Today Current Affairs: 23rd July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Man-Portable Anti-Tank Guided Missile (MPATGM) And New Generation Akash Missile:

Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully flight tested indigenously developed low weight, fire and forget Man-Portable Anti-Tank Guided Missile (MPATGM).
- The missile is incorporated with state-of-the-art Miniaturized Infrared Imaging Seeker along with advanced avionics.
- The man-portable missile is launched using a tripod is designed for a maximum range of 2.5 km with a launch weight of less than 15 Kg.
- Control Flight Tests have been successfully carried out and Guided Flight Tests (with IIR Seeker) are planned.
Akash Missile:
- Defence Research and Development Organisation, DRDO successfully flight-tested the New Generation Akash Missile, a surface-to-air Missile from Integrated Test Range off the coast of Odisha.
- The missile system has been developed by Defence Research and Development Laboratory, Hyderabad in collaboration with other DRDO laboratories.
- The new version of the Akash missile (Akash-NG) can strike targets at a distance of around 60 km and fly at a speed of up to Mach 2.5.
- The New Generation Akash Missile will prove to be a force multiplier for the air defence capability of the Indian Air Force.
H5N1 Avian Influenza:
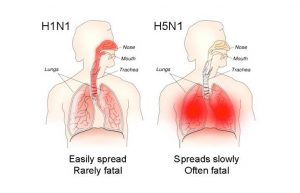
On July 21, an 11-year-old boy died of H5N1 avian influenza in Delhi. This is the first recorded death due to the bird flu in India this year. In January, bird flu was confirmed in several states with thousands of birds, including migratory species, being found dead.
- Bird flu or avian influenza is a disease caused by avian influenza Type A viruses found naturally in wild birds worldwide.
- The virus can infect domestic poultry including chickens, ducks, turkeys and there have been reports of H5N1 infection among pigs, cats, and even tigers in Thailand zoos.
- Avian Influenza type A viruses are classified based on two proteins on their surfaces – Hemagglutinin(HA) and Neuraminidase(NA). There are about 18 HA subtypes and 11 NA subtypes. Several combinations of these two proteins are possible e.g., H5N1, H7N2, H9N6, H17N10, etc.
- There have been reports of avian and swine influenza infections in humans including A(H1N1), A(H1N2), A(H5N1), A(H7N9), etc. The first report of human H5N1 infection was in 1997.
- The most common route of virus transmission is direct contact — when a person comes in close contact with infected birds, either dead or alive
China-South Asian Initiative:

Bangladesh has invited India to join the China-led South Asian initiative for Covid-19 vaccines and poverty alleviation.
- It includes the creation of the China-South Asian Countries Emergency Supplies Reserve, and a Poverty Alleviation and Cooperative Development Centre set up in China.
About China-South Asian Initiative:
- Members: China, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- India, Bhutan and the Maldives are the other SAARC countries that are not part of this initiative.
- Intended Vision: China has different kinds of strategic, maritime, political and ideological interests with different South
- Asian nations so it is increasing its engagements with each country on equal footing to counterbalance India.
- India’s Stand: Given continuing tensions over Chinese PLA aggression at the Line of Actual Control in Ladakh, India’s stand is that other bilateral relations cannot move ahead without a resolution of the boundary stand-off.
- Associated Issues: This initiative seems to be China ‘s strategy to contain and undermine India’s role in South Asia. This can be reflected in the following arguments:
- Minus-India Initiative: Combinations of all SAARC member countries (other than India, Bhutan and Maldives) led some experts to suggest this was meant to be a “Minus India” initiative.
- Diluting India’s Role in South Asia: This initiative is one of China’s attempts to make inroads into South Asia.
- The Chinese push to this regional grouping comes also at a time when India has been reluctant to revive SAARC, turning its focus more on yet another regional bloc–BIMSTEC.
- Countering Quad: The China-led bloc could be its plan to create what some call a northern Himalayan Quad aimed at countering the US-led Quad of which India is an active member.
Insolvency And Bankruptcy Board Of India (IBBI): Amendment:

The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) has amended the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Persons) Regulations, 2016.
- The amendments are aimed at enhancing the discipline, transparency, and accountability in corporate insolvency proceedings.
- In March 2021 a sub-committee of the Insolvency Law Committee (ILC) recommended a pre-pack framework within the basic structure of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
- The amendment requires an Insolvency Professional (IP) conducting Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) to disclose all former names and registered office address(es) so changed in the two years preceding the commencement of insolvency along with the current name and registered office address of the Corporate Debtor (CD), in all its communications and records.
- CIRP includes necessary steps to revive the company such as raising fresh funds for operation, looking for a new buyer to sell the company as a going concern, etc.
- CD is any corporate organization which owes a debt to any person.
- A CD may have changed its name or registered office address prior to commencement of insolvency.
- Therefore the stakeholders may find it difficult to relate to the new name or registered office address and consequently fail to participate in the CIRP.
- The amendment provides that the Interim Resolution Professional (IRP) or Resolution Professional (RP) may appoint a professional, other than registered valuers, if he is of the opinion that the services of such professional are required and such services are not available with the CD.
- Such appointments shall be made on an arm’s length basis following an objective and transparent process.
- The RP is duty bound to find out if a CD has been subject to avoidance transactions, namely, preferential transactions, undervalued transactions, extortionate credit transactions, fraudulent trading and wrongful trading, and file applications with the Adjudicating Authority seeking appropriate relief.
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code:
- The IBC was enacted in 2016.
- Objective:
- To streamline and speed up the resolution process of failed businesses.
- To consolidate provisions of the existing legislative framework to form a common forum for debtors and creditors of all classes to resolve insolvency.
- To stipulate that the resolution process of a stressed company will have to be completed in a maximum of 270 days.
Bureau Of Energy Efficiency (BEE):

“Aiming for Sustainable Habitat: New Initiatives in Building Energy Efficiency 2021” was launched by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- These initiatives seek to enhance energy efficiency in the building sector and were launched as part of ‘Azadi Ka Amrut Mahotsav’.
Initiatives Launched:
Eco Niwas Samhita 2021:
- It is an Energy Conservation Building Code for Residential Buildings (ECBC-R) to give a further fillip to India’s energy conservation efforts.
- It specifies code compliance approaches and minimum energy performance requirements for building services, and verification framework with Eco Niwas Samhita 2021.
Hand Book for Learning:
- The web-based platform ‘The Handbook of Replicable Designs for Energy Efficient Residential Buildings’ as a learning tool, which can be used to create a pool of ready-to-use resources of replicable designs to construct energy-efficient homes in India.
Online Directory of Building Materials:
- Creating an Online Directory of Building Materials that would envisage the process of establishing standards for energy efficient building materials.
NEERMAN Awards:
- NEERMAN Awards, (National Energy Efficiency Roadmap for Movement towards Affordable & Natural Habitat) were announced, with the goal of encouraging exceptionally efficient building designs complying with BEE’s Energy Conservation Building Codes.
Online Star Rating Tool:
- It provides performance analysis to help professionals decide the best options to pick for energy-efficiency of their homes.
- It was launched for Energy Efficient Homes, created to improve energy-efficiency and reduce energy consumption in individual homes.
Training:
- Training of over 15,000 Architects, Engineers and Government officials on Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) 2017 and Eco Niwas Samhita 2021.
About Bureau of Energy Efficiency:
- The BEE is a statutory body established through the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 under the Union Ministry of Power.
- It assists in developing policies and strategies with the primary objective of reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy.
- BEE coordinates with designated consumers, designated agencies, and other organizations to identify and utilize the existing resources and infrastructure, in performing its functions.
Speedy Trial Is A Fundamental Right:

In the Bhima Koregaon caste violence case, highlighting the issue of undertrials, the Supreme Court has said that “speedy trial is a fundamental right”.
- Charges are not framed in the case. Many witnesses are still being examined. They are languishing in jail without trial.
About the Constitutional Right to Speedy Trial:
- The main aim of the Right to Speedy trial is to inculcate Justice in the society.
- It was first mentioned in that landmark document of English law, the Magna Carta.
- In India, it is covered under Article 21 which declares that “no person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to the procedure laid by law.”
Evolution of the right to speedy trial:
- 1978 Babu Singh v. State of UP: The court remarked, “Our justice system even in grave cases, suffers from slow motion syndrome which is lethal to ‘fair trial’ whatever the ultimate decision.
- Speedy justice is a component of social justice since the community, as a whole, is concerned in the criminal being condignly and finally punished within a reasonable time and the innocent being absolved from the inordinate ordeal of criminal proceedings.”
- Hussainara Khatoon v. State of Bihar, 1979: It formed the basis of the concept of the Speedy Trial. It was held that where under trial prisoners have been in jail for duration longer than prescribed, if convicted, their detention in jail is totally unjustified and in violation to fundamental rights under article 21.
- Katar Singh v. State of Punjab 1994: It was declared that the right to speedy trial is an essential part of fundamental right to life and liberty.
Factors For Pendency Of The Cases:
- Delay in disposition of cases because of huge pendency.
- Delay due to lawyers/ advocates.
- Infrastructure issue: The Courts have no convenient building or physical facilities due to which it takes more time to dispose off a case.
- Provision for adjournment.
- Vacation of the court.
- The Investigation agencies such as Police also play a role in Delay of cases.
Historic Urban Landscape Project:

In Madhya Pradesh, Gwalior and Orchha cities have been selected by UNESCO under ‘Historic Urban Landscape Project’, which was started in the year 2011, for the inclusive and well-planned development of fast-growing historical cities while preserving the culture and heritage.
- Chief Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan virtually launched UNESCO’s ‘Historic Urban Landscape’ project for Gwalior and Orchha cities of the state through video conferencing.
- Six cities of South Asia, including Ajmer and Varanasi in India are already involved in this project.
- Orchha and Gwalior have been included as the 7th and 8th cities.
- The cities will be jointly developed by UNESCO, Government of India and Madhya Pradesh by focusing on their historical and cultural improvement.
- This project will help MP tourism get a new dimension. Additional employment opportunities will also be created along with the development of tourism.
Liverpool:

Liverpool has been stripped of its World Heritage status after a UN committee found developments threatened the value of the city’s waterfront.
- The decision was made following a secret ballot by the UNESCO Committee at a meeting in China. UNESCO had previously warned that the developments, including the new Everton FC stadium, had resulted in a “serious deterioration” of the historic site.
- The city was awarded the much-coveted title in 2004 in recognition of its historical and architectural impact, joining places including the Taj Mahal, Egypt’s Pyramids and Canterbury Cathedral.
Liverpool:
- Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England.
- Liverpool is on the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary. Its growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution.
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in 2018 identified 351 polluted river stretches in India.:

The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in 2018 identified 351 polluted river stretches in India.
- CPCB study reveals that discharge of untreated wastewater is one of the main causes of river pollution.
- The assessment of water quality for identification of polluted river stretches found that 31 states and Union territories (UT) had rivers and streams that did not meet the water quality criteria.\
Findings of CPCB:
- Concentration of Polluted River Stretches: Almost 60% of polluted river stretches exist in eight states: Maharashtra, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Gujarat, Odisha, West Bengal and Karnataka.
- Maharashtra has the maximum number of polluted river stretches in the country.
- Disproportionate Sewage Treatment: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) in 2019 directed that 100% treatment of sewage needed to be ensured before 31st March, 2020.
- However, these states have sewage treatment capacity disproportionate to the sewage generated.
- According to the CPCB report National inventory of sewage treatment plants 2021, about 72,368 million litres per day (MLD) of sewage was generated against which operational treatment capacity was only 26,869 MLD in 2021.
- Increasing Biological Oxygen Demand: This huge amount of sewage is left untreated/partially treated and discharged directly into rivers and pollutes rivers by increasing the biological oxygen demand.
Drug Menace In India::

India has signed 26 bilateral pacts, 15 memoranda of understanding and two agreements on security cooperation with different countries for combating illicit trafficking of narcotic, drugs and psychotropic substances, besides chemical precursors.
Drug Menace In India:
- The menace of drug addiction has spread fast among the youth of India.
- India is sandwiched between two largest Opium producing regions of the world that is the Golden triangle on one side and the Golden crescent on other.
- The golden triangle area comprises Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam and Laos.
- The golden crescent area includes Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran.
- According to the World Drug Report 2021, prescription drugs and their ingredients or ‘precursors’ are being increasingly diverted for recreational use in India–the largest manufacturer of generic drugs in the world.
- India is also linked to shipment of drugs sold on the 19 major darknet markets analysed over 2011-2020.
- As per the report Magnitude of Substance Use in India released by All India Institute Of Medical Science (AIIMS) in 2019:
- Around 5 crore Indians reported to have used cannabis and opioids at the time of the survey (conducted in the year 2018).
- It has been estimated that there are about 8.5 lakh people who inject drugs.
- Of the total cases estimated by the report, more than half of them are contributed by states like Punjab, Assam, Delhi, Haryana, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim and Uttar Pradesh.
- About 60 lakh people are estimated to need help for their opioid use problems.
National Security Act (NSA):

The Supreme Court has directed the release of Manipur-based activist Erendra Leichongbom, detained under the National Security Act for his social media posts allegedly on the efficacy of cow dung and urine as cures for COVID-19 in the context of the death of a BJP leader.
- The court said his continued detention would be a violation of his fundamental right to life and the due process of law.
- The court also expressed concern because the government was using preventive detention in cases where even ordinary penal sections did not apply.
About the National Security Act (NSA):
- The NSA is a preventive detention law.
- Preventive Detention involves the detainment (containment) of a person in order to keep him/her from committing future crimes and/or from escaping future prosecution.
- Article 22 (3) (b) of the Constitution allows for preventive detention and restriction on personal liberty for reasons of state security and public order.
- Article 22(4)states that:
- No law providing for preventive detention shall authorise the detention of a person for a longer period than three months unless:
- An Advisory Board reports sufficient cause for extended detention.
- The 44th Amendment Act of 1978 has reduced the period of detention without obtaining the opinion of an advisory board from three to two months. However, this provision has not yet been brought into force, hence, the original period of three months still continues.
- The maximum period for which one may be detained is 12 months. But the term can be extended if the government finds fresh evidence.
- A person can be held for 10 days without being told the charges against them. The person can appeal before a high court advisory board but will not be allowed a lawyer during the trial.
- Article 22 (1) of the Indian Constitution says an arrested person cannot be denied the right to consult, and to be defended by, a legal practitioner of his choice.
- According to Section 50 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CRPC), any person arrested has to be informed of the grounds of arrest and has the right to bail.
- However, under National Security Act, none of these rights are available to the person detained. The government holds the right to conceal information which it considers to be against public interest to disclose.




