Today Current Affairs: 27th April 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Pratapsingh Rane : Lifetime Status Of The Rank Of Cabinet Minister

The BJP govt had honoured the veteran Congress leader – Pratapsingh Rane – for his 50 years as MLA by providing the “lifetime status of the rank of Cabinet minister”.
- Pratapsingh Rane is a six-time Chief Minister of Goa and a legislator for a full 50 years.
- A case in the HC now says this move violated the 91st Amendment.
- Goa has a 12-member Cabinet, and the conferment of Cabinet status on Rane results in the number of Cabinet ranks rising to 13, which exceeds the ceiling mandated by the Constitution.
- There are 40 seats in the unicameral Goa Assembly.
- The Constitution (91st Amendment) Act, 2003 inserted clause 1A in Article 164, which says “the total number of Ministers, including the Chief Minister, in the Council of Ministers in a State shall not exceed fifteen per cent of the total number of members of the Legislative Assembly of that State provided that the number of Ministers, including the Chief Minister in a State shall not be less than twelve”.
Governor’s Powers To Appoint VCs Of State Universities:

Tamil Nadu has passed two Bills proposing to take away the Governor’s powers to appoint VCs of state universities.
Highlights of the Bill:
- The Bills stress that “every appointment of the Vice-Chancellor shall be made by the Government from out of a panel of three names” recommended by a search-cum-selection committee.
- The Bills also seek to empower the state government to have the final word on the removal of VCs, if needed.
- Removal will be carried out based on inquiries by a retired High Court judge or a bureaucrat who has served at least as a Chief Secretary.
- Chief Minister MK Stalin said the Bills were required as the Governor was disregarding the state government’s opinion on the appointments of VCs.
- The elected governments have repeatedly accused the Governors of acting at the behest of the Centre on various subjects, including education.
- Education comes under the Concurrent List, but entry 66 of the Union List gives the Centre substantial authority over higher education.
- Here, the University Grants Commission (UGC) plays standard-setting role, even in the case of appointments in universities and colleges.
- According to the UGC Regulations, 2018, “Visitor/Chancellor” — mostly the Governor in states — shall appoint the VC out of the panel of names recommended by search-cum-selection committees.
- Higher educational institutions, particularly those that get UGC funds, are mandated to follow its regulations.
- The Supreme Court, in March 2022, quashed the appointment of Shirish Kulkarni as the Vice-Chancellor of Sardar Patel University in Gujarat.
Judgment:
- Any appointment as a Vice Chancellor contrary to the provisions of the UGC Regulations can be said to be in violation of the statutory provisions, warranting a writ of quo warranto”.
- Every subordinate legislation of the UGC flows from the parent UGC Act, 1956. Therefore, being a subordinate legislation, UGC Regulations become part of the Act.
- In case of any conflict between state legislation and central legislation, central legislation shall prevail by applying the rule/principle of repugnancy as enunciated in Article 254 of the Constitution as the subject ‘education’ is in the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020:

Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 has been amended based on the approvals accorded by Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) in respect of the following:
- Going forward all modernisation requirements of the Defence Services and Indian Coast Guard are to be indigenously sourced irrespective of the nature of procurement.
- Import of defence equipment/sourcing from Foreign Industry of capital acquisitions should only be an exception and undertaken with specific approval of DAC/Raksha Mantri.
- Requirement of Integrity Pact Bank Guarantee (IPBG) has been dispensed with. Instead, Earnest Money Deposit (EMD) will be taken as a bid security for all acquisition cases with Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) cost more than Rs 100 crore.
- The procurement process under iDEX procedure of DAP 2020 has been simplified. With this simplification, time taken from grant of AoN to signing of contract will be reduced to 22 weeks.
- Make-II procedure of DAP-2020 has been simplified by incorporating Single Stage Composite Trials of prototypes and dispensing off with quantity vetting and scaling for initial procurements in the delegated cases.
International Religious Freedom Report 2022:

The US Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) has recommended for the second year in the row to put India on a list (Countries of Particular Concern or CPCs) for the worst violations of religious freedoms in 2021.
- Earlier, the US State Department released a strong and critical report on human rights in India in 2021.
Highlights:
The Report’s primary focus is on two groups of countries:
- Country of Particular Concern (CPC): It is a designation by the US Secretary of State of a nation engaged in severe violations of religious freedom under IRFA (International Religious Freedom Act of 1998).
- Special Watch List: A “Special Watch List” country is one that is deemed not to meet all the CPC criteria but engages in or tolerates severe violations of religious freedom.
The Report also includes USCIRF’s recommendations of violent nonstate actors for designation by the US State Department as Entities of Particular Concern (EPCs), under International Review of Financial Analysis (IRFA).
- The report also highlights important global developments and trends related to religious freedom during 2021—including in countries that do not meet the criteria for CPC or SWL recommendations.
- These include the Covid-19 pandemic and religious freedom, blasphemy and hate speech law enforcement, transnational repression, religious intolerance in Europe, deteriorating religious freedom conditions in South Asia, and political upheaval that raises religious freedom concerns.
USCIRF:
- It is an independent, bipartisan US federal government commission, dedicated to defending the universal right to freedom of religion or belief abroad.
- It is an advisory body to the US Congress.
- USCIRF’s 2022 Annual Report provides recommendations to enhance the U.S. government’s promotion of freedom of religion or belief abroad.
- It is Headquartered in Washington DC.
- Established by the US government in 1998 after the inaction of the International Religious Freedom Act, recommendations of USCIRF are non-binding on the state department.
- Traditionally, India does not recognize the view of USCIRF.
Kuril Islands:
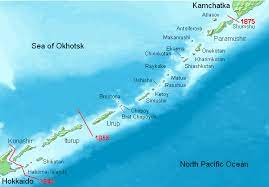
On April 22, Japan’s Diplomatic Bluebook for 2022 described the Kuril Islands (which Japan calls the Northern Territories and Russia as the South Kurils) as being under Russia’s “illegal occupation”.
- This is the first time in about two decades that Japan has used this phrase to describe the dispute over the Kuril Islands.
- Japan had been using softer language since 2003, saying that the dispute over the islands was the greatest concern in Russia-Japan bilateral ties.
- These are a set of four islands situated between the Sea of Okhotsk and the Pacific Ocean near the north of Japan’s northernmost prefecture, Hokkaido.
- Both Moscow and Tokyo claim sovereignty over them though the islands have been under Russian control since the end of World War II.
- The Soviet Union had seized the islands at the end of World War II and by 1949 had expelled its Japanese residents. Tokyo claims that the disputed islands have been part of Japan since the early 19th century.
- According to Tokyo, Japan’s sovereignty over the islands is confirmed by several treaties like the Shimoda Treaty of 1855, the 1875 Treaty for the exchange of Sakhalin for the Kuril Islands (Treaty of St. Petersburg), and the Portsmouth Treaty of 1905 signed after the Russo-Japanese war of 1904-05 which Japan had won.
- Russia, on the other hand, claims the Yalta Agreement (1945) and the Potsdam Declaration (1945) as proof of its sovereignty and argues that the San Francisco Treaty of 1951 is legal evidence that Japan had acknowledged Russian sovereignty over the islands.
Self-Amplifying mRNA Vaccine:
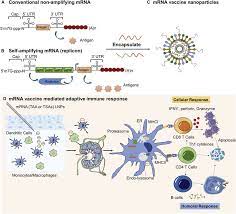
A self-amplifying mRNA vaccine — one in which the delivered RNA multiplies inside the body — has shown promising results against Covid-19 in ongoing phase 1/2/3 trials.
- The vaccine, ARCT-154, has been developed by Arcturus Therapeutics Holdings, based in San Diego, California, and its trials are in progress in Vietnam.
- An mRNA vaccine, such as those from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna, use messenger RNA that encodes the spike protein of the coronavirus.
- In other words, the mRNA directs the cell to produce copies of the spike protein, so that the immune system will recognise the spike if and when actual infection takes place, and mount a response.
- A self-amplifying mRNA vaccine is an improvement on the traditional RNA platform.
- It encodes four extra proteins in addition to the vaccine antigen, and these enable amplification of the original strand of RNA once inside the cell.
- The basic advantage is that it requires a smaller dose.
Emmanuel Macron : French President

French President Emmanuel Macron comfortably won re-election to a second term by defeating Marine Le Pen in French election.
- In the midst of Russia’s war on Ukraine, the result offered the European Union the reassurance of stable leadership in the bloc’s only nuclear-armed power and was immediately hailed by France’s allies.
- A second five-year term for the 44-year-old centrist spared France and Europe from the seismic upheaval of a shift of power to firebrand populist Marine Le Pen.
- During her campaign, Ms Le Pen pledged to dilute French ties with the 27-nation EU, NATO and Germany, moves that would have shaken Europe’s security architecture as the continent deals with its worst conflict since World War II.
- Ms Le Pen also spoke out against EU sanctions on Russian energy supplies and faced scrutiny during the campaign over her previous friendliness with the Kremlin.
Military Spending : Data

According to the latest data published by Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), world military spending continued to grow in 2021, reaching an all-time high of USD 2.1 trillion despite the economic fallout of the pandemic.
- As a result of a sharp economic recovery in 2021, the global military burden—world military expenditure as a share of world Gross Domestic Product (GDP)—fell by 0.1 percentage points, from 2.3% in 2020 to 2.2% in 2021.
Top Spenders:
- The five largest spenders in 2021 were the US, China, India, the UK and Russia.
- They accounted together for 62% of expenditure and the US and China alone accounted for 52%.
- The military spending in Asia and Oceania totaled USD586 billion in 2021.
- Spending in the region was 3.5% higher than in 2020, continuing an uninterrupted upward trend dating back to at least 1989.
- The increase in 2021 was due primarily to growth in Chinese and Indian military spending.
- Together, the two countries accounted for 63% of total military expenditure in the region in 2021.
- Russia increased its military expenditure by 2.9% in 2021, to USD65.9 billion, at a time when it was building up its forces along the Ukrainian border.
- NATO Members Spending: Eight European North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) members reached the Alliance’s target of spending 2% or more of GDP on their armed forces in 2021.
- This is one fewer than in 2020 but up from two in 2014.
- India’s military spending of USD76.6 billion ranked third highest in the world.
- This was up by 0.9% from 2020 and by 33% from 2012.
- Amid ongoing tensions and border disputes with China and Pakistan that occasionally spill over into armed clashes, India has prioritized the modernization of its armed forces and self-reliance in arms production.
- In a drive to strengthen the indigenous arms industry, 64% of capital outlays in the 2021 Indian military budget were earmarked for acquisitions of domestically produced arms.




