Today’s Current Affairs: 22nd March 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
SRIJAN Portal:

Minister of State for Defence said in the Rajya Sabha that 26 thousand defence items have been uploaded on SRIJAN Portal.
- SRIJAN Portal : The Department of Defence Production has developed an indigenization portal
- It will give information on items that can be taken up for indigenization by the private sector.
- On this portal, DPSUs/OFB/SHQs can display the items which they have been importing or are going to import which the Indian Industry can design, develop and manufacture as per their capability or through a joint venture with OEMs.
- The Indian Industry will be able to show their interest. The concerned DPSUs/OFB/SHQs, based on their requirement of the items and their guidelines & procedures will interact with the Indian industry for indigenization.
Navroz : Iranian New Year

Google Doodle is celebrating the Iranian New Year Navroz, a festival that is celebrated by Parsis all across the globe.
- Navroz is an Iranian and Persian New year. The word ‘now’ means ‘new’ and roz means ‘day’.
- Therefore, the word translates to a new day.’
- It marks the beginning of the spring seasonand is celebrated with great fervour by members of the Parsi community across the globe.
- The festival of Nowruz is named after the Persian king, Jamshed, who is credited for creating the Persian or the Shahenshahi calendar.
- It is said that the festival came to India courtesy of an 18th-century wealthy tradesman from Surat, Nusservanji Kohyaji,who often travelled to Iran and began celebrating Nowruz in India.
- It is listed in the list of UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity of India.
- In India, the festival is observed around August 16-17 by the Parsi community following the Shahenshahi calendar which does not account for leap years,
Letter of Comfort (LoC):

The Finance Ministry recently asked central public sector undertakings (CPSUs) to issue letters of comfort (LoCs) based on their own financial strength.
- An LoC is a letter issued to a lending institution by a stakeholder of the company acknowledging the support of the attempt for financing asked by that company.
- They are usually issued by a third party or a stakeholder in the transaction.
- For instance, a holding company can give an LoC on behalf of its subsidiary, or a government can issue a letter of comfort for PSUs.
- It is not legally binding and does not imply that the parent company guarantees repayment of the loan being sought by the subsidiary company.
- It merely gives reassurance to the lending institution that the parent company is aware of the credit facility being sought by the subsidiary company and supports its decision.
- This provides some comfort to the financial institution to lend money for the short term or long term.
- It, thus, is a moral rather than a legal obligation for the borrower.
- It can also be issued by banks, NBFCs, and auditors.
- It lays down the contract conditions and steps to complete the transaction successfully.
Zealandia : Missing Continent
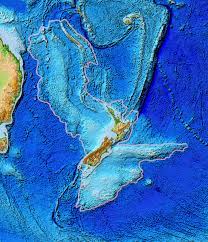
Scientists have recently confirmed the existence of a “missing” continent known as Zealandia
- Zealandia is a long, narrow microcontinentthat is mostly submerged in the South Pacific Ocean.
- Zealandia was formally one of the constituent continents of the ancient supercontinent called Gondwana, which also included Western Antarctica and Eastern Australia over 500 million years ago.
- It began to “pull away” from Gondwana roughly 105 million years ago.
- As Zealandia started pulling away, it began to sink beneath the waves, with over 94 percent remaining underwater for millennia.
- It is approximately 1.89 million square miles (4.9 million square km) in size, about half the size of Australia.
- The vast majority of this new continent lies beneath 6,560 feet (2km) of water.
- The part of Zealandia which is above water forms the foundation of New Zealand’s north and south islands as well as the island of New Caledonia.
- The existence of Zealandia was first recorded in 1642 by Dutch businessman and sailor Abel Tasman, who was on a mission to find the “great Southern Continent,” or Terra Australis.
International Day Of Forests 2023:

The International Day of Forests, also known as World Forests Day, is celebrated each year on March 21 to raise awareness about the importance of forests and trees for the survival of humanity and the planet.
- The theme for 2023 is ‘Forests and Health.’
- The history of the International Day of Forests can be traced back to 1971 when the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) established World Forestry Day.
- The day was established to create and raise awareness of the importance of forests for people and the planet.
- In 2011, the United Nations declared the years 2011 to 2020 as the International Decade of Forests.
- Its objective was to promote sustainable management, conservation, and development of all types of forests.
- In 2012, the International Day of Forests was established.
Status of Forests in India:
- As per the India State of Forest Report-2021, forest and tree cover in the country increased by 2,261 square kilometres since the last assessment in 2019.
- India’s total forest and tree cover was 80.9 million hectares, which accounted for 24.62% of the geographical area of the country.
- The report said 17 States and Union Territories had more than 33% of their area under forest cover.
- Madhya Pradesh had the largest forest cover, followed by Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Maharashtra.
- The top five States in terms of forest cover as a percentage of their total geographical area were Mizoram (84.53%), Arunachal Pradesh (79.33%), Meghalaya (76%), Manipur (74.34%) and Nagaland (73.90%).
Multiple Indicator Survey:

The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) carried out the Multiple Indicator Survey (MIS) covering the entire country in its 78th round.
Key Findings:
- Kerala, Manipur, Nagaland, and Jharkhand have less than 90% access to an improved source of drinking water.
- Among major states, Assam, Jharkhand, Bihar, and Odisha are among the worst in access to tapped drinking water for both rural and urban households.
- Among the major states Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha have the lowest proportion of rural households with access to an exclusive toilet.
- In the states like Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Nagaland and Madhya Pradesh, for more than 70% of households, firewood is the primary source of energy for cooking. These states along with Jharkhand have less than 25% of households using LPG for cooking– the lowest among all states and UTs
- Among big states, Uttarakhand, Odisha, Kerala, and Delhi have the highest proportion (more than 20%) of men aged 15 to 24 who were not in education, employment, or training at the time of the survey.
- For females, the proportion was highest in Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Odisha, Gujarat, West Bengal, and Bihar.
Multiple Indicator Survey:
- A MIS is a type of survey designed to collect data on a range of key indicators related to the well-being of individuals, households, and communities.
- The survey typically covers topics such as health, education, water and sanitation, nutrition, and child protection.
Synthesis Report Of IPCC AR6:

The IPCC finalized the Synthesis Report for the Sixth Assessment Report during the Panel’s 58th Session held in Interlaken, Switzerland from 13 – 19 March 2023
- According to an IPCC report, climate change is a threat to human well-being and planetary health and a window of opportunity to secure a liveable and sustainable future for all is fast closing
Key Findings:
- Human-induced global warming of 1.1 degrees Celsius has spurred changes to the Earth’s climate that are unprecedented in recent human history.
- Already, with 1.1 degrees Celsius of global temperature rise, changes to the climate system that are unparalleled over centuries to millennia are now occurring in every region of the world, from rising sea levels to more extreme weather events to rapidly disappearing sea ice.
- Climate impacts on people and ecosystems are more widespread and severe than expected, and future risks will escalate rapidly with every fraction of a degree of warming.
- Adaptation measures can effectively build resilience, but more finance is needed to scale solutions.
- Climate policies in at least 170 countries now consider adaptation, but in many nations, these efforts have yet to progress from planning to implementation. Measures to build resilience are still largely small-scale, reactive and incremental, with most focusing on immediate impacts or near-term risks.
- Current global financial flows for adaptation are insufficient for, and constrain implementation of, adaptation options, especially in developing countries.
- There is a more than 50% chance that global temperature rise will reach or surpass 1.5 degrees Celsius between 2021 and 2040 across studied scenarios, and under a high-emissions pathway, specifically, the world may hit this threshold even sooner — between 2018 and 2037.
- India has many such examples of maladaptation, resulting in vulnerable communities becoming more helpless to the impacts of climate change rather than being able to adapt to them.
- Maladaptation is defined as the changes in natural or human systems that inadvertently increase vulnerability to climate stimuli.
- It is an adaptation measure that does not succeed in reducing vulnerability but increases it instead.
- Odisha has one of the most dynamic coasts in the country, with sea levels rising at a rate more than the average for the rest of the country.
- It is also the most cyclone-prone state in India.
Jharniyojan Portal : Jharkhand Govt

The Jharkhand government has launched a portal called ‘Jharniyojan’ to ensure 75% local quota in pvt sector
The portal requires:
- All private establishments in the state register themselves.
- Employers to adhere to the ‘Jharkhand State Employment of Local Candidates in Private Sector Act, 2021
- The act reserves 75% of jobs in private sectors with salaries up to Rs 40,000 for “locals” in the state.
- It applies to all establishments which are in the private sector and where 10 or more people are employed.
LVM3 : ISRO

The Indian space agency, ISRO, has announced that it will launch its largest rocket, LVM3, on March 26th for its second commercial mission.
- The upcoming mission will be carried out through ISRO’s commercial arm NSIL (NewSpace India Limited).
- It will carry 36 OneWeb Gen-1 satellites with a total mass of 5,805 kg, into a 450 km circular Low Earth Orbit with an inclination of 87.4°.
- LVM3 Rocket Design is a three-stage vehicle.
- It has two S200 solid motors as the first stage, L110 twin liquid engines as the second stage and a final C25 cryogenic upper stage.
- This 43.5 m tall vehicle has a lift-off mass of 643 tonnes.
- Its cryogenic stage is uniquely designed to orient and re-orient in orthogonal direction to meet the customer requirements of injecting satellites precisely and with a gap to avoid a collision.
YUVIKA Program : ISRO

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has initiated the Yuva Vignani Karyakram (YUVIKA) program to encourage students to pursue careers in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) and develop a passion for space science.
- The YUVIKA program is open to students in the 9th standard (or equivalent) from all over India.
- The program selects three students from each state/union territory, and they are invited to participate in a two-week residential training program at various ISRO centers across the country.
- The program aims to provide an opportunity for young children to explore the wonders of space science, space applications, and space technology.
- YUVIKA program is to create awareness among young children about the emerging trends in space science and technology.
- The program provides a platform for students to interact with experts in the field of space science and technology and gain insights into the latest developments and advancements in the field.
- This helps students to stay updated with the latest trends in the space sector and prepare for the future challenges.
Background Radiation:
Background radiation refers to the radiation emitted from natural sources such as rocks or mountains.
- A recent study conducted by scientists at the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) found that certain areas in Kerala are experiencing nearly three times more background radiation than previously assumed.
- The study is significant, as it sheds light on the natural radiation levels in India, which has important implications for the country’s nuclear energy plans.
- The study conducted by BARC scientists measured radiation levels from nearly 100,000 locations across India.
- The study found that the average natural background levels of gamma radiation in India were 94 nGy/hr.
- However, in Kollam district, the levels were found to be 9,562 nGy/hr, which is about three times more than the assumed levels.
- The higher radiation levels in Kollam, a district in Kerala, are attributed to the presence of monazite sands that are high in thorium, a natural radioactive element.
- Thorium is a common radioactive element that is found in small amounts in soil, rocks, and water.
First Polio Outbreak In 30 Years : Burundi
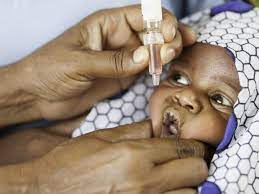
Burundi, a landlocked east-African country, has declared its first polio outbreak in 30 years.
- The outbreak was confirmed after a four-year-old child in the Isale district of western Burundi, along with two other children he was in contact with, were diagnosed with vaccine-linked polio.
- Additionally, poliovirus type 2 was detected in five samples from environmental surveillance of wastewater from the region.
- Poliovirus type 2 is a weakened strain of the virus contained in the oral polio vaccine.
- The virus can circulate among under-immunised populations for a long time, leading to vaccine-linked infections.
- The WHO has noted that the type 2 infection can cause acute flaccid paralysis in children, which is characterized by the acute onset of weakness or paralysis with reduced muscle tone.




