Today’s Current Affairs: 27th December 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Buccal Mucosa Cancer:
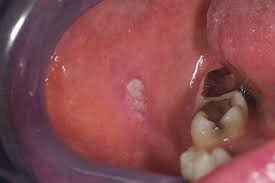
Alcohol consumption, even in small amounts, significantly increases the risk of Buccal Mucosa Cancer (BMC), a common and aggressive form of oral cancer in India, according to a recent study.
- It refers to a type of oral cancer that originates in the inner lining of the cheeks, called the buccal mucosa.
- It usually occurs in the thin, flat cells called squamous cells that line the buccal mucosa and other parts of the mouth. Hence, most BMC cases are Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC).
- It is the predominant form of oral cancer in the Indian subcontinent.
- It primarily affects individuals with risk factors such as tobacco use and alcohol use, which causes cellular changes in the cheek lining.
- Symptoms commonly include persistent sores, lumps, pain, and difficulty chewing or moving the cheek.
- Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the cancer stage.
- Early detection is essential for improving prognosis and the buccal mucosa cancer survival rate.
Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme: In News

Installation of rooftop solar power plants is being expedited in Rajasthan under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) to reduce transmission and distribution losses and improve power supply quality.
- It was launched by the Ministry of Power, Government of India to transform the electricity distribution sector.
- It is a Reforms-based and Results-linked Scheme.
- It seeks to modernise India’s power distribution sector through smart metering, network strengthening, and financial reforms, with the goal of creating financially sustainable and operationally efficient DISCOMs.
- The scheme aims to reduce the Aggregate Technical and Commercial (AT&C) losses to pan-India levels of 12-15% and Gap between Average Cost of Supply (ACS) and Average Revenue Realised (ARR) to zero by 2024-25.
- The Scheme has two major components:
- Part A: Financial support for Prepaid Smart Metering & System Metering and upgradation of the Distribution Infrastructure.
- Part B: Training & Capacity Building and other Enabling & Supporting Activities.
- Financial assistance to DISCOMs is provided for upgradation of the Distribution Infrastructure and for Prepaid Smart Consumer Metering & System Metering based on meeting pre-qualifying criteria and achieving basic minimum benchmark in reforms.
Dhasan River:

The National Green Tribunal (NGT), Principal Bench, New Delhi, recently dismissed an appeal challenging the cancellation of environmental clearance granted for sand mining in the river Dhasan in Jhansi district.
- It is a right bank tributary of the Betwa River, which itself is a tributary of the Yamuna.
- It flows in the Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- The river originates in Madhya Pradesh and forms the southeastern boundary of the Lalitpur District of Uttar Pradesh.
- The river was known as the Dasharna in the ancient period.
- Lehchura Dam is built on this river. It is primarily an irrigation dam providing water for agricultural use via the Dhasan Canal System (DCS).
Dulhasti Stage-II Hydropower Project:

A panel under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change recently approved the 260-megawatt Dulhasti Stage-II hydropower project on the Chenab river in Jammu and Kashmir’s Kishtwar district.
- It is a 260-megawatt hydropower project proposed on the Chenab River in the Kishtwar District of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is an extension of the existing 390 MW Dulhasti Stage-I Hydroelectric Project (Dulhasti Power Station).
- The project also includes a surge shaft, a pressure shaft, and an underground powerhouse.
Vallanadu Wildlife Sanctuary:

The blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra) population at the Vallanadu sanctuary has witnessed a surge, recording a total of 300.
- Vallanadu Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Tamil Nadu.
- It was established to protect blackbuck antelopes.
- It is a scrub forest
- Fauna: Blackbuck, Spotted Deer, Bonnet Macaque, Jungle Cat, Small Indian Civet, Black-naped Hare; Rose-ringed Parakeet; Common Indian Monitor Lizard etc. are found here.
- Blackbuck is a species of antelope native to India and Nepal.
- The blackbuck mostly lives in open grasslands, dry scrub areas, and thinly forested areas.
- It is widespread in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and other areas throughout peninsular India.
- It has been declared as the state animal by the governments of Punjab, Haryana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Conservation Status: It is classified as ‘Least Concerned’ under the IUCN Red List.
Somaliland:
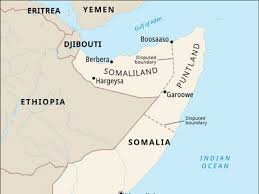
Israel formally recognised the self-declared Republic of Somaliland as an independent and sovereign state.
- It is located in the Horn of Africa.
- It borders Djibouti, Ethiopia, Somalia, and the Puntland region, with a strategic coastline along the Gulf of Aden.
- Capital City: Hargeisa
- It functions as a de facto independent state with its own constitution, elected government, judiciary, security forces, currency, and national symbols.
- Governance combines modern democratic institutions with traditional clan-based mechanisms, ensuring stability and conflict resolution.
- It has a bicameral legislature, including the House of Elders (Guurti), and conducts regular elections contributing to institutional legitimacy.
- Berbera Port is being developed as a regional trade and logistics corridor, particularly serving landlocked Ethiopia.
- The economy is largely livestock-based, with exports to Gulf countries forming a major revenue source.
Nitrate:
According to a submission by Central Groundwater Board, over 20% of groundwater samples collected in Delhi in 2023 had nitrate levels exceeding the permissible limit of 45 mg/l.Nitrate is a compound of nitrogen and oxygen. It is naturally found in air, soil and water. Plants and animals require nitrates for their survival and growth, and the human body also produces this compound.It gets into water from fertilizer in runoff, manure from animal feeding operations and wastewater treatment plant discharge.Excessive nitrate in groundwater causes methemoglobinemia, reducing the ability of red blood cells to carry oxygen, particularly affecting infants and vulnerable populations.Elevated nitrate levels in groundwater can lead to algal blooms in lakes and ponds, severely degrading aquatic ecosystems by depleting oxygen and harming biodiversity.
Thailand and Cambodia Agree to Ceasefire Amid Border Clashes:
Thailand and Cambodia have agreed to halt weeks of fierce border clashes marking a significant step towards de-escalation in one of the most serious confrontations between the two Southeast Asian neighbors in recent years. The truce comes after nearly three weeks of intense fighting involving artillery barrages, rocket fire, and fighter jet sorties which resulted in heavy casualties and large-scale displacement on both sides of the border. The agreement aims to stabilize the situation and prevent further deterioration while opening space for longer-term diplomatic efforts.
ISRO Plans Third Launch Pad at Shriharikota:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced plans to develop a third launch pad at Shriharikota. The new facility is expected to be commissioned within four years. This step is crucial for launching heavier satellites and advanced launch vehicles.ISRO is developing a third launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC).The agency has started the procurement process and is identifying suitable vendors.The plan was confirmed by Padmakumar ES, Director of SDSC.ISRO aims to place bigger satellites weighing 12,000–14,000 kg into various orbits.Such missions require larger and more powerful launch vehicles.Existing launch pads may not be sufficient for future mission frequency and scale.A third pad will provide operational flexibility and backup capability.
Gujarat Became a Tiger State After 33 Years NTCA Declares:
Gujarat has been officially reinstated as a tiger bearing state after a gap of 33 years. The decision was taken by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), which has confirmed Gujarat’s inclusion in the All India Tiger Estimation (AITE) 2026 following sustained evidence of tiger presence in the Ratanmahal Sanctuary. This move marks Gujarat’s return to India’s official tiger map which is strengthening the country’s conservation narrative under Project Tiger.




