Today’s Current Affairs: 20th October 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
State Mining Readiness Index:

The Ministry of Mines released the State Mining Readiness Index (SMRI)
- It serves as a tool for benchmarking State performance and encouraging healthy competition, accelerating the pace of mining reforms and sustainable resource management across India.
- Published by Ministry of Mines
- The index evaluates States on parameters like: auction performance, early mine operationalisation, focus on exploration, and sustainable mining practices related to non-coal minerals.
- These indicators aim to capture the overall readiness and efficiency of States in facilitating mining activity and implementing reforms.
- Under the SMRI framework, States have been divided into three categories based on their mineral endowment:
- Category A – States rich in mineral resources
- Category B – States with moderate mineral resources
- Category C – States with limited mineral resources
- State rankings of SMRI 2025:
- Category A: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Gujarat secured the top three positions.
- Category B: Goa, Uttar Pradesh, and Assam ranked in the top three.
- Category C: Punjab, Uttarakhand, and Tripura achieved the top three ranks.
Markanda River:

The National Green Tribunal (NGT) recently directed the State Pollution Control Boards of Himachal and Haryana and the Sirmaur deputy commissioner to file detailed reports on the status of water pollution caused by industries in the Markanda River in the Sirmaur district of Himachal Pradesh.
- Markanda River is a tributary of the Ghaggar
- It was historically known as Aruna and is linked to the mythological Saraswati River.
- It originates from the lower Shiwalik hills in the Nahan area of Sirmaur district, Himachal Pradesh.
- It flows through Kala Amb, entering at Bikram Bag and exiting at Sadhora Bridge.
- The river then enters Haryana, covering 130 km before joining the Ghaggar River at Ismailabad.
- It is a rain-fed river and has extremely low flow in the winter and summer months but rises suddenly in the monsoon.
- The Markandeshwar Temple, dedicated to Maharshi Markandeya, stands on its banks
- The Markanda River Basin consists of several small seasonal streams, mainly from the Shivalik Hills, which contribute to its flow during the monsoon.
Blackbuck:

Over the last five years, the Chhattisgarh government has successfully reintroduced the blackbuck back into the state’s forests through its five-year reintroduction plan.
- Blackbuck is a species of antelope native to India and Nepal.
- Scientific Name: Antilope cervicapra
- It is widespread in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and other areas throughout peninsular India.
- It has been declared as the state animal by the governments of Punjab, Haryana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- The blackbuck mostly lives in open grasslands, dry scrub areas, and thinly forested areas.
- Features:
- It is a medium-sized
- It is known for its beautiful spiraling horns. Only the male blackbucks have these They can grow quite long, sometimes over 20 inches.
- Male blackbucks are usually dark brown or black on their backs and sides. They have white fur on their bellies, inner legs, and around their eyes.
- This creates a striking contrast.
- Young males and females are lighter in color, often yellowish-brown.
- They have very good eyesight and are also very fast runners, which comprise their main defense against predators. They can reach speeds of up to 50 miles per hour.
- They are gregarious and social animals with herds generally ranging from 5 to 50 animals.
- Conservation Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concerned.
IN-RoKN Exercise:

Indian Naval Ship (INS) Sahyadri recently arrived at Busan Naval Harbour, South Korea, on 13 October 2025 to participate in the inaugural India–Republic of Korea Navy (IN–RoKN) Bilateral Exercise.
- It is the Indian Navy (IN)–Republic of Korea Navy (RoKN) bilateral naval exercise.
- The inaugural IN–RoKN Exercise is taking place in South Korea.
- It will be conducted in two phases—harbour and sea—to deepen interoperability, enhance coordination, and promote professional exchanges between the two navies.
- As part of the harbour phase, IN and RoKN officials will engage in reciprocal cross-deck visits, sharing of best practices, cross-training sessions, and sport fixtures.
- The Commanding Officer of INS Sahyadri will also call on senior officers of the Republic of Korea Navy, local dignitaries, and representatives from the Indian community in South Korea, reaffirming India’s diplomatic goodwill and naval outreach.
- The harbour phase will be followed by the sea phase, wherein, INS Sahyadri and ROKS Gyeongnam will undertake joint exercises.
- INS Sahyadri commissioned in 2012, INS Sahyadri (F49) is the third ship of the Shivalik Class of Guided Missile Stealth Frigates.
- It was designed and built indigenously by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), Mumbai.
- Armed with advanced stealth features, state-of-the-art weapon systems, and cutting-edge sensors, INS Sahyadri can conduct multi-dimensional warfare operations—surface, subsurface, and air—making it a versatile asset for India’s blue-water naval ambitions.
- The frigate is based at Visakhapatnam, under the Eastern Fleet of the Eastern Naval Command.
Public Trust Doctrine:

The Supreme Court recently held that the doctrine of public trust is not confined only to natural waterbodies such as rivers, lakes, and wetlands but also extends to man-made or artificially created waterbodies that serve ecological or environmental purposes.
- It is a legal principle establishing that certain natural and cultural resources are preserved for public use.
- Rooted in Roman law and developed through English common law, this doctrine encompasses various public assets such as tidal waters, lakes, rivers, wetlands, and ecosystems.
- It rests on the principle that certain resources have such great importance to the people as a whole that it would be wholly unjustified to make them a subject of private ownership.
- The public is considered the owner of the resources, and the government protects and maintains these resources for the public’s use.
- The doctrine enjoins upon the government to safeguard the resources for the enjoyment of the final public instead of to allow their use for personal possession or industrial functions.
- Three types of restrictions on governmental authority are often thought to be imposed by the public trust:
- the property subject to the trust must not only be used for a public purpose, but it must be held available for use by the general public;
- the property may not be sold, even for a fair cash equivalent;
- the property must be maintained for particular types of uses.
Taftan Volcano:

New research shows that Taftan volcano in Iran seems to be waking up after a 700,000-year-long sleep.
- It is a 12,927-foot (3,940 meters) semi-active stratovolcano located in southeastern Iran, 56 km from the Pakistan border.
- It is the only active volcano in the Makran continental volcanic arc.
- It is situated among a rump of mountains and volcanoes that was formed by the subduction of the Arabian ocean crust under the Eurasian continent.
- It hosts an active hydrothermal system and smelly, sulfur-emitting vents called fumaroles.
- The volcano contains two summits (Narkuh and Matherkuh).
- It isn’t known to have erupted in human history.
- Stratovolcano is a tall, steep, and cone-shaped type of volcano.
- Unlike flat shield volcanoes, they have higher peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
- Stratovolcanoes comprise the largest percentage (~60%) of the Earth’s individual volcanoes, and most are characterized by eruptions of andesite and dacite, lavas that are cooler and more viscous than basalt.
Henley Passport Index 2025:

India’s passport has slipped to 85th rank in Henley Passport Index 2025, down five places from the previous year.
- Henley Passport Index is a popular ranking of global passports that measures passport strength by the number of destinations that holders can visit without a prior visa.
- The index ranks countries based on statistics provided by the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- It started in 2006 as the Henley & Partners Visa Restrictions Index (HVRI).
- The index includes 199 different passports and 227 different travel destinations
- The stronger the passport, the more countries its holders can enter without a prior visa — a privilege that reflects diplomatic ties, economic influence, and international trust.
Key Highlights of Henley Passport Index:
- Globally, Singapore leads the 2025 list with visa-free access to 193 destinations, followed by South Korea (190) and Japan (189).
- Several European nations, including Germany, Italy, Spain, Luxembourg, and Switzerland, share the next few ranks with access to around 188–189 countries.
- The United States has slipped out of the top 10 for the first time in two decades, ranking 12th this year with access to 180 destinations.
- Afghanistan sits at the bottom (106th) offering visa-free access to just 24–26 countries.
Celestial body -Chiron:

Astronomers for the first time observed a ring system formation around icy celestial body Chiron.
- Chiron is part of a class of objects called centaurs (which populate the outer solar system between Jupiter and Neptune), displaying characteristics of both asteroids and comets.
- It was discovered in 1977 by astronomer Charles Kowal.
- Features of Celestial body –Chiron
- It has a diameter of about 200 kilometers (125 miles) and takes about 50 years to complete one orbit around the sun.
- Ring system: Its observations clearly showed that it is surrounded by well-defined 4 rings. The three inner rings are embedded within dust swirling around in a disk-like shape.
- These rings are likely composed mainly of water ice mixed with small amounts of rocky material, like those of Saturn.
- It mainly consists of rock, water ice and complex organic compounds.
- Chiron exhibits occasional comet-like activity – ejecting gas and dust into space.
- A method called stellar occultation was used by a team including Brazilian, French and Spanish researchers to observe the rings.
MERCOSUR Group:

India and Brazil agreed to significantly expand their existing trade agreement between India and the MERCOSUR bloc.
- The Southern Common Market(MERCOSUR for its Spanish initials) is a South American regional economic organization.
- It is the fourth largest integrated market after the European Union (EU), North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and ASEAN.
- It was created in 1991 by signing the Treaty of Asunción.
- Objective is Free movement of goods, services, capital and people and it became a customs union in January 1995.
- It originally comprised Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay as its members.
- Bolivia and Venezuela joined it later. (Venezuela has been suspended since December 1, 2016).
- Mercosur also counts Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, and Suriname as associate members.
- Headquarters: Montevideo, Uruguay.
- Its official working languages are Spanish and Portuguese.
- It is bloc’s highest decision-making body, provides a high-level forum for coordinating foreign and economic policy.
- The group consists of the foreign and economic ministers of each member state, or their equivalent, and decisions are made by consensus.
- The group’s presidency rotates every six months among its full members.
- India and MERCOSUR signed a Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) in 2004.
United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific:

India has been elected as Co-Chair of the Regional Committee of the United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) for a three-year term till 2028.
- The UN-GGIM-AP is one of the five regional committees of the United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management.
- It is the apex inter-governmental mechanism for making joint decisions and setting directions with regard to the production, availability and use of geospatial information within national, regional and global policy frameworks.
- It was initially established in 1995 as the Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (PCGIAP).
- It was rebranded as UN-GGIM-AP in 2012, subsequent to the establishment of UN-GGIM in 2011.
- Aim is to address global challenges regarding the use of geospatial information.
- It is represented by the National Geospatial Information Agencies of 56 countries in Asia and the Pacific region.
- It works to maximize the economic, social, and environmental benefits of geospatial information through cooperation, capacity development, and shared solutions.
- Secretariat: United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) serves as secretariat since 2018.
Ayushman Bharat and Universal Health Coverage:

The National Health Authority’s (NHA) Annual Report 2024–25 has revealed that under the Ayushman Bharat–Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) while government hospitals make up the majority of empanelled institutions, most beneficiaries are actually availing treatment in private hospitals, often at higher costs.
Key Findings Regarding the AB-PMJAY: hj
- Of the 31,005 hospitals empanelled under AB-PMJAY, only 45% are private, yet they account for 52% of the 9.19 crore hospitalisations and receive 66% of the total ₹1.29 lakh crore treatment cost.
- Since 2018, 14% of treatments under AB-PMJAY have been for haemodialysis, followed by fever (4%), gastroenteritis (3%), and animal bites (3%).
- In 2024‑25, the top specialties were General Medicine, Ophthalmology, and General Surgery.
- A key feature of Ayushman Bharat is portability, enabling treatment across states.
- Top in-migration destinations are Chandigarh (19%), Uttar Pradesh (13%), and Gujarat (11%), while states with highest out-migration are Uttar Pradesh (24%), Madhya Pradesh (17%), and Bihar (16%).
- The government’s digital health ecosystem is progressing fast: 6 in 10 people have an ABHA number, 50 crore health records are linked, 38% of health facilities and 26% of health personnel are registered on the system.
- ABHA number is a 14-digit ID that creates a cloud-based account for securely storing digital health records.
President of Mongolia Visit to India:

The President of Mongolia undertook a State Visit to India, commemorating the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations and the 10th anniversary of the Strategic Partnership between the two nations.
- India launched a capacity-building programme for Mongolia’s border security forces and strengthened defence ties via training programmes and a Defence Attache at the Indian Embassy.
- The visit confirmed the USD 1.7 billion Oil Refinery Project in Mongolia, funded by an Indian Line of Credit, marking India’s largest global development partnership and pivotal for Mongolia’s energy security.
- Cooperation in critical minerals, rare earths elements, and coking coal was highlighted as a priority, with India considering logistical routes through Vladivostok (Russia) and Tianjin port (China) for importing Mongolian coking coal.
- India will send the holy relics of Lord Buddha’s disciples, Sariputra and Maudgalyayana, to Mongolia, and an MoU was signed between the Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council and Arkhangai Province to boost cultural ties.
- India will also send a Sanskrit teacher to the Gandan Monastery (Mongolia) and launch a project to digitize one million ancient Mongolian manuscripts.
- Both sides signed pacts on cultural exchange, immigration cooperation, disaster management, and Bogd Khan Palace (Mongolia) renovation, while India’s developmental role was highlighted via the Atal Bihari Vajpayee Centre of Excellence for IT and the India-Mongolia Friendship School.
India-Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor:
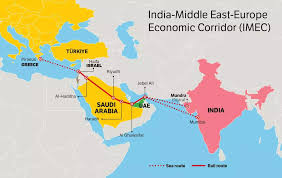
The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), unveiled at the 2023 G20 Summit, aims to link India with Europe through the Middle East.
- However, ongoing conflicts in West Asia and emerging Arctic routes pose serious challenges to its implementation and strategic viability.
- IMEC is a strategic multi-modal connectivity initiative launched through a MoU at the G20 Summit 2023, New Delhi. It has two corridor segments Eastern Corridor (connects India to the Gulf region) and Northern Corridor (connects the Gulf region to Europe).
- IMEC signatories include India, US, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, Italy, and the EU. It is part of the G7’s Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII, 2021).
- The IMEC emerged in 2023 amid favourable geopolitics, supported by the Abraham Accords and improving India-UAE, Saudi Arabia, and US ties. It aims to link Israel’s Haifa port with Jordanian railways and Gulf ports.
- IMEC aims to develop an integrated network of ports, railways, roads, sea lines, energy pipelines, and digital infrastructure (undersea digital cables) to enhance trade and economic cooperation between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- IMEC is designed as a transparent, sustainable, and debt-free alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), ensuring infrastructure development without compromising national sovereignty.
- Economic & Strategic Benefits for India: IMEC reduces logistics costs by ~30% and transport time by ~40% versus the Suez Canal route, boosting export competitiveness.
- For India, IMEC is a strategic opportunity to diversify trade routes, reducing reliance on chokepoints like the Suez Canal. The corridor enhances access to European markets via the Mediterranean, providing an alternative to China’s BRI.
- With the EU as one of India’s largest trading partners (USD 136 billion in 2024-25), stronger connectivity could boost export competitiveness.
- IMEC also aligns with India’s Act West policy, deepening engagement with the Middle East for energy security, remittances, and diaspora links, while countering Pakistan’s regional strategic influence.
- It aligns with India’s One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative to harness solar and green hydrogen energy from the Middle East and supports India’s transition to a low-carbon economy.
Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PM-FME) Scheme:

The Union Finance Minister of India announced the release of ₹3,791.1 crore to States and Union Territories under the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PM-FME) Scheme.
- PM-FME aims to strengthen micro food enterprises, promote ‘Vocal for Local’ products, and integrate rural entrepreneurs into the formal economy.
- Launched on 29 June 2020, the PM-FME Scheme is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- It was launched for a duration of 2020–21 to 2025–26 with a total outlay of ₹10,000 crore.
- Salient Features of the Scheme:
- Common Infrastructure: FPOs, Cooperatives, SHGs, and Government agencies setting up food processing units with shared facilities are eligible for a 35% credit-linked subsidy, up to ₹3 crore.
- Credit-Linked Subsidy: Individuals, FPOs, NGOs, Cooperatives, SHGs, and Pvt. Ltd. firms can avail a 35% subsidy, up to ₹10 lakh per unit, for upgrading or setting up new units.
- One District One Product (ODOP): Implements an ODOP approach to promote scale, value chain development, and marketing support- covering 713 districts in 35 States/UTs with 137 unique products.
- Seed Capital for Self Help Groups: Provides ₹40,000 per member, up to ₹4 lakh per SHG, as seed capital for working capital and small tools, disbursed through SHG federations.
- Marketing & Branding: Offers a 50% grant for branding and marketing initiatives by FPOs, SHGs, Cooperatives, or SPVs to promote processed food products.
- Capacity Building: Provides training under the Food Processing Entrepreneurship Development Programme to enhance technical and business skills of beneficiaries.
- Cost Sharing Pattern: 60:40 between Centre and States, 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan States, 60:40 for UTs with legislature, and 100% Central funding for other UTs.
GPS Spoofing : In News
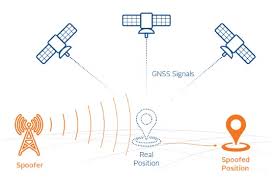
An Air India flight operating from Vienna to Delhi was forced to divert after a suspected GPS signal spoofing over the Middle East disrupted its navigation. The spoofing of signals caused severe degradation of the aircraft’s flight control systems, including failures in autopilot, autothrust, flight director, and autoland functions.
- It is a cyberattack in which fake or counterfeit GPS signals are sent to receivers, causing them to compute incorrect position, navigation, or time information.
- Attackers use ground-based transmitters to broadcast strong counterfeit GPS signals that override genuine satellite signals.
- The GPS receiver locks onto these fake signals, producing incorrect location or time readings.
- Spoofing can cause aircraft navigation systems including autopilot, flight director, and autoland, to malfunction, leading to misrouting, cockpit confusion, false warnings, and risks of entering restricted airspace or collisions.
- Unlike jamming, which blocks or disrupts signals, spoofing feeds false data, making detection and response more difficult.
- Robust backup navigation systems like Inertial Reference Systems (IRS) offer alternative location data during spoofing.
- Anti-spoofing technologies, multi-constellation GNSS, advanced signal processing, and pilot training are essential to enhance resilience.
Onset of the northeast monsoon:
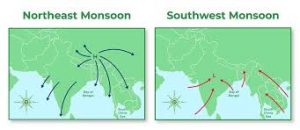
The timely onset of the northeast monsoon in October 2025 has brought much-needed relief to Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh, regions that rely heavily on it for both agriculture and water security.
- Northeast Monsoon (October to December): As the southwest monsoon (June to September) begins to fade, the northeast monsoon sets in by October.
- This is also called the retreating monsoon. It is shorter and less widespread but still important, especially for southern India.
- By October, the land starts to cool faster than the ocean. This creates a high-pressure area over the Indian subcontinent and a low-pressure area over the surrounding seas.
- The direction of wind flow reverses and winds blow from land to sea.
- These are called northeasterlies.
- Since these winds pass over the Bay of Bengal before reaching the southeastern coast, they pick up some moisture.
- As they reach Tamil Nadu, south Andhra Pradesh and parts of Sri Lanka, they provide abundant moisture for rainfall activity.
- This rain is crucial for regions like Tamil Nadu that do not receive much during the southwest monsoon. It supports rabi crops and replenishes reservoirs in the southern peninsula.
Tomahawk Missiles:

The U.S. President has indicated that Washington may consider supplying long-range Tomahawk cruise missiles to Ukraine if Russia does not undertake credible measures to de-escalate the ongoing conflict.
- The Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile. It can be launched from ships and submarines for precision strikes on high-value or heavily defended targets.
- The missile’s low-altitude flight path and advanced guidance systems allow it to evade radar and navigate complex terrain.
- The missile fires a solid propellant at launch, then runs on a turbofan that emits minimal heat, so it’s hard to spot with infrared sensors.
- Uses GPS, Inertial Navigation System (INS), TERCOM (terrain mapping), and DSMAC (digital scene matching) for high precision.
- Modern variants allow mid-flight reprogramming, enabling real-time target adjustments or mission aborts.
Indigenous Military Combat Parachute System:

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully tested the indigenously developed Military Combat Parachute System (MCPS) from a record altitude of 32,000 feet, marking a major milestone in indigenous defence innovation and self-reliance.
- MCPS is developed by DRDO’s Aerial Delivery Research & Development Establishment (Agra) and Defence Bioengineering & Electromedical Laboratory (Bengaluru).
- High-Altitude Capability: It is the only parachute system in operational use by the Indian Armed Forces capable of functioning above 25,000 feet.
- Integrated with Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC), MCPS provides secure, interference-free operations and resilience against external jamming or denial-of-service threats.
- Designed with a lower descent rate, superior steering control, accurate navigation, and pre-determined landing zone deployment, ensuring greater paratrooper safety and mission efficiency.
- MCPS enhances operational autonomy, reduces dependency on foreign systems, and ensures quicker maintenance turnaround during wartime or emergencies.
State of Finance for Forests (SFF) 2025 Report:

The first State of Finance for Forests (SFF) 2025 Report by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) highlights that global investments in forests must triple by 2030 to achieve climate, biodiversity, and land restoration goals.
- Only US billion was invested in forests in 2023—91% public, 9% private—while US billion is needed annually by 2030 to meet global climate goals.
- Governments contributed US billion, led by China and the U.S., with tropical forest nations accounting for just 17% of domestic spending, showing major regional disparities.
- Private Forest finance was US billion, mainly via certified commodity chains (39%) and impact investing (23%), while high-risk tropical commodities got minimal funds despite causing 97% of global deforestation.
- Environmentally damaging agricultural subsidies reached US billion in 2023, and banks financed US trillion to firms with deforestation risk—vastly exceeding green investments.
- Achieving Rio Convention targets requires expanding 1 billion ha by 2030, with protected forests and avoided deforestation needing US billion annually, while reforestation requires US billion.
COP30 and Global Climate Diplomacy:

The upcoming 30th Conference of Parties (COP30) to the UNFCCC, scheduled for November 2025 in Belém, Brazil, comes amid heightened climate anxiety — the 1.5°C target slipping away, the U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, and growing scepticism over multilateral climate processes.
- COP30 marks a shift from target-setting to implementation and financing mechanisms.
- The Brazilian Presidency has declared it the “COP of Action,” focusing on deploying funds and practical solutions rather than new promises.
- Developed nations are expected to scale up climate finance to billion annually by 2035, up from the long-standing billion goal. The focus is now on allocation efficiency between mitigation and adaptation.
- A proposed roadmap aims to mobilize trillion in climate finance by 2035 through public-private coordination and innovative green instruments.
- The Amazon and Beyond: Hosting COP in Belém, gateway to the Amazon, underlines Brazil’s intent to integrate forest conservation, biodiversity protection, and indigenous participation in climate policy.
- Developing countries are set to push back against the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), arguing for climate equity and fair trade, while promoting voluntary carbon markets and green industrialization.
Synchronous All India Elephant Estimation (SAIEE) 2021–25:

After over a year’s delay, the Synchronous All India Elephant Estimation (SAIEE) 2021–25 results were released in Dehradun by the Union Environment Ministry and Wildlife Institute of India (WII), reporting 22,446 elephants across India.
- SAIEE is India’s nationwide synchronized census of Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) conducted every five years to estimate their population, distribution, and habitat health.
- Jointly released by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) and the Wildlife Institute of India (WII).
- Aim is to create a harmonized, data-driven baseline for elephant population monitoring by synchronizing it with the tiger estimation framework to ensure scientific accuracy and comparability.
- Key Results:
- Total Elephant Population: 22,446 individuals across India.
- Western Ghats: 11,934 elephants – largest cluster in the country.
- Northeastern Hills & Brahmaputra Plains: 6,559 elephants.
- Shivalik Hills & Gangetic Plains: 2,062 elephants.
- Central India & Eastern Ghats: 1,891 elephants.
- Top States by Population: Karnataka (6,013), Assam (4,159), Tamil Nadu (3,136), Kerala (2,785), Uttarakhand (1,792).
- Decline in Jharkhand (-68%) and Odisha (-54%) due to mining and habitat degradation.
- Rise in Chhattisgarh (+82.6%) and Madhya Pradesh, attributed to migration from disturbed eastern regions.
United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP):

India has been elected as the Co-Chair of the United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) for a three-year term (2025–2028).
- The UN-GGIM-AP is one of the five regional committees of the United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM).
- It coordinates regional efforts to promote geospatial governance, data sharing, and sustainable development through mapping and information systems.
- Originally set up in 1995 as the Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific (PCGIAP).
- Rebranded as UN-GGIM-AP in 2012 following the creation of UN-GGIM in 2011, integrating regional geospatial initiatives under the UN umbrella.
- Represents 56 national geospatial authorities from countries across Asia and the Pacific.
- India’s Co-Chair term will run till 2028, reflecting its growing role in shaping global geospatial policy and data ecosystems.
- Aim is to maximize the social, economic, and environmental value of geospatial data through regional collaboration and innovation, to strengthen spatial data infrastructure (SDI), enhance policy frameworks, and facilitate data-driven decision-making for achieving the SDGs.
Akkai Padmashali becomes the first transgender person from Karnataka to join a Supreme Court-appointed committee:
Trans rights activist Akkai Padmashali has been appointed to a Supreme Court panel tasked with formulating an equal opportunity policy for the protection of transgender rights. She is the first transgender person from Karnataka to serve on such a committee, marking a historic step for representation and inclusivity in policymaking at the national level. It Allows direct contribution to shaping policies for transgender persons in India.
First SC-appointed committee with transgender community representation.Ms. Padmashali aims to work towards Ambedkar’s vision of equality and social justice.
Nirmal Kumar Minda takes over as President of Assocham, with Axis Bank’s Amitabh Chaudhry named Senior Vice‑President:
Nirmal Kumar Minda, the Executive Chairman of Uno Minda Group, assumed the role of President of the Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (Assocham). Alongside him, Amitabh Chaudhry, Managing Director & CEO of Axis Bank, has been named as the Senior Vice‑President of Assocham, though his appointment is subject to RBI approval.Nirmal Kumar Minda has been a prominent figure in the auto component industry for over five decades.He has been credited with shaping supply chains in the sector and placing innovation at the core of his group’s strategies. His leadership style is noted for being customer‑centric and people‑oriented.
UIDAI Launches Aadhaar Mascot Design:
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has announced a nationwide Mascot Design Contest aimed at finding an official visual ambassador for Aadhaar. The competition is being hosted on the MyGov platform and is open until 31 October 2025. Participants — either individuals or teams — can submit original mascot designs along with a concept note explaining how their creation embodies Aadhaar’s spirit. The winning designs will receive cash awards totaling up to ₹1 lakh, plus certificates of recognition.
11th India International Science Festival to Be Held in Chandigarh:
The India International Science Festival (IISF) is India’s flagship science outreach initiative that brings together scientists, students, innovators, and the public. The 11th edition of IISF is scheduled from 6 to 9 December 2025 in Chandigarh, with the theme “Vigyan se Samruddhi: For Atma Nirbhar Bharat”. This festival aims not only to celebrate scientific achievements across the country but also to underscore India’s journey toward self‑reliance (Atma Nirbhar Bharat) through science and technology.
Harsh Sanghavi Becomes Gujarat Deputy CM in Cabinet Shake-Up:
Harsh Sanghavi was sworn in as the Deputy Chief Minister of Gujarat, signaling a significant shift in the state’s political leadership. This move came as part of a massive cabinet reshuffle led by Chief Minister Bhupendra Patel, who inducted 25 ministers in a fresh bid to restructure governance, improve regional representation, and prepare for future electoral challenges. The oath-taking ceremony took place at the Mahatma Mandir Convention Centre in Gandhinagar, in the presence of Governor Acharya Devvrat, who administered the oaths to the new ministers.
BLS International to Operate Indian Visa Centres in China:
BLS International Services Ltd has secured a three-year contract from India’s Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) to establish and operate Indian Visa Application Centres (IVACs) in China. The contract, which became effective on October 14, 2025, authorizes BLS to manage visa services in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou, three major Chinese cities. This move follows India’s recent decision to resume tourist visa issuance to Chinese nationals after a prolonged suspension.
India’s Trade Deficit Hits $32.15 Billion in September 2025:
India’s merchandise trade deficit widened sharply to $32.15 billion in September 2025, marking an 11-month high, according to data released by the Commerce Ministry on October 15. This surge, significantly above expectations, reflects a faster rise in imports than exports—compounded by recent US tariff hikes on key Indian goods. This development comes just days before critical trade negotiations with Washington, where India is expected to increase its US energy imports and defend its Russian oil purchases amid growing geopolitical scrutiny.
Bajaj Finserv AMC Launches ‘Pay with Mutual Fund’ via UPI:
Bajaj Finserv AMC has unveiled a groundbreaking feature that bridges investing and daily payments—the ‘Pay with Mutual Fund’ facility. In collaboration with fintech firm Curie Money, this innovation allows investors to use their mutual fund units to make UPI transactions, seamlessly blending the world of asset growth with real-time spending needs.The new feature enables investors to scan any UPI QR code and make payments directly using their mutual fund investmentsThe transaction is routed via the investor’s bank account, while the underlying amount is redeemed from a liquid mutual fund in real time.This system allows investors to keep their funds growing at higher returns compared to a traditional savings account, while still enjoying instant liquidity for day-to-day transactions.




