Today Current Affairs: 1st June 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Operation Rakth Chandan:

Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) has recovered 14.63 MT of Red Sanders worth Rs. 11.70 crore under Operation Rakth Chandan.
- Red Sanders is a flora-species that is endemic to a distinct tract of forests in Eastern Ghats region of Andhra Pradesh and fall under ‘endangered list’ in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List.
- Red Sanders is also listed in Appendix-II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wildlife Fauna and Flora (CITES).
- Its rich hue and therapeutic properties are responsible for its high demand across Asia, particularly China, for use in cosmetics, medicinal products and high-end furniture/woodcraft.
- The export of Red Sanders from India is prohibited as per the Foreign Trade Policy.
Gen Next Democracy Network:

Indian Council for Cultural Relations’s (ICCR) ten days programme Gen Next Democracy Network concluded.
- Youth from democratic countries come to India under the Gen Next Democracy Network programme.
- During the programme, they get acquainted with India’s heritage, culture and functioning of Indian democracy.
- In the closing ceremony, 27 delegates from six countries- Ghana, Bangladesh, Peru, Nepal, Brunei and Norway shared their experiences of visiting India.
Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR):
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India.
- The ICCR Headquarter is situated in New Delhi.
- It was founded in 1950 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the first Education Minister of independent India.
- It is involved in India’s global cultural relations, through cultural exchange with other countries and their people.
- The council also operates missions internationally, with established cultural centres in various countries.
- It also administers the Jawaharlal Nehru Award for International Understanding, established by the Government of India in 1965, whose last award was in 2009.
Cardinal (Catholic Church):

Pope Francis announced that he will create 21 new Cardinals, including two from India at a Consistory on, 27 August, 2022.
- The two Cardinals from India are Archbishop Filipe Neri António Sebastião di Rosário Ferrão, Archbishop of Goa and Damão and -Archbishop Anthony Poola, Archbishop of Hyderabad.
- These cardinals represent the Church worldwide, and reflect a wide variety of cultures, contexts and pastoral ministries.
- He also said that he will meet from August 29 and 30 with all the cardinals to reflect on the new Apostolic Constitution Praedicate evangelium.
- A cardinal (literally “cardinal of the Holy Roman Church”) is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church, immediately behind the pope in the order of precedence.
- Collectively, they constitute the College of Cardinals, and are appointed for life.
Privatisation Of Public Sector Bank:

The government is in the process of taking ‘advanced action’ to take forward the privatisation of public sector banks, top finance ministry officials asserted.
- In the Union Budget for 2021-22, Union Finance Minister had announced privatisation of two PSBs besides IDBI Bank.
- However, this year’s Budget Speech had skipped the mention of the progress made for the privatisation of two PSBs.
- Even as the NITI Aayog has suggested names of two PSBs for privatisation, the Centre is yet to make an enabling provision in the law for the divestment of the government’s stake sale below the 51 per cent threshold.
- The government had listed the introduction of Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1970, in the Winter Session, but the Bill was not tabled. The Aayog had reportedly suggested privatisation of Central Bank of India and Indian Overseas Bank.
- According to the amendments to the Banking Companies Act moved last year, the government is looking to retain at least 26 per cent stake in PSBs post privatisation.
- The approval to privatise the two PSBs is yet to be considered by the Core Group of Secretaries on Divestment (CGD) headed by cabinet secretary.
- Once approved by the CGD, the proposal will be sent to the Alternative Mechanism (AM) that comprises Union Finance Minister Sitharaman and Union Minister of Roads Nitin Gadkari.
- After their nod, the Cabinet will take up the proposal.
Top Sugar Producing States:

After a five-year gap, Maharashtra has overtaken Uttar Pradesh to regain its position as India’s top sugar producer.
- The state’s output for the 2021-22 crushing year (October-September) is expected at 138 lakh tonnes (lt).
- That is an all-time-high, beating the previous 107.21 lt of 2018-19.
- This record production is attributed to three factors.
- The first is the bountiful rainfall since the 2019 southwest monsoon.
- The second is higher yields from farmers taking extra care of their crop.
- The third factor is a huge jump in “unregistered” cane cultivation.
- The large “unregistered” area has meant that there is un-harvested cane still in the fields and mills will continue to crush till the first week of June.
Indus Water Treaty:
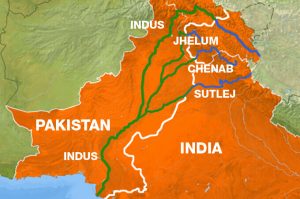
India and Pakistan have begun another round of the Permanent Indus Commission meeting that is held annually under Indus Water Treaty (IWT) 1960.
- The Indus talks have survived the freeze in ties as both countries see it as mandatory under the IWT.
- Under the provisions of the treaty, the two sides are required to meet at least once every year, alternately in India and Pakistan.
- The last meeting, held on March 23-24, 2021 in New Delhi.
About the Indus Water Treaty:
- It is a Water-Distribution Treaty, signed in Karachi on 1960, between India (Pm Jawaharlal Nehru) and Pakistan (President Ayub Khan), brokered by the World Bank.
- Under the provisions of the Indus Waters Treaty, signed between India and Pakistan in 1960, all the waters of the eastern rivers — the Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi — amounting to around 33 MAF (million acre-feet) annually is allocated to India for unrestricted use.
- The waters of western rivers — Indus, Jhelum, and Chenab — amounting to around 135 MAF annually are largely for Pakistan.
- Under the Treaty, India has been given the right to generate hydroelectricity through a run of the river projects on the western rivers subject to specific criteria for design and operation.
- It also gives the right to Pakistan to raise concerns on the design of Indian hydroelectric projects on western rivers.
- The Permanent Indus Commission is a bilateral commission of officials from India and Pakistan, created to implement and manage goals of the Indus Waters Treaty, 1960.
- The Commission according to the treaty must meet regularly at least once a year, alternately in India and Pakistan.
50% Of Rural Households Covered Under The Jal Jeevan Mission:

50% of rural households in India have now been covered under the Jal Jeevan Mission.
- At the time of launch of Jal Jeevan Mission in 2019, only 3.23 Crore households i.e. 17% of the rural population had access to drinking water through taps.
- Certain state and union territories such as Goa, Telangana, A&N Islands, D&N Haveli and Daman & Diu, Puducherry and Haryana have already achieved 100% household connections.
- Punjab, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh and Bihar have coverage of more than 90% and are progressing fast towards attaining the status of ‘Har Ghar Jal (water in every household)’.
- JJM envisages supply of 55 litres of water per person per day to every rural household through Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) by 2024.
- It is under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- It was launched in 2019.
- The Mission is based on a community approach to water and includes extensive Information, Education and Communication as a key component of the mission.
- JJM looks to create a jan andolan for water, thereby making it everyone’s priority.
- The fund sharing pattern between the Centre and states is 90:10 for Himalayan and North-Eastern States, 50:50 for other states, and 100% for Union Territories.
INS Gomati:

The Indian Navy Ship (INS) Gomati was decommissioned from the naval dockyard in Mumbai.
- INS Gomati derives her name from the vibrant river Gomti.
- Gomati River, also called Gumti, tributary of the Ganga River.
- When decommissioned, INS Gomati was also the oldest of the guided-missile frigates in the Western Fleet.
- It was commissioned in 1988 at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Bombay.
- Participated in: Operations Cactus, Parakram and Rainbow, and several bilateral and multinational naval exercises.
- 1988: Under Operation Cactus the Indian Armed Forces have helped the government of Maldives in the neutralization of the coup attempt.
- 2001: Operation Parakram launched in the wake of terrorist attack on Parliament, was the first full-scale mobilisation since the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- 2004: The Rainbow initiative was launched to assist those affected by the Tsunami, in partnership with the Sri Lankan government.
- Awarded twice the coveted Unit Citation, once in 2007-08 and again in 2019-20.
Non CO2 Pollutants:

According to a new study, world needs to target both non-CO2 pollutants and CO2 pollutants to achieve climate targets.
- Global temperatures are likely to exceed 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial levels by 2035 and 2°C by 2050 if the focus is merely on decarbonisation efforts.
- The Non-CO2 Pollutants include methane, black carbon, hydrofluorocarbons (HFC), tropospheric ozone and nitrous oxide.
- Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. It contributes to the formation of ozone.
- Black carbon is a major component of PM2.5 and a potent warming agent in the atmosphere, and contributes to regional environmental disruption and accelerates glacier melting.
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are greenhouse gases (GHGs) commonly used in refrigeration, air-conditioning (AC), building insulation, fire extinguishing systems, and aerosols.
- Tropospheric ozone is formed by the interaction of sunlight, particularly ultraviolet light, with hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, which are emitted by automobile tailpipes and smokestacks.
- Nitrous oxide is a greenhouse gas which is 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2). A major proportion of the N2O emissions came from the agricultural sector.
- These gases are emitted from a broad range of sectors and sources, namely:
- Methane is mostly emitted from extraction, distribution and combustion of fossil fuel, industrial processes, enteric fermentation, rice cultivation, manure management, other agricultural sources, and the waste sector.
- N2O is mostly emitted from industrial processes, agricultural soils, manure management and wastewater.
- F-gases are mostly emitted from industrial processes.
- The share of non-CO2 pollutants contributing to global warming is almost as much as carbon dioxide.
- IPCC WGI reports have shown that the contribution of CO2 and non-CO2 greenhouse gases to global heating was 52-57% and 43-48 %, respectively.
Indo Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness Initiative
QUAD grouping consisting of India, Australia, Japan and the US rolled out an Indo-Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA) initiative for information sharing and maritime surveillance across the Indo Pacific region.
- But Infrastructure constraints and continued delay in posting Indian liaison officers limit India’s ability to further expand its role.
- Indo Pacific Maritime Domain Awareness Initiative (IPMDA) initiative was announced at the Quad Leaders’ Summit in Tokyo, 2022 to track “dark shipping” and to build a “faster, wider, and more accurate maritime picture of near-real-time activities in partners’ waters” integrating three critical regions in the Indo-Pacific — the Pacific Islands, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Dark ships are vessels with their Automatic Identification System (AIS) – a transponder system – switched off so as not to be detectable.
- It will also allow tracking other tactical-level activities, such as rendezvous at sea, as well as improve partners’ ability to respond to climate and humanitarian events and to protect their fisheries, which are vital to many Indo-Pacific economies.
- The IPMDA will help QUAD countries as well as littoral states in the backdrop of expanding Chinese naval presence across the region.
- This will further increase the existing role of Indian Liaison Officers in building linkages with various agencies in their home countries.
Second-Year Anniversary Of National AI Portal:

The second-year anniversary of National AI Portal was celebrated on 30th May, 2022.
- National AI Portal Launched in 2020, it is a joint initiative by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), National e-Governance Division (NeGD) and NASSCOM (National Association of Software and Services Companies).
- The portal focuses on creating and nurturing a unified AI ecosystem in the country to drive excellence and leadership in knowledge creation to develop an AI-ready robust workforce for the future and use AI to foster economic growth.
Artificial Intelligence:
- It describes the action of machines accomplishing tasks that have historically required human intelligence.
- It includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self algorithms etc.
- AI involves complex things such as feeding a particular data into the machine and making it react as per the different situations.
- AI is being used across different industries including finance and healthcare.
- As per a report by PwC, India reported a 45% increase in the use of AI, the highest among all countries, following the outbreak of the virus.
Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme:

The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises has approved the extension of the Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) for five years till FY26.
- The PMEGP has now been approved for continuation over the 15th Finance Commission Cycle for five years from 2021-22 to 2025-26 with an outlay of Rs 13,554.42 crore.
- The Government of India approved the introduction of a credit linked subsidy programme called Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) in 2008 for generation of employment opportunities through establishment of micro enterprises in rural as well as urban areas.
- It allows entrepreneurs to set up factories or units.
- It is a central sector scheme being administered by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME).
- Implementing Agency at the National Level: Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) – a statutory organization under the administrative control of the Ministry of MSME.
- Eligibility:
- Any individual, above 18 years of age.
- Only new projects/units are considered for sanction of loans.
- Self-help groups that have not availed benefits under any other public scheme, societies, production co-operative societies, and charitable trusts.
- Maximum Cost of Project/Unit Admissible:
- Manufacturing Sector: Rs. 50 lakh
- Service Sector: Rs.20 lakh
- Government Subsidy:
- Rural Areas: 25% for general category and 35% for special category, which includes SC/ST/OBC/Minorities, NER, Hill and Border Areas, transgender, physically disabled, north eastern region, aspirational and border district applicants.
- Urban Areas: 15% for general category and 25% for special category.
- Role of Banks: Loans are provided by Public Sector Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Co-operative Banks and Private Scheduled Commercial Banks approved by respective State Task Force Committee.
World No Tobacco Day:

31st May is observed as ‘World No Tobacco Day’ every year to spread awareness around the deadly effects of tobacco consumption.
- The Member States of the World Health Organization created World No Tobacco Day in 1987 to draw global attention to the tobacco epidemic and the preventable death and disease it causes.
- In 1988, Resolution WHA 42.19 was passed, calling for the celebration of World No Tobacco Day, every year on 31 May.
- The theme of World No Tobacco Day 2022 is “Protect The Environment”.
- As per WHO, “The harmful impact of the tobacco industry on the environment is vast and growing, adding unnecessary pressure to our planet’s already scarce resources and fragile ecosystems.”
- Every year, the WHO honours governments, organisations and individuals for their efforts and contributions to curbing tobacco use.
- This year, the WHO has selected Jharkhand for the World No Tobacco Day (WNTD) Award-2022.
What Are Unicorns?

The number of unicorns in India reached the 100-mark.
- The total valuation of these unicorns is USD 330 billion, that is over Rs 25 lakh crore.
- The average annual growth rate of Indian unicorns is more than that of the U.S., the U.K. and many other countries.
- India has become the third-largest startup ecosystem in the world after the US and China.
- A unicorn is any privately owned firm with a market capitalization of more than USD 1 billion.
- One unicorn means a startup of at least Rs 7,500 crore turnover.
- There are several categories like fintech, Edtechs, B2B (Business-to-Business) companies, etc.
PARAM ANANTA India’s Latest Super Computer

PARAM ANANTA is India’s latest super computer.
- It has 838 TeraFlops supercomputing capability.
- It was commissioned at IIT Gandhinagar under National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- It has been developed jointly by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) and the Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar.
- Param Ananta will rank behind C-DAC’s Param Siddhi-AI, which as of November 2021 was the 102nd most powerful supercomputer in the world.
- Under NSM, till date 15 supercomputers have been installed across the nation with aggregate compute capacity of 24 petaflops.
- All these supercomputers have been manufactured in India and operating on indigenously developed software stack.




