Today Current Affairs: 28th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Defence Corridors In Uttar Pradesh And Tamil Nadu.:
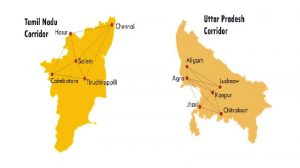
During a webinar on India-Sweden Defence Industry Cooperation, Rajnath Singh invited Swedish firms to invest in Defence Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- To support the growth of the Defence sector and enhance manufacturing capacity in the sector, Two Defence Industrial Corridors are being set up in India, one in Uttar Pradesh and another in Tamil Nadu.
- Promoting Make in India, the Defence Industrial Corridors will catalyse indigenous production of defence and aerospace-related items.
- This will reduce our imports and promote the export of these items to other countries.
- Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor consists of the following six nodal points with the potential to develop defence industries in the corridor: Agra, Aligarh, Chitrakoot, Jhansi, Kanpur and Lucknow.
- The Tamil Nadu Defence Corridor, being set up by the Government of Tamil Nadu, consists of the following five nodal points: Chennai, Coimbatore, Hosur, Salem and Tiruchirappalli
India’s First Voltage Source Convertor (VSC) Based High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) System.:

POWERGRID has fully commissioned India’s First Voltage Source Convertor (VSC) based High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) System.
- It has commissioned Monopole-I of the 2000 Mega-Watt (MW), Pugalur (Tamil Nadu) – Thrissur (Kerala) Voltage Source Convertor (VSC) based High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) System.
- This Project strengthens the power system of Southern Region of our Country.
- Monopole-II of the project was inaugurated by PM Modi in February, 2021 and with the commissioning of Monopole-I, the project has attained its full capacity.
- The Pugalur-Thrissur HVDC system, costing Rs. 5070 crore, is a part of the Raigarh-Pugalur-Thrissur 6000 MW HVDC system and enables transfer of 2000 MW to Kerala through the VSC HVDC station at Thrissur.
Voltage Source Convertor (VSC)
- An HVDC converter converts electric power from high voltage alternating current (AC) to high-voltage direct current (HVDC), or vice versa.
- Electronic converters for HVDC are divided into two main categories.
- Line-commutated converters (HVDC classic) are made with electronic switches that can only be turned on.
- Voltage-sourced converters are made with switching devices that can be turned both on and off. It uses transistors, usually the Insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT).
- The VSC technology significantly reduces the land requirement compared to the conventional HVDC systems and is particularly suitable for areas, where land is scarce.
- It also facilitates development of smart grid and improves system resilience under various operating conditions.
- The state-of-the-art VSC Technology has been brought to India for the first time by POWERGRID through this Project.
India Plastic Challenge – Hackathon 2021:

Environment minister announced the “India Plastic Challenge – Hackathon 2021” to spur innovation and entrepreneurship in area of tackling plastic waste pollution and elimination of single use plastic.
- It is a unique competition calling upon start-ups /entrepreneurs and students of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) to develop innovative solutions to mitigate plastic pollution and develop alternatives to single use plastics.
- PM Modi gave a clarion call to phase out single use plastics by 2022
- Government of India has already banned import of plastic waste in the country.
- Ministry of Environment brought out Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, for handling plastic waste in an environmentally sound manner. Under the rules plastic carry bags below 50 microns have been banned.
- Further, the Ministry has issued a draft notification in March 2021 for amending the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, with respect to prohibiting identified 12 single use plastic items such as disposable plastic cutlery etc.”
Cyber Capability:

According to a report by International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS), an influential think tank, India’s offensive cyber capability is “Pakistan-focused” and “regionally effective”, and not tuned towards China.
Countries Under Observation:
- The report has done a qualitative assessment of cyber power in 15 countries.
- Four members of the Five Eyes intelligence alliance – the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia.
- Three cyber-capable allies of the Five Eyes states – France, Israel and Japan.
- Four countries viewed by the Five Eyes and their allies as cyber threats – China, Russia, Iran and North Korea.
- Four states at earlier stages in their cyber power development – India, Indonesia, Malaysia and Vietnam.
The report has divided the 15 states into three tiers of cyber power:
- First Tier: States with world-leading strengths across all the categories in the methodology. The United States of America is the only country in this tier.
- Second Tier: States that have world-leading strengths in some of the categories. Australia, Canada, China, France, Israel, Russia and the United Kingdom are in this tier.
- Third Tier: States that have strengths or potential strengths in some of the categories but significant weaknesses in others. India, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Malaysia, North Korea and Vietnam are in this tier.
- This report provides confirmation of the likely durability of US digital-industrial superiority for at least the next ten years.
International MSMEs Day:

Every year, Micro, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) Day is celebrated on 27th June to recognise the contribution of these industries in the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The United Nations (UN) designated 27th June as Micro, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Day through a resolution passed in the UN General Assembly in April 2017.
- In May 2017, a program titled ‘Enhancing National Capacities for Unleashing Full Potentials of MSMEs in Achieving the SDGs in Developing Countries’ was launched.
- It has been funded by the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Sub-Fund of the United Nations Peace and Development Fund.
- The UN wants countries to recognise sustainable development goals and create awareness about them.
- An International Trade Centre survey on Covid-19 impact among businesses in 136 countries has shown that nearly 62% of women-led small businesses have been strongly affected by the crisis, compared to just over half of firms led by men, and women-owned are 27% more likely not to survive the pandemic.
- Formal and informal MSMEs make up over 90% of all firms and account, on average, for 70% of total employment and 50% of GDP. As such, they are key actors in achieving a green recovery.
- 2021 Theme: MSME 2021: Key to an inclusive and sustainable recovery.
Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay:

Indian Prime Minister paid homage to Rishi Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay on his Jayanti on 27th June.
- He was one of the greatest novelists and poets of India.
- He was born on 27th June 1838 in the village of Kanthapura in the town of North 24 Parganas, Naihati, present day West Bengal.
- He composed the song Vande Mataram in Sanskrit, which was a source of inspiration to the people in their freedom struggle.
- In 1857, there was a strong revolt against the rule of East India Company but Bankim Chandra Chatterjee continued his studies and passed his B.A. Examination in 1859.
- The Lieutenant Governor of Calcutta appointed Bankim Chandra Chatterjee as Deputy Collector in the same year.
- He was in Government service for thirty-two years and retired in 1891.
- He died on 8th April, 1894.
- His epic Novel Anandamath – set in the background of the Sanyasi Rebellion (1770-1820), when Bengal was facing a famine too – made Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay an influential figure on the Bengali renaissance.
- He kept the people of Bengal intellectually stimulated through his literary campaign.
- India got its national song, Vande Mataram, from Anandamath.
- He also founded a monthly literary magazine, Bangadarshan, in 1872, through which Bankim is credited with influencing the emergence of a Bengali identity and nationalism.
- Bankim Chandra wanted the magazine to work as the medium of communication between the educated and the uneducated classes.
- The magazine stopped publication in the late 1880s, but was resurrected in 1901 with Rabindranath Tagore as its editor.
- While it carried Tagore’s writings – including his first full-length novel Chokher Bali – the ‘new’ Bangadarshan retained its original philosophy, nurturing the nationalistic spirit.
- During the Partition of Bengal (1905), the magazine played a vital role in giving an outlet to the voices of protest and dissent. Tagore’s Amar Sonar Bangla – the national anthem of Bangladesh now – was first published in Bangadarshan.
- He had studied Sanskrit and was very interested in the subject, but later took on the responsibility to make Bengali the language of the masses. However, his first published work – a novel – was in English.
- His famous novels include Kapalkundala (1866), Debi Choudhurani, Bishabriksha (The Poison Tree), Chandrasekhar (1877), Rajmohan’s wife and Krishnakanter Will.
India Smart Cities Awards 2020:

The Union ministry of housing and urban affairs has released the list of India smart cities awards (ISCA) 2020.
- Uttar Pradesh emerged on the top among all states, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Indore (Madhya Pradesh) and Surat (Gujarat) won the award jointly for their overall development.
- Ahmedabad bagged the ‘Smart Cities Leadership Award’ and Chandigarh, the award for union territories, while Indore won the “Innovative Idea Award”.
Parameters used for ranking:
- These rankings were arrived at by the government on the basis of several parameters such as social aspects, governance, culture, urban environment, sanitation, economy, built environment, water, urban mobility.
- For the year of the pandemic, additional parameters of sustainable business model of Integrated Command and Control Centres and innovation in Covid-19 management were also counted for the awards.
Smart Cities mission:
- GoI launched the smart cities mission in 2015.
- The objective is to integrate city functions, utilize scarce resources more efficiently, and improve the quality of life of citizens.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
The Gujarat Prohibition Act, 1949:

The Gujarat Prohibition Act, 1949 is being challenged before the Gujarat High Court, more than seven decades after it came into effect as the Bombay Prohibition Act.
- The state government says that it is “committed to the ideals and principles of Mahatma Gandhi and firmly intends to eradicate the menace of drinking liquor.”
- The right of privacy is violated, which was given voice by the Supreme Court in 2017 in Puttaswamy judgment.
- The Right is associated with the citizens’ right to eat and drink as per their choice.
- Ground of manifest arbitrariness: The law grants health permits and temporary permits to out-of-state tourists.
- The petition says there are no intelligible differences in the classes thus being created by the state on who gets to drink and who does not and violates the Right to Equality under Article 14 of the Constitution.
The Gujarat Prohibition Act, 1949:
- Introduced by the then Bombay province as Bombay Prohibition Act, 1949 to overhaul the law relating to intoxicating drugs and narcotics total prohibition.
- It is an Act relating to the promotion and enforcement of alcohol prohibition in the Bombay State.
- The Bombay state was divided into the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat in 1960.
- Gujarat adopted the prohibition policy in 1960 and subsequently chose to enforce it with greater rigidity.
- In 2011, it renamed the Act as Gujarat Prohibition Act.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U):

The Government approved 708 proposals for construction of 3.61 lakh houses under Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U).
- With this, as on date, the total number of sanctioned houses under PMAY(U) is now 112.4 of which 48.31 lakh have been completed/delivered
- PMAY- U Awards 2021 – 100 Days Challenge
- In addition, ‘PMAY- U Awards 2021 – 100 Days Challenge’ was also launched by Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs (MoHUA) .
- The awards are given to recognize and celebrate the outstanding performances by States, Union Territories (UTs), Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and beneficiaries for successful implementation of the Mission.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (URBAN)
- Implementation period: The Mission will be implemented during 2015-2022.
- Mission: To achieve the goal of Housing for All in Urban areas by 2022, when the Nation completes 75 years of its Independence.
- Features: Under it, central assistance will be provided to Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and other implementing agencies through States/UTs for:
- In-situ Rehabilitation of existing slum dwellers using land as a resource through private participation
- Credit Linked Subsidy
- Affordable Housing in Partnership
- Subsidy for Beneficiary-led individual house construction/enhancement
- Credit linked subsidy component will be implemented as a Central Sector Scheme while other three components will be implemented as Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS).
- Eligibility: All statutory towns as per Census 2011 and towns notified subsequently would be eligible for coverage under the Mission.
Sardar Sarovar Dam:

Sardar Sarovar Dam is providing irrigation water in summer for the first time in history.
- The Sardar Sarovar Narmada Dam is a terminal dam built on the Narmada river at Kevadia in Gujarat’s Narmada district.
- According to the 1979 award of the Narmada Water Dispute Tribunal, the power benefits from the project are to be shared in the following ratio: Madhya Pradesh at 57 per cent, Maharashtra at 27 per cent, and Gujarat at 16 per cent
- Garudeshwar weir is being constructed on the river Narmada near the Statue of Unity.
- The total height of the weir will be 31.75 metre.
- It is located at Garudeshwar at a distance of 9 kilometre from Sadhu bet island and 12 kilometre downstream from Sardar Sarovar dam.
Turnover And Borrowing Thresholds For Small And Medium Sized Companies (SMC):

The Corporate Affairs Ministry has expanded the turnover and borrowing thresholds for Small and Medium sized Companies (SMC).
- The Corporate Affairs Ministry has increased the turnover threshold for SMCs to Rs 250 crore from Rs 50 crore, and the borrowing threshold to Rs 50 crore from Rs 10 crore.
- SMCs are permitted to avail a number of exemptions under the Company (Accounting Standards) Rules 2021 to reduce the complexity of regulatory filings for smaller firms.
The move would promote ease of doing business for the firms that would now be included under the definition of SMC.
- SMC are completely exempted from having to file cash flow statements and provide a segmental break up of their financial performance in mandatory filings.
- They can also avail partial reporting exemptions in areas including reporting on employee benefits obligations such as pensions.
- They are exempted from having to provide a detailed analysis of benefit obligations to employees, but are still required to provide actuarial assumptions used in valuing the company’s obligations to employees.
- SMCs are also allowed to provide an estimated value in use of assets carried on their balance sheets, and are not required to use present value techniques to arrive at the value in use of assets.
- They are also exempted from having to report diluted earnings per share in their filings.
Exceptions:
- Banks, monetary establishments, insurance coverage firms and listed firms can’t be labelled as SMCs.
Any firm which is both the holding firm and subsidiary of an organization that’s not an SMC can’t be labelled as an SMC.
S
African swine fever : Four Districts Of Mizoram Have Been Declared As Epicentres:

African Swine Fever (ASF) was first reported in Manipur in December 2020 and there have been no cases since. Illegal import of pigs might have introduced the infection to the state, officials of the state veterinary department suspect.
- Recently, four districts of Mizoram have been declared as epicentres of the African swine fever (ASF).
About African Swine Fever (ASF):
- ASF is a highly contagious and fatal animal disease that infects domestic and wild pigs, typically resulting in an acute form of hemorrhagic fever.
- It was first detected in Africa in the 1920s.
- The mortality is close to 100 per cent, and since the fever has no cure, the only way to stop it spreading is by culling the animals.
- As of now, there is no approved vaccine, which is also a reason why animals are culled to prevent the spread of infection.
‘The India Story’ Booklet:

The Minister of State for New & Renewable Energy launched ‘The India Story’ booklet, a compilation of Indian initiatives that are shaping India’s energy transition.
- The booklet was launched at the event on Accelerating Citizen Centric Energy Transition organized by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
- It was organized in collaboration with the Permanent Mission of India (PMI) to the United Nations and the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW).
- The Minister also launched a website which will act as a repository of energy transition related knowledge resources from around the world.
- In the last 6 years, India’s installed Renewable Energy (RE) capacity has increased by over two and a half times and stands at more than 141 Giga Watts (including large Hydro).
- It is about 37% of the country’s total capacity.
- The installed solar energy capacity has increased by over 15 times, and stands at 41.09 GW.
- India’s RE capacity is the 4th largest in the world. Its annual RE addition has been exceeding that of coal based thermal power since 2017.
LGBTQIA:

LGBTQIA+ stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, intersex, asexual and such others’ (LGBTQIA+) community
- Empathising with the LGBTQIA+ community, the Madras High Court directed the Union Ministry of Social Justice to enlist NGOs that could provide counselling, monetary support, legal assistance and protection to them until a law could be enacted to protect them.
- Ministry should upload the details of the NGOs on its website within eight weeks and revise the information periodically.
- Any person who faced an issue because he/she/they belonged to the LGBTQIA+ community could approach any of the enlisted NGOs for safeguarding their rights.
- NGOs should also coordinate with the police with respect to offences committed against them.
- Appropriate changes should be made to the existing government short stay homes, anganwadi shelters, Garima Greh (shelter home for transgender persons) for providing accommodation, food, medical care facilities to those from the community in need of such assistance.
- Sensitisation programmes could also be conducted for stakeholders, including police and prison authorities, judges, physical and mental health professionals, educational institutions, health workers, public and private workplaces.




