Today’s Current Affairs: 22ndt Jul 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023 : Rajasthan

The Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023, introduced by the Rajasthan government, aims to provide additional income support to people in the state. The Bill seeks to help citizens cope with inflation and improve their financial stability.
- The Bill has three broad categories: right to minimum guaranteed income, right to guaranteed employment, and right to guaranteed social security pension.
Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023:
- The Bill guarantees a minimum income for every adult citizen for 125 days a year.
- Each adult citizen will receive minimum income through the Indira Gandhi Shahri Rozgar Guarantee Yojana in urban areas and the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in rural areas.
- The state will add 25 days of employment to MGNREGA’s 100 days for rural areas.
- The government will pay minimum wages weekly or fortnightly after the completion of work in urban and rural employment schemes.
- A designated officer will ensure job sites are within five kilometers of the registered job card address.
- If employment is not provided within 15 days of application, the applicant will receive a weekly unemployment allowance “and in any case not later than a fortnight.”
- The Bill ensures that people falling under categories like old age, specially abled, widows, and single women receive a pension.
- The pension will see an annual increase of 15% in two installments, starting from the financial year 2024-2025.
Distinguishing from Cash Transfer Schemes: - The Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill is unique as it legally guarantees both minimum income support and guaranteed employment and pensions, setting it apart from regular cash transfer schemes.
- It reflects Mahatma Gandhi’s vision of comprehensive welfare measures.
- The Bill covers all families in the state, offering employment and pension support to various vulnerable groups.
- Cash transfer schemes may have limited coverage.
- The Bill includes annual increment in pensions, ensuring they keep pace with inflation. Cash transfer schemes may not have such provisions.
- The Bill takes a comprehensive approach towards social security, aiming to benefit vulnerable sections of society.
India Bans Non-Basmati White Rice Exports:

The Indian government has imposed an immediate ban on the export of non-basmati white rice, except for certain ongoing shipments.
- This variety of rice had accounted for 25% of the total rice exports from the country.
- This step was taken in response to the 11.5% increase in domestic rice prices in 2022 and a subsequent 35% surge in exports of this rice variety during 2022-23.
- The Ministry attributed this surge in exports to various factors, including high international prices driven by geopolitical scenarios, El Nino influences, and extreme climatic conditions in other rice-producing countries.
- The ban aims to stabilize the domestic market and ensure adequate availability of non-basmati white rice for Indian consumers, while export policies for basmati rice and non-basmati parboiled rice remain unchanged.
Vision Document To Achieve 2070 Net Zero Target : Jharkhand

Jharkhand, a state known for its rich mineral resources and significant contribution to India’s industrial development, is now gearing up for a remarkable transition towards sustainability and a low-carbon economy.
- The state’s Department of Forest, Environment, and Climate Change recently released a vision document outlining a comprehensive plan to achieve the net-zero target by 2070.
- The document outlines eight thematic areas that are crucial for Jharkhand to achieve its net-zero target by 2070.
- These areas encompass a wide spectrum of measures, ranging from renewable energy adoption to environmental preservation.
- One of the pivotal thematic areas identified is “Coal Transition.”
- Being a major source of energy in India, Jharkhand has played a significant role in coal production, contributing more than 16% of the country’s total output.
- The vision document recognizes the importance of transitioning away from non-renewable resources to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
- A key component of the plan is the establishment of a ‘centre of excellence’ on sustainable transition.
- This center will play a vital role in helping Jharkhand diversify its economy, moving away from dependence on non-renewable resources and fostering innovation in sustainable practices.
Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
The Government recently introduced the Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill, 2023 in Rajya Sabha.
- Cinematograph (Amendment) Bill 2023 seeks to amend the Cinematograph Act 1952.
- It has provisions for harsher punishment for film piracy and the introduction of new-age categories for classifying films.
- It has provisions to classify films on the basis of age group instead of the current practice of rating them “U” (unrestricted public exhibition), “A” (restricted to adult audiences), and “UA” (unrestricted public exhibition subject to parental guidance for children below the age of 12).
- The amendments seek to add new classifications – ‘UA-7+’, ‘UA-13+’, and ‘UA-16+’ in place for 12 years.
- It also seeks to bring about uniformity in categorisation of films and content across platforms.
- The Bill holds stricter punishment for those responsible for piracy. This includes three years of imprisonment and a Rs 10 lakh penalty for those engaged in piracy.
- Once the Bill is released, the act of piracy will be considered an offence legally and will include even transmitting pirated content punishable.
mRNA Vaccines : Target And Stimulate Protective Immune Cell Responses
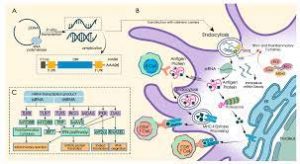
Researchers have recently developed an mRNA-based vaccine that can effectively target and stimulate protective immune cell responses against the malaria-causing parasite Plasmodium
- mRNA is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis.
- mRNA is made from a DNA template during the process of transcription.
- The role of mRNA is to carry protein information from the DNA in a cell’s nucleus to the cell’s cytoplasm (watery interior), where the protein-making machinery reads the mRNA sequence and translates each three-base codon into its corresponding amino acid in a growing protein chain.
- So, mRNA really is a form of nucleic acid which helps the human genome, which is coded in DNA, to be read by the cellular machinery.
- mRNA vaccines work by introducing a piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein, usually a small piece of a protein found on the virus’s outer membrane.
- By using this mRNA, cells can produce the viral protein.
- As part of a normal immune response, the immune system recognizes that the protein is foreign and produces specialized proteins called antibodies.
- Once produced, antibodies remain in the body, even after the body has rid itself of the pathogen, so that the immune system can quickly respond if exposed again.
- Antibodies help protect the body against infection by recognizing individual viruses or other pathogens, attaching to them, and marking the pathogens for destruction.
- If a person is exposed to a virus after receiving mRNA vaccination for it, antibodies can quickly recognize it, attach to it, and mark it for destruction before it can cause serious illness.
- Individuals who get an mRNA vaccine are not exposed to the virus, nor can they become infected with the virus by the vaccine.
Zombie Fire:

As global temperatures rise, fires are also spreading farther north and into the Arctic , which is causing an increase in “zombie fires.”
- Zombie fire is a fire from a previous growing season that can smoulder under the ground which is made up of carbon-rich peat.
- These fires also produce more smoke because of their lower temperature of combustion.
- It occurs as the organic-rich Arctic soils dry up because of changing climate conditions, they can burn slowly and release vast amounts of smoke into the atmosphere.
- One major culprit is the rising temperature: The Arctic is warming nearly four times faster than the rest of the world, a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification.
- Among the changing conditions that favour wildfires are changes in atmospheric circulation that create periods of extreme heat, dry out vegetation and reduce moisture in soils, and, importantly, lead to more frequent lightning strikes that can spark blazes.
- As the Arctic warms and fires move farther northward, peat soils rich in dead plant material burn at an accelerated rate.
- The burning peat also removes the layer insulating permafrost, the region’s frozen carbon-rich soil.
Credit Guarantee Scheme : For Livestock Sector

The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying (DAHD) has introduced the ‘Credit Guarantee Scheme’ under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to support the Livestock sector’s Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme aims to strengthen the credit delivery system and ensure smooth access to finance for entrepreneurs engaged in the Livestock sector.
- The main objective is to encourage lenders to focus on the viability of projects and provide credit facilities based on the primary security of the assets being financed.
- By providing access to financial assistance, it promotes investments in various areas of the livestock sector, such as dairy and meat processing, animal feed plants, breed improvement technology, waste management, and veterinary vaccine and drug manufacturing facilities.
- The DAHD has set up a credit guarantee fund trust of Rs 750 crore, which will cover up to 25 per cent of credit facilities extended to eligible MSMEs by lending institutions.
- The trust, formed in partnership with NAB Sanrakshan Trustee Company Private Ltd, a subsidiary of NABARD, ensures credit guarantee for MSMEs under the AHIDF scheme.
- Key features include:
- Interest subvention of three per cent
- Loan of up to 90 per cent of the total project cost from any Scheduled Bank, National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
Panel Of Vice Chairpersons : Reconstituted

Rajya Sabha Chairman reconstituted the panel of vice chairpersons of the Parliament’s Upper House with half of them being women.
- Under the Rules of Rajya Sabha, the Chairman nominates from amongst the members a panel of vice-chairpersons.
- Any one of them can preside over the House in the absence of the Chairman or the Deputy Chairman.
- He/she has the same powers as the Chairman when so presiding.
- He/she holds office until a new panel of vice-chairpersons is nominated.
- When a member of the panel of vice chairpersons is also not present, any other person as determined by the House acts as the Chairman.
- It must be emphasised here that a member of the panel of vice chairpersons cannot preside over the House, when the office of the Chairman or the Deputy Chairman is vacant.
- During such time, the Chairman’s duties are to be performed by such member of the House as the president may appoint for the purpose.
- The elections are held, as soon as possible, to fill the vacant posts.




