Today’s Current Affairs:24th September 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Paradip Port:

A decomposed body was discovered in a coal wagon at Paradip port’s coal handling plant, marking the second such incident recently.
- Paradip Port is one of the major ports of India.
- It is the only major port in the State of Odisha, situated 210 nautical miles south of Kolkata and 260 nautical miles north of Visakhapatnam.
- It is situated on the Bay of Bengal on the delta of the Mahanadi River at the mouth of one of its branches.
- It is strategically situated so as to serve a vast hinterland spreading over the states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal.
- The Port of Paradip, an autonomous body under the Major Port Trusts Act, 1963, functioning under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, is administered by a Board of Trustees set up by the Government of India headed by the Chairman.
- The Trustees of the Trust Board are nominated by the Government of India from various users of the Port such as shippers, ship owners, Government Departments concerned and also port labour.
- Paradip Port achieved a milestone by joining the 150 million metric tonne (MMT) club and maintaining its top position in cargo handling among India’s major ports by recording 150.41 MMT cargo in 2024-25.
CPCB Report on Polluted River Sites:

The CPCB 2023 report shows India’s polluted river sites declined slightly to 807 (2023) from 815 (2022), with fewer “Priority-1” stretches needing urgent remediation.
CPCB Report on Polluted River Sites:
- A nationwide assessment by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) on the health of rivers.
- Uses Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) as a proxy for organic pollution.
- BOD > 3 mg/L → water unfit for bathing and BOD > 30 mg/L → Priority-1 (most polluted).
Report (2023 vs 2022):
- Polluted Sites – Reduced from 815 (2022) to 807 (2023).
- Polluted River Stretches (PRS) – 296 PRS across 271 rivers (down from 311 across 279 rivers in 2022).
- State-wise – Maharashtra (54) highest PRS, followed by Kerala (31), MP & Manipur (18 each), Karnataka (14).
- Priority-1 Stretches – Reduced to 37 (2023) from 45 (2022).
- Monitoring Network – 4,736 locations including rivers, lakes, canals, drains.
Sarcophagus : Discovery

The first-ever scientific dating of a sarcophagus (terracotta coffin) found recently in Kilnamandi village in Tiruvannamalai district indicates that Tamil Nadu might have had trade contact with the north during the time of the Late Harappan civilisation.
- Sarcophagus used to bury leaders and wealthy residents in ancient Egypt, Rome, and Greece, a sarcophagus is a coffin or a container to hold a coffin.
- They were intended to be displayed above ground, but they were sometimes entombed or placed in burial chambers.
- The word “sarcophagus” comes from ancient Greek words. Sarx means “flesh,” and phagein means “to eat.” So, “sarcophagus” literally means “flesh-eating.”
- This name came from a special type of limestone that people believed could help bodies decompose quickly.
- First used in Ancient Egypt and Ancient Greece, the sarcophagus gradually became popular throughout the ancient world.
- The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C.E.
- Example: The most famous Egyptian sarcophagus is perhaps the golden sarcophagus of King Tutankhamun.
Barren Island : Volcano Eruption

Minor volcanic eruptions were noticed twice in a span of eight days at Barren Island in Andaman and Nicobar Islands recently.
- Barren Island is a volcanic island located in the Andaman Sea.
- Popularly known as a submarine emergent volcano, the island is a part of the Indian union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- It lies about 138 kilometers northeast of the territory’s capital, Port Blair.
- It lies above the subduction zone of India and Burmese plates.
- It is the only active volcano in the Indian subcontinent.
- It is a stratovolcano composed of lava, rock fragments, and volcanic ash.
Impatiens selvasinghii:
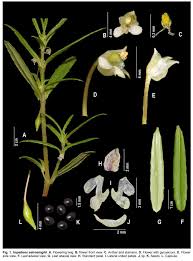
Researchers recently found a new plant species named Impatiens selvasinghii in the Kudremukh range of the Western Ghats.
- Impatiens selvasinghii is a new species of flowering plant.
- It was discovered in the Kudremukh range of the Western Ghats in Karnataka.
- It is one of the smallest flowered balsams from the Western Ghats.
- It has an exceptionally small flower size and prominently-lobed wing petals, which makes it unique.
- In India, the genus Impatiens is represented by more than 280 taxa, chiefly distributed in the Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- Over 210 taxa are endemic to India, of which 130 are endemic to the Western Ghats, and 80% of taxa in the Western Ghats are categorized as endangered.
Adi Yuva Fellowship & Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme:

The Ministry of Tribal Affairs, in partnership with the United Nations in India, launched the Adi Yuva Fellowship and the Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme under the Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan.
- Adi Yuva Fellowship is supported by United Nations India.
- It is a first-of-its-kind programme designed to empower tribal youth through structured learning, mentorship, and career development.
- Under this initiative selected tribal youth will undertake a 12-month paid Fellowship, with a tailored learning plan that balances knowledge-building, on-the-job experience, and reflective practice.
- Fellows will receive monthly allowances, comprehensive health and life insurance, and access to high-quality UN and commercial learning platforms.
- This programme will link Fellows to national skilling and employability schemes such as PMKVY 4.0, NAPS, and PM Viksit Bharat Rozgar Yojana.
- The fellows will be selected through a competitive process and placed with UN agencies at the national, state, and district levels.
- Adi Karmayogi Volunteers Programme is supported by UNFPA.
- It will equip tribal youth to act as catalysts for grassroots change and strengthen last-mile service delivery in tribal regions.
- 82 UN Community Volunteers as Adi karmayogi Volunteers have been deployed across 82 blocks in 13 districts of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthanfor an intensive two-month grassroots engagement.
- Under this, volunteers will support Village Vision 2030 planning, awareness drives, outreach, and improved access to schemes and services.
Tropical Forests Forever Facility:

Brazil will become the first country to announce an investment in the Tropical Forests Forever Facility.
- Tropical Forests Forever Facility is an innovative multilateral global permanent fund dedicated to supporting tropical forest conservation over the long-term.
- It is a global initiative led by the Government of Brazil.
- The idea for the fund was presented by the Brazilian government in 2023, at COP28 in the United Arab Emirates.
- The TFFF is a blended finance structure that seeks to mobilize US$125 billion in capital from public and private sector sources.
- The fund would be used to pay the tropical forest countries (TFC) a fixed amount of money per hectare of standing forest.
- It aims to raise capital from two main sources, sponsors and market investors through financial markets by issuing debt instruments such as bonds
- Sponsors would be the ‘high income’ countries as classified by the World Bank, along with philanthropies. (account for 20 per cent of the total corpus)
- Institutional investors, sovereign wealth funds, and endowments (account for 80 per cent of the total corpus) investing through debt instruments.
- Funds are managed via a Multilateral Development Bank (MDB), e.g., World Bank.
Smog Eating Photocatalytic Coatings:

The Delhi government will conduct a time-bound study on “smog-eating” photocatalytic coatings in Delhi to combat air pollution.
- Smog Eating Photocatalytic Coatings is designed to neutralise harmful gases like nitrogen dioxide and volatile hydrocarbons that contribute to toxic air.
- It usually uses titanium dioxide as a coating which has advantages for being low-cost and chemically stable.
- Titanium dioxide is also known for its compatibility with traditional construction materials.
- Photocatalytic activity helps fight pollution by breaking down harmful substances and organic waste into less toxic or harmless matters using light energy, thereby making air and water cleaner.
- Smog is used to refer to a type of air pollution caused by a combination of smoke (and other pollutants) and fog.
Himalayan Musk Deer:
The Central Zoo Authority (CZA) reports no captive Himalayan musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster) in recognized zoos, indicating no breeding programme has begun despite the 1982 Himalayan Musk Project. Himalayan Musk Deer is a deer species found in alpine regions above 2,500m in the Himalayan region of India, as well as in Nepal, Bhutan, and China.It is Sandy brown, hare-like deer. They lack antlers and have a gall bladder, distinguishing them from other deer. A musk deer breeding centre was established in Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary in 1982 with five deer, increasing to 28 by 2006, when it closed and the last deer was sent to Darjeeling Zoo. India currently lacks founder stock, the initial pairs needed to start a breeding programme.
Behavior & Communication: Solitary, sedentary, and crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk). They use a caudal gland to mark territory and display a distinctive bounding gait, capable of jumping up to 6m to evade predators. Conservation Status: Endangered on the IUCN Red List. Poaching for the musk sac (used in perfumes and medicine) drives population decline. Listed in CITES Appendix I.
Astronomers discovered the Arjuna 2025 PN7:
Astronomers discovered the Arjuna 2025 PN7, a new quasi-satellite of Earth; it was first spotted by the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope in Hawaii. 2025 PN7 belongs to the Arjuna asteroid class, named after the mythical figure Arjuna of the Mahabharata, symbolizing its fast, elusive nature. Quasi-Satellite Classification: 2025 PN7 is Earth’s seventh known quasi-satellite. These objects are considered quasi-moons because their orbits around the Sun closely follow Earth’s orbit, though they are not gravitationally bound to the planet. A quasi-satellite of Earth is an object that orbits the Sun in a similar path to Earth but is not gravitationally bound to Earth. Mini-moons and quasi-moons differ, while mini-moons orbit Earth temporarily, quasi-moons stay in sync with Earth’s orbit for hundreds to thousands of years. With a semi-major axis of 1.003 Astronomical Unit (AU) (almost identical to Earth’s orbit), 2025 PN7 follows a slightly elliptical orbit. 2025 PN7 orbits the Sun, not Earth, but stays near Earth due to a 1:1 orbital resonance, meaning it completes one orbit around the Sun in the same time as Earth.
Extreme Nuclear Transients:
Extreme Nuclear Transients (ENTs) are a newly discovered class of cosmic explosions, even more powerful than gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), which are the most intense flashes of electromagnetic radiation.Extreme Nuclear Transients (ENTs) are powered by the accumulation of stellar debris from massive stars, at least three times the mass of the Sun, which are torn apart by supermassive black holes.Extreme tidal forces stretch and compress the star near the event horizon, releasing enormous amounts of electromagnetic energy. ENTs can remain luminous in radio wavelengths for years, making them detectable across vast distances. While ENTs share similarities withTidal Disruption Events (TDEs), they differ in that ENTs occur in larger host galaxies and involve more massive central black holes. Fast X-ray transients (FXTs) are short-lived and less energetic than ENTs, originating from supernovae rather than interactions with supermassive black holes.
India approved a ₹27,000-crore programme to launch 52 surveillance satellites from 2026:
Reports suggest India is also considering “bodyguard satellites” to protect its space assets after near-miss incidents.Satellites are the backbone for communication, navigation (NavIC), weather forecasts, internet, defence and surveillance, making them critical for national security and economy. They face risks from space debris, collisions, hostile manoeuvres, jamming, spoofing, cyber intrusions, and solar storms that can disrupt services or destroy satellites. Launching and maintaining satellites involves billions; protecting them ensures return on investment and safeguards India’s strategic autonomy.
Phytosaur fossil:
Ancient fossilised remains discovered in Megha village, Jaisalmer, have sparked speculation of being a Phytosaur fossil dating back to the Late Triassic–Jurassic period. Phytosaurs are extinct, large, semi-aquatic reptiles resembling modern crocodiles, belonging to the order Phytosauria. They thrived during the Late Triassic and possibly Early Jurassic, showing features like long snouts, heavy armour, and diverse feeding adaptations. Found in Recent suspected fossil: Megha village, Fatehgarh subdivision, Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan. Earlier finds: Akal and Thaiyat (confirmed dinosaur remains), plus shark and marine fossils in the region.
Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff (HQ IDS) launched the Combined Operational Review and Evaluation (CORE) Programme in New Delhi:
Combined Operational Review and Evaluation (CORE) Programme is a five-day professional engagement programme on national and regional security issues. It Acts as a forum for civil–military dialogue, strategic review, and leadership development. HQ Integrated Defence Staff (IDS) as the nodal organiser. Participants include senior officers from Armed Forces, and ministries of Defence, External Affairs, and Home Affairs. Aim is to strengthen civil–military synergy in addressing multidimensional threats, to enhance strategic awareness and foster balanced decision-making among future leaders. Themes – regional/global security, tech transformation of warfare, strategic communication, inter-agency synergy.
Nine bonnet macaques were found dead:
Nine bonnet macaques were found dead in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, raising fears of poisoning or disease. Bonnet Macaques is primate species endemic to southern India, often found living close to human settlements.It is known for the distinctive “bonnet-shaped” hair whorl on its head.It is Found across Western Ghats, southern plains, and urban fringes. Thrive in evergreen forests, dry deciduous forests, plantations, and village edges. Highly arboreal but also terrestrial; adapt well near humans. IUCN Status: Listed as Least Concern (LC) due to wide distribution.
Tirah Valley : 23 people were killed in a blast
At least 23 people were killed in a blast in Pakistan’s Tirah Valley (Khyber Pakhtunkhwa). Tirah Valley is a mountainous region and tribal stronghold historically known for resistance to external control. Noted for fertile valleys, terraced agriculture, and as a hub of militant activity in recent decades.
Located in Lies in Khyber District and Orakzai District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Positioned between Khyber Pass and Khanki Valley.
Neighbouring Nations: Close to the Afghanistan–Pakistan border, making it strategically sensitive. Serves as a corridor between South Asia and Central Asia, historically contested by Mughals, British, and modern Pakistan.




