Today’s Current Affairs: 25th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Cyclone Remal:

A new low-pressure area has been found over the southwest and adjacent west central Bay of Bengal as of May 22, 2024, early in the morning.
- This storm will move northeast and is likely to turn into a depression by May 24.
- The storm is likely to get stronger as it stays on the same path.
- By the evening of May 25, it will be in the northeast and adjacent northwest Bay of Bengal.
- Based on predictions on the US Global Forecasting System (GFS) that Cyclone Remal could form in the northwest Bay of Bengal by the morning of May 26.
- Additionally, The Weather Channel (TWC) has admitted that a cyclonic storm is likely to happen, even though it says the chances of it becoming a severe cyclonic storm are low.
- IMD says that some districts in West Bengal and Odisha will get light to moderate rain, and other districts will get heavy rain.
- In northeast India, places like Mizoram, Tripura, and south Manipur are expected to have similar weather.
- Also, from May 26–28, TWC predicts heavy rain—possibly more than 200 millimeters—in states like Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, and Tripura.
CERT-In Warns Of Critical Flaws In Google Chrome:

The Center’s Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) just sent out a warning about major security holes found in Google Chrome.
- CERT-In’s warning note, CIVN-2024-0170, talks about this worry and stresses how important it is for users to update their browsers right away.
- The flaws that were found are considered very serious, and hackers can access user systems and data from afar.
- According to CERT-In’s statement, Google Chrome had three major security problems before versions 125.0.6422.76/.77 for Windows and Mac, and before 125.0.6422.76 for Linux.
- Heap Buffer Overflow in ANGLE and Dawn: It happens when too much data is written to a memory buffer, which can cause crashes or let bad code in.
- This flaw shows up when the browser tries to use memory that has already been freed up, which could cause code to run without permission or the system to crash.
- Type Confusion in V8 problem happens when data is handled wrong because of type confusion, which lets attackers get around security measures and maybe even add harmful code.
- These holes are very bad for security because anyone can use them to run any code, steal private data, cause systems to crash, or spread more threats.
G7 Commits To Net Zero Emissions By 2050:

The leaders of the G7 have recently kept their word to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- The government of Albanese has put forward a plan to create a Net Zero Economy Authority in order to encourage more investment in green technologies.
- Following the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26) in Glasgow, which tried to keep global warming below 1.5°C as required by the Paris Agreement, there has been a rise in net zero commitments.
Net Zero Emissions:
- Net zero means balancing the amount of greenhouse gases released with the same amount stored or offset so that the temperature has no effect at all.
- This idea came about when people realized that cutting down on emissions alone is not enough to stop climate change.
World’s Rangelands : Degraded

About half of the world’s rangelands are degraded and need policy interventions, and communities depending on them need focused support, according to a new report of the United Nations Convention on Combating Desertification (UNCCD).
- Rangelands cover 80 million sq km, which is 54 per cent of the earth’s land surface.
- They are characterised by low vegetation and comprise grasslands, shrublands, wetlands, desert, semi-arid land, mountain pastures, plateaus and tundra.
- In India, rangelands occupy about 1.21 million sq km, from the Thar Desert to Himalayan meadows, as per the UNCCD report.
- The UNCCD report found that nearly 50% of the world’s rangelands can be considered “degraded” and are facing a “silent demise”.
- Climate change, unsustainable land and livestock management practices, biodiversity loss, and the conversion of rangelands to farmlands are some of the primary drivers of rangeland degradation. Uncertainty over land rights among pastoralist communities also leads to their degradation.
- This, in turn, severely affects the communities dependent on rangelands as their deterioration impacts soil fertility and biodiversity, leading to a dip in incomes and rise in conflicts with authorities over grazing rights
Rangelands:
- The UNCCD report defines rangelands as natural or semi-natural ecosystems that are grazed by livestock or wild animals.
- Rangelands contain vegetation such as grasses, shrubs, bushes, open forests, and agroforestry systems (land which contains trees and crops or pastures).
- The exact nature of rangelands’ vegetation is influenced by rainfall, temperature, and other climate phenomena.
- Currently, rangelands cover 80 million sq km of Earth’s terrestrial surface area (over half of Earth’s land), and are thus the largest land cover or land use type in the world, the UNCCD report said.
- They act as carbon sinks (which absorb more carbon from the atmosphere than they release), storehouses of freshwater, and prevent desertification of land. Millions of people worldwide depend on rangelands for food security, and livelihoods.
- Rangelands generate 16% of global food production and 70% of feed for domesticated herbivores, most significantly in Africa and South America,” the UNCCD report stated.
National Council For Cement And Building Materials-Incubation Centre:

The National Council for Cement and Building Materials-Incubation Centre (NCB-IC) was inaugurated by the Joint Secretary, DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- At NCB-IC, the incubated startups/entrepreneurs will be mentored by the scientists of NCB and experts from the cement and building materials industry for further improvisation and development of market-ready products for commercialisation.
- The number of DPIIT-recognised startups has increased to 1,36,584.
- National Council for Cement and Building Materials (NCB) is an apex research and development organisation under the administrative control of DPIIT.
- NCB is dedicated to research, technology development & transfer, education & industrial services for cement, allied building materials & construction industries.
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) : Radioactive Discharge

The International Atomic Energy Agency urged increased caution against the trafficking of nuclear and radioactive materials, citing over 4,200 incidents in the past three decades as it began its fourth International Conference on Nuclear Security (ICONS) on nuclear security.
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organisation that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- It was established in 1957 as the world’s “Atoms for Peace” organisation within the UN, and governed by its own founding treaty – the Statute of the IAEA.
- It reports to both the UNGA and the UNSC and is headquartered at the UN Office at Vienna, Austria
- In 2005, it was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for its work for a safe and peaceful world.
- The IAEA has 178 member states, India being one of the founding members of it.
- International Conference on Nuclear Security (ICONS) is a significant event for the nuclear security community around the world.
Global Water Crisis : World Bank Report
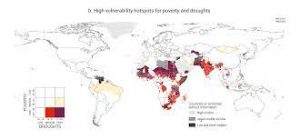
The World Bank’s new report “Water for Shared Prosperity,” released at the 10th World Water Forum in Bali, Indonesia, highlights the alarming global water crisis and its implications for human and economic development worldwide.
Key Highlights:
- Significant gaps exist in access to water and sanitation services globally.
- As of 2022, 2.2 billion people lack access to safely managed drinking water services and 3.5 billion lack access to safely managed sanitation.
- Eight out of ten people without basic drinking water and sanitation services reside in rural areas.
- Disparity in Freshwater Distribution: China and India, with 36% of the global population, hold only 11% of freshwater, while North America, with 5% of the population, possesses 52%.
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo holds over half of Africa’s water resources, yet regions like the Sahel, Southeastern Africa, and South and Central Asia remain water-stressed.
- These regions have seen a regression in access to safe drinking water, with an additional 197 million people lacking access since 2000.
- Disparities in access also affect marginalized groups based on gender, location, ethnicity, race, and other social identities.
GSAP SKILLS Platform:

The GSAP SKILLS Platform was launched at the Fourth meeting of the Subsidiary Body on Implementation, Convention on Biological Diversity.
- Global Species Action Plan(GSAP), the Species Conservation Knowledge, Information, Learning, Leverage and Sharing (SKILLS) platform brings the GSAP’s content online and allows the updating of technical tools and resources in real time.
- It aims to facilitate global collaboration and partnership, connecting decision makers, species conservation practitioners and experts at all levels.
- It provides real-time updates on technical tools and resources, ensuring accessibility and relevance.
- Each Global Biodiversity Framework target is accompanied by a brief summary and rationale for species conservation interventions, actions, and sub-actions, actors and technical tools and resources for those actions, facilitating the scaling-up of implementation efforts.
- This platform is managed proactively by IUCN to meet the needs from governments and all stakeholders to take actions for species.
- The development of the GSAP SKILLS platform has been principally supported by Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea, with additional resources from the Tech4Nature Initiative launched by IUCN and Huawei in 2020.
- Global Species Action Plan has been developed to support implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) and to address the increasing biodiversity loss worldwide.
Sweet sorghum:

Sweet sorghum is a hardy, nutritious, biofuel crop that offers solutions in drought-hit southern Africa because of El-Nino phenomenon.
- Sweet sorghum is the most important millet crop occupying largest area among the cereals next to rice.
- One of the key characteristics of sweet sorghum varieties is their drought resistance. It allows them to enter a dormant state during extended periods of dryness and resume growth afterwards.
- The crop does not prefer high rainfall as high soil moisture or continuous heavy rain after flowering may hamper sugar increase.
- All soils that have medium depth with good drainage are suited.
- Depending on the soil (red, black, laterite and loamy) and its depth water requirement may vary which in turn decide the suitability of the crop.
- It has ability to withstand low water and nitrogen inputs, as well as its tolerance for salinity and drought stress, makes it an ideal crop for farmers in arid regions
- Research has shown that, under intense water scarcity conditions, sweet sorghum makes use of its stalk juice to supplement its plant needs.
Mount Ibu : Erupted Again

Mount Ibu erupted again, sending ash 4 km high, as streaks of purple lightning flashed around its crater.
- The Ibu volcano is an active stratovolcano located along the NW coast of Halmahera Island in Indonesia.
- Mount Ibu’s activities follow a series of eruptions of different volcanoes in Indonesia, which sits on the Pacific “Ring of Fire” and has 127 active volcanoes.
- Stratovolcano is also called a composite volcano.
- This volcanic landform is characterized by a conical shape formed by layers of volcanic material deposited during successive volcanic eruptions.
- These volcanoes tend to slope gently at the base but rise quickly near the summit to form tall mountain peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
- These are build up on height by layering lava, ash and tephra. By definition, they have alternating layers of pyroclastic and lava
ASMPA Missile:

France has marked a significant milestone in its defence capabilities by successfully testing the updated ASMPA supersonic missile, capable of carrying a nuclear warhead.
- The Air-Sol Medium Range (ASMP/ASMP-A) is an air-launched land-attack supersonic cruise missile that carries a nuclear payload. It is a central component of France’s nuclear deterrent
- ASMP-A, an upgraded version of the ASMP, arrived into French service in 2009.
- This version had an extended range of up to 500 km, and supported a new 300 kt thermonuclear warhead.
- The ASMPA-R project is a renovated version of the AMSPA intended to add additional range and support another advance in its warhead.
- It is an inertial-guided, air-to-surface missile most likely directed by terrain-mapping and a pre-programmed onboard computer.
- The motor assembly is comprised of a solid-propellant engine which fires after the missile has been released from the aircraft.
- Upon ignition, the missile accelerates to Mach 2.0 in five seconds, after which the booster cartridge is ejected from the ramjet exhaust nozzle.
- Then, the liquid (kerosene)–powered ramjet motor takes over and accelerates to a maximum speed of Mach 3.0, depending on the altitude.
Neanderthals : Recent Study

Neanderthals who lived 50,000 years ago were infected with three viruses that still affect modern humans today, researchers have discovered recently.
- Neanderthals were an extinct relative of modern humans once found across Europe, extending into Central and Southwest Asia.
- Species: Homo neanderthalensis
- They are our closest extinct human relative.
- Current evidence from both fossils and DNA suggests that Neanderthal and modern human lineages separated at least 500,000 years ago.
- The last populations of Neanderthals are thought to have died out roughly 40,000 years ago, several thousand years or so after a wave of modern humans migrated deeper into Europe.
- Although they are long extinct, their genes are still present in modern human DNA.
- Some defining features of their skulls include the large middle part of the face, angled cheek bones, and a huge nose for humidifying and warming cold, dry air.
- Their bodies were shorter and stockier than modern humans, another adaptation to living in cold environments.
- But their brains were just as large as modern humans and often larger-proportional to their brawnier bodies.




