, neck, or face. Other symptoms may include itching, tingling, burning, headache, fever, and sensitivity to light or touch.
- The most common complication is postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), a persistent nerve pain that can last for months after the rash clears.
- Shingles is not contagious, but the virus can be spread to someone who has never had chickenpox.
- It is most common in people over 50 years of age or those with weakened immune systems.
- There is a vaccine called Shingrix available, which helps in preventing shingles and its complications.
- Antiviral medications can reduce the severity and duration of shingles, especially if started early.
Exercise Teesta Prahar:

The Army recently conducted a comprehensive integrated field training exercise named ‘Teesta Prahar’ at the Teesta field firing range.
- Exercise Teesta Prahar was a large-scale integrated field exercise conducted by the Indian Army.
- It was carried out at the Teesta field firing range in West Bengal, near the strategic Siliguri corridor, often referred to as “Chicken’s Neck”, the land that connects India’s northeast region with the rest of the country.
- It showcased the Army’s operational readiness and coordination among combat and support arms in riverine terrain.
- The exercise witnessed active participation from key combat and support arms, including the Infantry, Artillery, Armoured Corps, Mechanised Infantry, Para Special Forces, Army Aviation, Engineers, and Signals.
- A key highlight of the drill was the deployment and validation of newly inducted next-generation weapon systems, military platforms, and advanced battlefield technologies, as a part of the Indian Army’s emphasis on modernisation.
- In addition, the exercise emphasised jointness, synergy, and seamless coordination, reinforcing the Army’s ability to operate swiftly and effectively across varied terrain and adverse weather conditions.
- It featured tactical drills, battle rehearsals, and adaptive manoeuvres aimed at refining responses to dynamic combat scenarios
Tanot Mata Temple:

The historic Tanot Mata Temple, a 1,200-year-old sacred site near the India-Pakistan border in Jaisalmer, is set to reopen for visitors as border tensions subside.
- Tanot Mata Temple is an ancient Hindu temple situated in the Jaisalmer district of Rajasthan.
- It is dedicated to Tanot Rai, a manifestation of the Hindu goddess Hinglaj Mata.
- According to local legends, the temple was established by a group of local tribes who worshipped the goddess Tanot Rai.
- Over time, the temple grew in popularity and became a significant religious site for devotees.
- In 1965 and 1971, during the Indo-Pakistan War, Tanot Mata Temple gained widespread recognition when it survived heavy bombardment unharmed, which further strengthened the belief in the protective powers of the deity among locals and soldiers.
- Despite the shelling of thousands of bombs from the Pakistan border, not one exploded in the vicinity of the temple.
- The unexploded bombs are, till date, treasured in the Tanot Museum within the temple premises.
- After the 1971 war, the temple was handed over to the Border Security Force of India, who continues to manage the Temple.
- The Indian army built a Vijay Sthamba within the temple premises, and every year on December 16, a celebration takes place to commemorate the victory of India over Pakistan.
Rajon ki Baoli:

The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), in collaboration with the World Monuments Fund India (WMFI) and the TCS Foundation, has successfully completed the conservation work of ‘Rajon ki Baoli’, a 16th-century stepwell.
- Rajon ki Baoli, also known as Rajon ki Bain, is a significant historical stepwell located in south Delhi’s Mehrauli Archaeological Park.
- It was built in 1506 CE by Daulat Khan during the reign of Sikander Lodi, of the Lodi dynasty, which was the last pre-Mughal dynasty in India.
- It stands as a testament to Lodi-era architecture and traditional water engineering.
- It was used in its time as a water reservoir and a retreat during summers.
- The stepwell’s name, Rajon ki Baoli, translates to ‘Baoli of the Masons,’ reflecting its historical use by masons for drinking and cooking purposes.
- The stepwell is primarily subterranean, with only the topmost storey visible above ground.
- Its structure is built in four levels, each narrowing down as one approaches the well in the bottom.
- Spanning across an area of 1,610 square metres, this baoli descends to a depth of 13.4 metres, with the main tank measuring 23 by 10 metres at its base.
- It is a fine example of Indo-Islamic architecture, featuring intricate stone carvings, ornate arches, and a functional design that provided a natural respite from the heat.
Campus Calling’ Programme:

The National Commission for Women (NCW) recently launched the ‘Campus Calling’ programme.
- ‘Campus Calling’ Programme is an initiative of the National Commission for Women (NCW) that aims to enhance gender sensitivity, raise awareness on the prevention of sexual harassment, and address cybercrimes impacting students.
- The programme has been launched in collaboration with ‘Yuvamanthan’, a youth development platform.
- The programme aims to reach over 1,000 universities and colleges across the country, making it one of the most extensive youth-centric initiatives undertaken by the NCW.
- It seeks to equip students with the knowledge and skills to combat gender-based discrimination, harassment, and cybercrimes effectively.
- It will identify and appoint two male and two female campus ambassadors from each participating institution.
- These ambassadors will play a pivotal role in spearheading gender sensitization initiatives in their campuses, fostering a culture of safety, equality, and respect among their peers.
- They will act as key representatives, driving positive change and encouraging youth involvement in building inclusive and secure educational spaces.
Multi Agency Centre:

The Union Home Minister recently inaugurated the revamped Multi Agency Centre (MAC).
- MAC is a national intelligence-sharing fusion centre under the Intelligence Bureau (IB) where states and central agencies and police forces coordinate to share, store, collate, and analyse inputs on terrorism on a daily basis under four heads – J&K, Northeast, LWE, and Rest of India.
- It was created in December 2001 in the aftermath of the Kargil conflict but was strengthened in December 2008, following the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks.
- As many as 28 organisations, including the Research and Analysis Wing (RAW), armed forces, and State police, are part of the platform, and various security agencies share real-time intelligence inputs on MAC.
- The new MAC network connects all police districts in the country through a secured network and has been built at a cost of ₹500 crore.
- It incorporates futuristic capabilities such as embedded artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to harness the potential of the vast database with MAC and Geographic Information System (GIS) services.
- The upgraded network will enhance trend analysis, hotspot mapping, and predictive operations, offering more accurate and actionable outcomes.
- The new MAC network spanning the length and breadth of the country has weaved-in country’s Island territories, insurgency-affected areas, and mountainous high-altitude terrain, ensuring last-mile connectivity down to the level of district SPs in the remotest areas with a fast and standalone secure network.
- It will strengthen the country’s efforts to tackle serious threats like terrorism, extremism, organised crime, and cyberattacks.
What is the Gig Economy:

The gig workers’ meeting on “Current Developments, Challenges, and the Way Forward,” organized by the Gig Workers Association, highlighted critical issues within India’s gig economy and recommended the establishment of minimum wages, social security, and legal protections for gig and platform workers.
- It also called for the establishment of tripartite welfare boards at both state and national levels, including representatives of workers, employers, and the government.
- The new Labour Codes of 2019 defines a gig worker as “A person who performs work or participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of traditional employer-employee relationship”.
- It is a labor market of short-term, flexible jobs often enabled by digital platforms.
- Workers, as freelancers or independent contractors, are paid per task rather than through full-time contracts. Common activities include freelance services, food delivery, and digital work.
- A NITI Aayog report estimates 7.7 million gig workers in India in 2020–21, projected to reach 23.5 million by 2029–30, mostly in medium-skilled jobs.
- The gig economy provides flexible work that helps balance personal and professional life, especially benefiting women, while enhancing skills and earning potential.
“Child Wellbeing in an Unpredictable World” : UNICEF Report

A United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) report titled “Child Wellbeing in an Unpredictable World” reveals that children in the world’s wealthiest nations have experienced a steep decline in academic performance, mental health, and physical wellbeing since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- In India, most children with mental health issues remain undiagnosed and untreated.
- Even before Covid-19, 50 million children were affected, with 80–90% not seeking help.
- A 2021 UNICEF-Gallup survey found that only 41% of Indian youth supported seeking mental health help, highlighting widespread stigma and reluctance to seek support.
- It has been observed that suicide is the 4th leading cause of death among the late adolescent age groups (15–19 years) in India.
- According to UNICEF’s World Obesity Atlas 2022, India may have over 27 million obese children by 2030 (1 in 10 globally), with associated economic costs projected to surge from USD 23 billion in 2019 to USD 479 billion by 2060.
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) reduced from 39 per 1000 live births (2014) to 27 per 1000 live births (2021).
- Under-Five Mortality Rate (U5MR) dropped from 45 per 1000 live births (2014) to 31 per 1000 live births (2021).
Skills: - India has one of the largest school systems with over 240 million students and 9 million teachers, but learning outcomes, especially in literacy and numeracy, remain a major challenge.
- The Economic Survey 2024-25 notes that National Education Policy (NEP), 2020 aims for 100% Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) by 2030.
- Currently, GER is nearly universal at the primary level (93%) but lower at the secondary level (77.4%).
- Despite progressive enrollment, learning outcomes remain poor, particularly in foundational literacy and numeracy.
- According to the World Bank’s Learning Poverty Index (percentage of 10-year-olds unable to read a basic text), India’s learning poverty rate increased to 70% post Covid-19, from 55% in 2019.
- A survey by Smile Foundation reveals that 58% of teachers in India believe children missed out on social skills during Covid-19 and get distracted easily.
Algal Bloom Devastates Marine Life:

A massive toxic algal bloom, caused by algae Karenia mikimotoi (bloom-forming dinoflagellate), has severely impacted South Australia’s coastline, leading to the death of over 200 marine species.
- The algal bloom has spread over 150 km of coastline, affecting biodiversity hotspots like Kangaroo Island, Yorke Peninsula, and Fleurieu Peninsula.
- Karenia mikimotoi produces toxins that suffocate marine life by damaging gills, attacking red blood cells, and disrupting the nervous system, leading to abnormal behavior and mass mortality.
- Additionally, marine heatwaves raised sea temperatures by 2.5°C and depleted oxygen, triggering algae blooms whose thick spread reduces oxygen levels, suffocating marine life.
- MHWs are extreme ocean events with sea temperatures rising 3-4°C above average for at least five days, often lasting weeks.
- An algal bloom is a rapid increase in algae population in freshwater, marine, or brackish waters, often visible as green, blue-green, red, or brown patches.
- While most are harmless and support marine life, harmful blooms called Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs)—threaten human health and ecosystems.
- It is caused due to the introduction of a nutrient (such as nitrogen or phosphorus) into an aquatic ecosystem.
- A red tide occurs when certain algae grow excessively, turning the water red, as well as brown.
Neeraj Chopra Crosses 90m Mark, Finishes Second in Doha Diamond League 2025:
Neeraj Chopra breached the 90m mark for the first time in his career at the Doha leg of the 2025 Diamond League held on May 16. With a throw of 90.23m, Chopra became the first Indian and only the third Asian to achieve this feat in men’s javelin. However, despite leading for most of the competition, Chopra was overtaken in the final round by Germany’s Julian Weber, who clinched first place with a throw of 91.06m
Rohit Sharma Stand Inaugurated At Wankhede Stadium:
The Mumbai Cricket Association (MCA) unveiled the Rohit Sharma Stand at the iconic Wankhede Stadium in Mumbai, paying tribute to the Indian cricketing legend following his recent retirement from Test and T20 cricket. The event also saw the inauguration of stands named after Ajit Wadekar and Sharad Pawar, commemorating their invaluable contributions to Indian cricket and cricket administration.The MCA renamed four sections of the Wankhede Stadium on May 16, 2025, in honor of distinguished personalities in Indian cricket. The Rohit Sharma Stand was inaugurated shortly after his Test retirement on May 7, 2025, celebrating his legacy as a player and captain. The Sharad Pawar Stand and Ajit Wadekar Stand were also unveiled to recognize the roles played by the former MCA president and the late cricketing icon respectively.
Praggnanandhaa Clinches First Grand Chess Tour Title at Superbet Classic:
Indian chess prodigy Grandmaster R. Praggnanandhaa achieved a major milestone in his career by winning his first-ever Grand Chess Tour tournament — the Superbet Classic 2025 held in Bucharest, Romania. He emerged victorious after a tense tiebreak battle against top-ranked players including Maxime Vachier-Lagrave and Alireza Firouzja, marking a historic moment for Indian chess on the global stage
Yala Glacier Declared ‘Dead’ in Nepal:
The Yala Glacier in Nepal, once a crucial site for glaciological training and cryosphere research in the Hindu Kush Himalayas (HKH), has now been officially declared “dead” — marking a significant and symbolic loss in the global climate crisis. On May 12, 2025, scientists, local communities, and monks gathered in Langtang, Nepal, to hold a poignant memorial for the glacier, which has retreated dramatically over recent decades. This event highlights the severe impact of global warming on Himalayan glaciers, with profound consequences for water security and ecological stability across South Asia.The Yala Glacier, located in Langtang, Nepal, has lost 66% of its mass and retreated 784 meters since the 1970s.A plaque was installed with messages by authors Andri Snaer Magnason and Manjushree Thapa in English, Nepali, and Tibetan. The glacier funeral was attended by over 50 people, including monks, scientists, and locals from Nepal, India, China, and Bhutan.
India-Japan’s LUPEX Mission Enters Design Phase:
India and Japan have taken a major step in their joint lunar exploration effort with the Chandrayaan-5 mission, also known as LUPEX (Lunar Polar Exploration). The mission, which aims to study the presence of water and water-ice on the Moon’s surface and subsurface, is set to enter the design phase after finalizing instrument selections and completing engineering model testing. The 6.5-tonne spacecraft is scheduled to launch on Japan’s H3 rocket in 2027-28.
India Explores Human Sustainability in Space under BioE3 Policy:
India is poised to conduct its first-ever biological experiments aboard the International Space Station (ISS) as part of the AXIOM-4 mission, marking a crucial step in exploring the sustainability of human life in space. These experiments, in collaboration between ISRO and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), aim to study the behavior of microalgae and cyanobacteria in microgravity. The mission falls under the broader vision of the BioE3 Policy, which promotes the use of biotechnology for sustainable development.




