Today Current Affairs: 27th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Periodic Labour Force Survey 2019-20:

The National Statistical Office (NSO) released the third annual report on Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), conducted between July 2019 and June 2020.
- Labour indicators recorded an all-round improvement in 2019-20 compared with the previous two years i:e 2017-18 and 2018-19.
Unemployment Rate:
- The unemployment rate fell to 4.8% in 2019-20. In 2018-19, it stood at 5.8% and 6.1% in 2017-18.
Worker Population Rate:
- It improved to 38.2% in 2019-20 compared with 35.3% in 2018-19 and 34.7% in 2017-18.
Labour Force Participation Ratio:
- It increased to 40.1% in 2019-20 from 37.5% and 36.9%, respectively, in the last two years. The higher the LFPR, the better.
Gender Based Unemployment Rate:
- The data showed the jobless rate for both male and female fell to 5.1% and 4.2%, respectively, in 2019-20 from 6% and 5.2% in 2018-19.
- WPR and LFPR also comparatively improved during the year.
OCI Card Holders::

The Delhi High Court has said that the Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO) cannot insist on the physical or virtual presence of both the spouses for processing Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) card applications for one of them.
- The High Court’s order came while asking the FRRO to accept the OCI card application of an Iranian woman, who has been living separately in Bengaluru after her relationship with her husband, an Indian citizen, turned sour.
- The Government of India launched the ‘Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Scheme’ by making amendments to the Citizenship Act, 1955 in 2005.
- On 09 January 2015, the Government of India discontinued the PIO card and merged it with OCI card.
Eligibility:
- The Government of India allows the following categories of foreign nationals to apply for OCI Card.
Benefits for OCI cardholders:
- Lifelong Visa to visit India multiple times. (special permission needed for research work in India).
- No need to register with Foreigners Regional Registration Officer (FRRO) or Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) for any length of stay.
- Except for acquisition of agricultural and plantation properties, OCI card holders have similar facilities that are extended to NRIs in economic, financial and educational fields.
- Same treatment as of NRIs in respect to Inter-country adoption of Indian children.
- Also treated at par with NRIs regarding – entry fees for national monuments, practice of professions like doctors, dentists, nurses, advocates, architects, Chartered Accountants & Pharmacists.
- At par with NRIs to participate in All India Pre-medical tests and such.
- Treated at par with Indian citizens in matters of traffic in airfares in Indian domestic sectors.
- Same entry fee as for Indians for entry into India’s national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
- OCI booklet can be used as identification to avail services. An affidavit can be attached with local address as residential proof.
‘PM CARES For Children’ Scheme.:

Ministry of Women and Child Development launches web-based portal pmcaresforchildren.in to facilitate submission of applications, identification of children eligible to receive support under the ‘PM CARES for Children’ scheme.
- The scheme has been launched for support & empowerment of Covid affected children.
- Eligibility: All children who have lost both parents or surviving parent or legal guardian/adoptive parents due to Covid 19 will be supported under the scheme.
Features of the scheme:
- Fixed Deposit in the name of the child: A corpus of Rs. 10 lakh will be allocated to each of these children from the PM CARES fund.
- This corpus will be used to give a monthly stipend from 18 years of their age, for the next five years and on reaching the age of 23 years, he or she will get the corpus amount as one lump-sum for personal and professional use.
- School Education: For children under 10 years: Admission will be given in the nearest Kendriya Vidyalaya or in a private school as a day scholar.
- School Education: for children between 11-18 years: The child will be given admission in any Central Government residential school such as Sainik School, Navodaya Vidyalaya etc.
- Support for Higher Education: The child will be assisted in obtaining education loan for Professional courses / Higher Education in India as per the existing Education Loan norms.
- Health Insurance: All children will be enrolled as a beneficiary under Ayushman Bharat Scheme (PM-JAY) with a health insurance cover of Rs 5 lakhs.
Wolf Warrior Diplomacy: China:

China’s assertive new diplomatic approach in the Xi Jinping era has come to be dubbed “wolf warrior diplomacy”, marked by a muscular posture in pursuing China’s interests.
- “Wolf-warrior diplomacy,” named after famous Chinese movies, describes offensives by Chinese diplomat to defend China’s national interests, often in confrontational ways.
- It reinforces a presumed transition of Chinese diplomacy from conservative, passive, and low-key to assertive, proactive, and high-profile.
- In last one year the Chinese foreign ministry has taken an increasingly strident tone against the United States, India, Australia, and other countries.
- In April last year, Chinese coastguard ship allegedly sank a Vietnamese fishing trawler near the Paracel Islands.
- When Vietnam protested, the Chinese foreign ministry responded by saying Vietnam’s claims to the area are “illegal.”
- Then, China announced the naming of 80 islands, reefs, seamounts, shoals, and ridges in the South China Sea, triggering angry protests from other claimants.
- China also tried to enter India at various places.
G20 Climate Meet:

At the recent G20 Climate Meet, India urged the group of 20 nations (G20) having per capita greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions above the global average to bring it down to the world average, thereby vacating ‘some’ carbon space for developing nations.
- This will support the developmental aspirations of the developing nations.
- Presently, Italy holds the G20 Presidency and the Climate Meet is being seen as a prelude to the UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP 26) meeting in Glasgow, Scotland in November 2021.
India’s Stand:
- There is a need to cut absolute emissions rapidly while taking into account the Paris Agreement which emphasized on:
Respective historical responsibilities, - Delivery of promised climate finance and technologies at low cost keeping in perspective per capita emissions,
Differences in per capita GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and The unfinished agenda for sustainable development. - India noted the pledges made by some countries to achieve Net Zero GHG emissions or carbon Neutrality by or around mid century.
- However, this may not be adequate in view of fast depleting available carbon space.
- Keeping in view the legitimate need of developing countries to grow, it urged G20 countries to commit to bringing down per capita emissions to Global average by 2030.
- Carbon neutrality means having a balance between emitting carbon and absorbing carbon from the atmosphere in carbon sinks.
- Carbon space is the amount of carbon (or CO2) that can be put into the atmosphere without this leading to a level of warming—or underlying concentrations of CO2—that can be considered dangerous or otherwise undesirable.
- Stressed on Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) to combat climate change.
- Mentioned its plans of installing 450 GW (Giga Watt) of RE (Renewable Energy) by 2030, enhanced ambitions in bio-fuels, India’s NDCs (Nationally Determined Contributions) and various other initiatives taken by India on Urban Climate Action.
UN’s Survey On Digital And Sustainable Trade Facilitation 2021:

India has scored 90.32% in United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia Pacific’s (UNESCAP) Global Survey on Digital and Sustainable Trade Facilitation.
- This is a remarkable jump from 78.49% in 2019.
- The survey is conducted every two years by UNESCAP and includes an assessment of 58 trade facilitation measures covered by the World Trade Organization’s Trade Facilitation Agreement.
- 58 measures include publications of existing import-export rules on the internet, risk management, advance ruling on tariff classification, pre-arrival processing, independent appeal mechanism, expedited shipments, automated customs system, among others.
- A higher score for a country helps businesses in their investment decisions.
- The UN Regional Commissions jointly conduct the UN Global Survey on Digital and Sustainable Trade Facilitation.
- The Survey currently covers 143 economies around the globe. For Asia Pacific, it is conducted by UNESCAP.
- It pointed out India’s improvement in the scores on all five key indicators.
- Transparency: 100% in 2021 (from 93.33% in 2019)
- Formalities: 95.83% in 2021 (from 87.5% in 2019)
- Institutional Arrangement and Cooperation: 88.89% in 2021 (from 66.67% in 2019)
- Paperless Trade: 96.3% in 2021 (from 81.48% in 2019).
- Cross-Border Paperless Trade: 66.67% in 2021 (from 55.56% in 2019).
PDS 70:
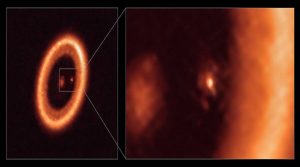
Scientists for the first time have spotted a moon-forming region around a planet beyond our solar system – a Jupiter-like world surrounded by a disc of gas and dust massive enough that it could spawn three moons the size of the one orbiting Earth.
- The researchers used the ALMA observatory in Chile’s Atacama desert to detect the disc of swirling material accumulating around one of two newborn planets seen orbiting a young star called PDS 70, located 370 light years from Earth.
- A light year is the distance light travels in a year, about 9.5 trillion km.
- More than 4,400 planets have been discovered outside our solar system, called exoplanets. No circumplanetary discs had been found until now because all the known exoplanets resided in “mature” – fully developed – solar systems, except the two infant gas planets orbiting PDS 70.
- The orange-coloured star PDS 70, roughly the same mass as our Sun, is about 5 million years old. The two planets are even younger.
- Both planets are similar (although larger) to Jupiter, a gas giant. It was around one of the two planets, called PDS 70c, that a moon-forming disc was observed.
SCs And STs In Census:

The Government of India informed Lok Sabha that it has decided as a matter of policy not to enumerate caste-wise population other than SCs and STs in Census. Subsequently many leaders demanded a caste-based census.
- Every Census in independent India from 1951 to 2011 has published data on Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, but not on other castes. Before that, every Census until 1931 had data on caste.
- However, in 1941, caste-based data was collected but not published.
- In the absence of such a census, there is no proper estimate for the population of OBCs, various groups within the OBCs, and others.
- The Mandal Commission estimated the OBC population at 52%, some other estimates have been based on National Sample Survey data.
- Demand for a caste census usually come from among those belonging to Other Backward Classes (OBC) and other deprived sections, while sections from the upper castes oppose the idea.
Socio Economic Caste Census (SECC)
- The UPA government decided to go for a full-fledged SECC, which was conducted by the Ministry of Rural Development in rural areas and the Ministry of Housing & Urban Poverty Alleviation in urban areas.
- The SECC data excluding caste data was finalised and published by the two ministries in 2016.
- The raw caste data was handed over to the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, which formed an Expert Group under former NITI Aayog Vice-Chairperson Arvind Pangaria for classification and categorisation of data.
- It is not clear whether it submitted its report; no such report has been made public.
Agri product::

India has entered the top 10 list of the countries exporting agricultural produce in the year 2019 with a sizable share in the export of rice, cotton, soya beans and meat.
- As per a report by World Trade Organization (WTO) on the trends in world agricultural trade in the past 25 years, India and Mexico with 3.1% and 3.4% share in global Agri exports, respectively, replaced New Zealand (9th) and Malaysia (7th) as the largest exporters across the globe.
- The United States of America (USA), which topped the list in 1995 with 22.2% share of world Agri export, was overtaken by the European Union (EU) in 2019 with 16.1% global Agri share.
- Notably, the top exporting nations of rice in 1995 were Thailand (38%), India (26%), and the US (19%). In 2019, India with a lead of 33% overtook Thailand (20%) to top the list, while Vietnam (12%) overtook the US and climbed to the third spot.
- Further, India is also the third-largest cotton exporter (7.6%), and the fourth-largest importer (10%) in 2019.
- In the largest traded Agri product, soya beans, India (0.1%) has a meagre share, but was ranked ninth in the world.
- In the “meat and edible meat offal” category, India secured 8th rank in the world with a global share of 4%.
- India’s share of foreign value-added content in its Agri exports clocked 3.8% share primarily due to high tariffs on Agri imports to boost the domestic markets and local farmers.
I-STEM Project:

I-STEM project has been accorded extension for five years, until 2026 and enters its second phase with added features.
- The Indian Science Technology and Engineering facilities Map (I-STEM), the national web portal for sharing R&D facilities was formally launched in January 2020 by the Honorable Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi.
- I-STEM is an initiative of Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Govt. of India (PSA, GOI) under the aegis of Prime Minister Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) mission.
- The goal of I-STEM is to strengthen the R&D ecosystem of the country by connecting researchers with resources, in part by promoting technologies and scientific equipment development indigenously, and providing necessary supplies and supports to researchers by enabling them an access to existing publicly funded R&D facilities in the country through the I-STEM web portal.
- Under Phase II, the portal will hostindigenous technology products listedthrough a digital catalogue. The portal will also provide a platform for the various City Knowledge and Innovation Clusters.
India’s 39th World Heritage Site:

India’s nomination of Rudreswara Temple, (also known as the Ramappa Temple) at Palampet, Mulugu district, near Warangal in the state of Telangana has been inscribed on UNESCO’s World Heritage list. This is India’s 39th World Heritage Site.
- The decision was taken at the 44th session of the World Heritage Committee of UNESCO today.
- Ramappa temple, a 13th century engineering marvel is named after its architect, Ramappa.
- The Rudreswara temple was constructed in 1213 AD during the reign of the Kakatiya Empire by RecharlaRudra, a general of Kakatiya king Ganapati Deva.
- The presiding deity here is Ramalingeswara Swamy.
- The temple complexes of Kakatiyas have a distinct style, technology and decoration exhibiting the influence of the Kakatiyan sculptor.
- The foundation is built with the “sandbox technique”, the flooring is granite and the pillars basalt.
- The lower part of the temple is red sandstone while the white gopuram is built with light bricks that reportedly float on water.




